J Korean Fract Soc.
2010 Jan;23(1):34-41. 10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.34.
Treatment of Proximal Tibia Fractures Using LCP by MIPO Technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. leejy88@chosun.ac.kr
- KMID: 1461570
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12671/jkfs.2010.23.1.34
Abstract
- PURPOSE
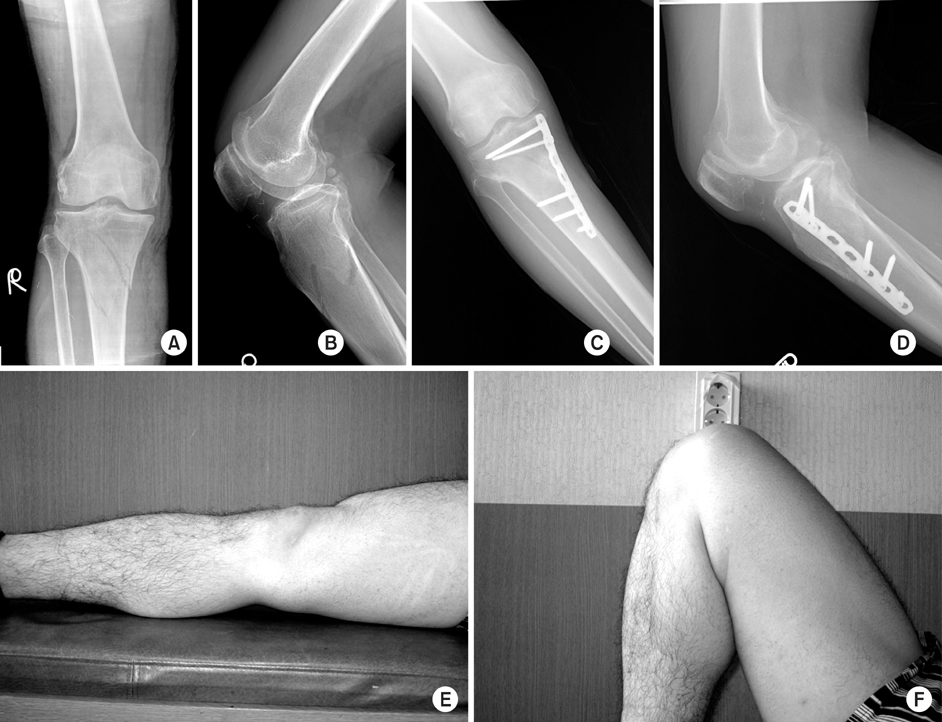
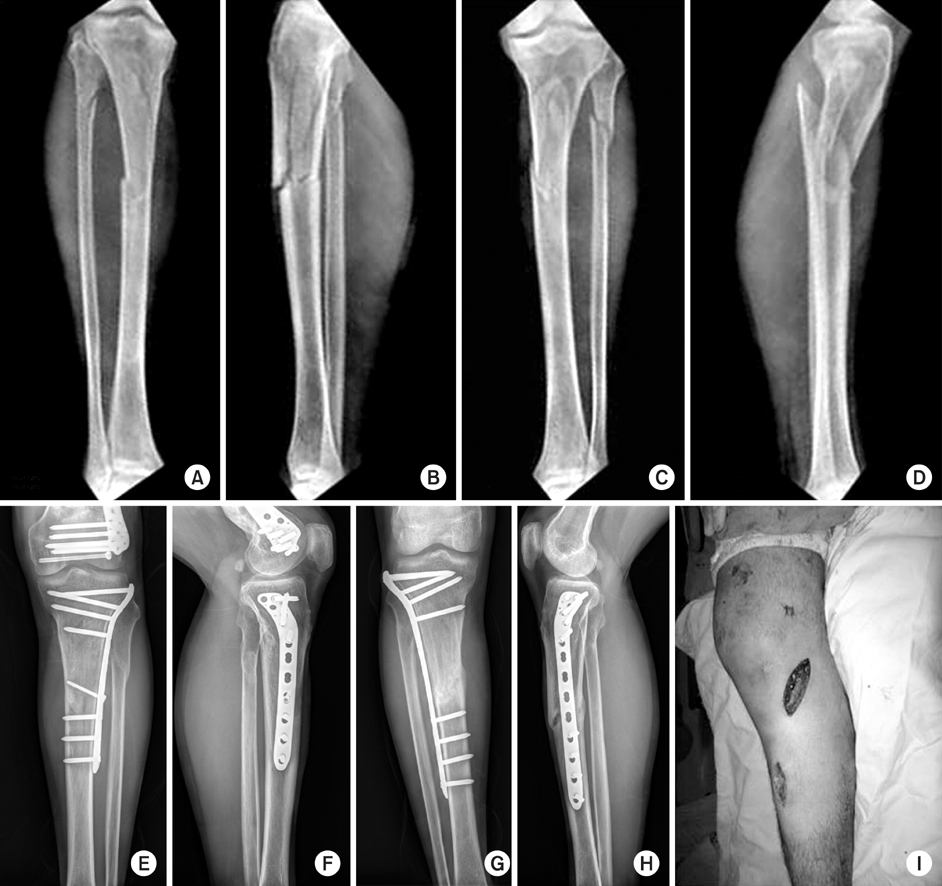
We wanted to evaluate the efficacy of MIPO (minimal invasive plate osteosynthesis) technique by LCP (locking compression plate) for treating proximal tibia fractures.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty-three patients, who had operation due to proximal tibia fracture and available for follow up for more than 1 year were included in this study. Cause of injury and accompanied injuries were checked. Operation time, period to bone union, range of joint motion and alignment were evaluated with complications.
RESULTS
Mean bone union time was 13.7 weeks (10~20). Twenty-one cases of the patients showed angulation of less than 5 degrees and 17 cases had normal range of motion. Five cases showed skin irritation by the plate and 2 cases had superficial infection.
CONCLUSION
LCP by MIPO technique for treating proximal tibia fracture showed excellent results. Delicate technique is required for the proper adjustment of LCP and the alignment of the lower leg.
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Stabilization Using a Medial Locking Plate for Proximal Tibial Fractures - Technical Note -
Jae Ang Sim, Beom Koo Lee, Kwang Hui Kim, Yong Seuk Lee
J Korean Fract Soc. 2013;26(4):327-332. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.4.327.Medial Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Plate Osteosynthesis in Proximal Tibial Comminuted Fractures
Jae-Ang Sim, Kwang-Hui Kim, Yong-Seuk Lee, Sang-Jin Lee, Beom-Koo Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2014;49(4):278-284. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2014.49.4.278.
Reference
-
1. Baumgaertel F, Buhl M, Rahn BA. Fracture healing in biological plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C3–C6.
Article2. Bolhofner BR. Indirect reduction and composite fixation of extraarticular proximal tibial fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 315:75–83.
Article3. Bone LB, Johnson KD. Treatment of tibial fractures by reaming and intramedullary nailing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68:877–887.
Article4. Buehler KC, Green J, Woll TS, Duwelius PJ. A technique for intramedullary nailing of proximal third tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 1997. 11:218–223.
Article5. Canadian Orthopaedic Trauma Society. Open reduction and internal fixation compared with circular fixator application for bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Results of a multicenter, prospective, randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:2613–2623.6. Court-Brown CM, Christie J, McQueen MM. Closed intramedullary tibial nailing. Its use in closed and type I open fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990. 72:605–611.
Article7. Duwelius PJ, Rangitsch MR, Colville MR, Woll TS. Treatment of tibial plateau fractures by limited internal fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. 339:47–57.
Article8. Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): the results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19:448–455. discussion 456.9. Gaudinez RF, Mallik AR, Szporn M. Hybrid external fixation of comminuted tibial plateau fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 328:203–210.
Article10. Gerher A, Ganz R. Combined internal and external osteosynthesis a biological approach to the treatment of complex fractures of the proximal tibia. Injury. 1998. 29:Suppl 3. C22–C28.
Article11. Henley MB. Intramedullary divices for tibia fracture stabilization. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989. (240):87–96.12. Hutson JJ Jr, Zych GA. Infections in periarticular fractures of the lower extremity treated with tensioned wire hybrid fixators. J Orthop Trauma. 1998. 12:214–218.
Article13. Kumar A, Whittle AP. Treatment of complex (Schatzker Type VI) fractures of the tibial plateau with circular wire external fixation: retrospective case review. J Orthop Trauma. 2000. 14:339–344.
Article14. Lang GJ, Cohen BE, Bosse MJ, Kellam JF. Proximal third tibial shaft fractures. Should they be nailed? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995. 315:64–74.15. Lee BK, Jo H, Eom GS, Kim JW. Treatment of comminuted fractures of proximal tibia using MIPO technique. J Korean Soc Fract. 2002. 15:243–250.
Article16. Miclau T, Martin RE. The evolution of modern plate osteosynthesis. Injury. 1997. 28:Suppl 1. A3–A6.
Article17. Muller ME, Allgower M, Schneider R, Willenegger H. Manual of internal fixation. Techniques Recommended By the AOASIF. 1990. 3rd ed. Berlin: Springer-Verlag;574–576.18. Oh CW, Oh JK, Jeon IH, et al. Double plating of proximal tibial fractures using minimally invasive percutaneous osteosynthesis technique. J Korean Fract Soc. 2005. 18:250–255.
Article19. Peindl RD, Zura RD, Vincent A, Coley ER, Bosse MJ, Sims SH. Unstable proximal extraarticular tibia fractures: a biomechanical evaluation of four methods of fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2004. 18:540–545.20. Perren SM. Minimally invasive internal fixation history, essence and potential of a new approach. Injury. 2001. 32:Suppl 1. SA1–SA3.21. Phisitkul P, McKinley TO, Nepola JV, Marsh JL. Complications of locking plate fixation in complex proximal tibia injuries. J Orthop Trauma. 2007. 21:83–91.
Article22. Sarmiento A, Gersten LM, Sobol PA, Shankwiler JA, Vangsness CT. Tibial shaft fractures treated with functional braces. Experience with 780 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989. 71:602–609.
Article23. Schatzker J, Lambert DC. Supracondylar fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:77–83.
Article24. Stamer DT, Schenk R, Staggers B, Aurori K, Aurori B, Behrens FF. Bicondylar tibial plateau fractures treated with a hybrid ring external fixator: a preliminary study. J Orthop Trauma. 1994. 8:455–461.
Article25. Stokel EA, Sadasivan KK. Tibial plateau fractures: standardized evaluation of operative results. Orthopedics. 1991. 14:263–270.26. Tornetta P 3rd, Collins E. Semiextended position of intramedullary nailing of the proximal tibia. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 328:185–189.27. Young MJ, Barrack RL. Complications of internal fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Rev. 1994. 23:149–154.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Comminuted Fractures of Proximal Tibia using MIPO technique
- Double Plating of Proximal Tibial Fractures Using Minimally Invasive Percutaneous Osteosynthesis Technique
- Treatment of The Pilon Fracture involving Tibial Shaft using Two Staged MIPO Technique
- Medial Plating of Distal Femoral Fracture with Locking Compression Plate-Proximal Lateral Tibia: Cases' Report
- Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis in Unstable Fractures of the Distal Tibia