Yonsei Med J.
2013 May;54(3):679-685. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.679.
Cholesterol Depletion in Cell Membranes of Human Airway Epithelial Cells Suppresses MUC5AC Gene Expression
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ydrhinol@yuhs.ac
- 2Human Barrier Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1727882
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.3.679
Abstract
- PURPOSE
If cholesterol in the cell membrane is depleted by treating cells with methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (MbetaCD), the activities of transmembrane receptors are altered in a cell-specific and/or receptor-specific manner. The proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1beta is potent inducers of MUC5AC mRNA and protein synthesis in human airway epithelial cells. Cells activated by IL-1beta showed increased phosphorylation of extracellular signal regulated kinase (ERK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Thus, we investigated the effects of cholesterol depletion on the expression of MUC5AC in human airway epithelial cells and whether these alterations to MUC5AC expression were related to MAPK activity.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
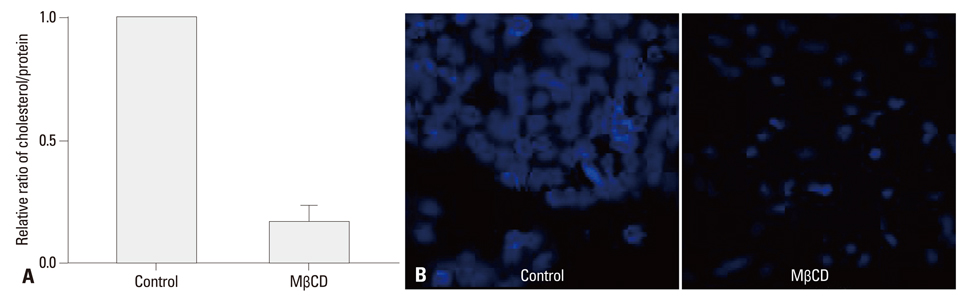
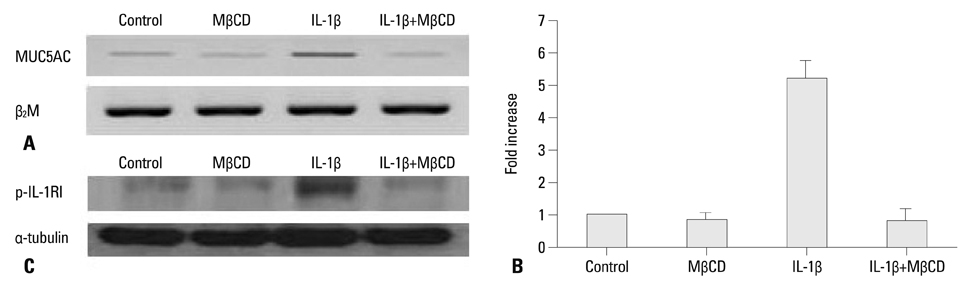
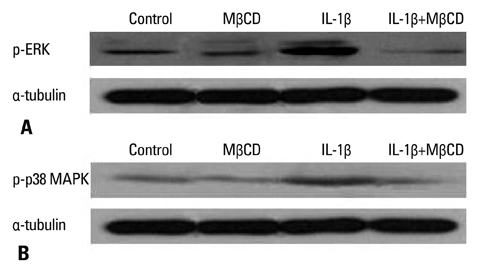
After NCI-H292 cells were pretreated with 1% MbetaCD before adding IL-1beta for 24 hours, MUC5AC mRNA expression was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and real time-PCR. Cholesterol depletion by MbetaCD was measured by modified microenzymatic fluorescence assay and filipin staining. The phosphorylation of IL-1 receptor, ERK and p38 MAPK, was analyzed by western blot.
RESULTS
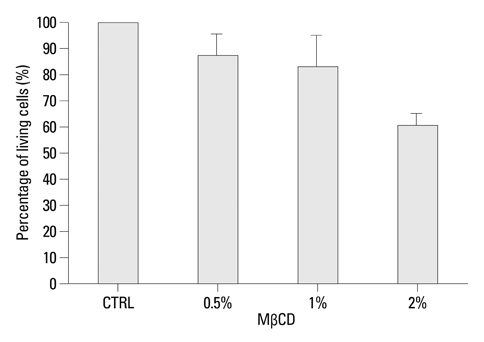
Cholesterol in the cell membrane was significantly depleted by treatment with MbetaCD on cells. IL-1beta-induced MUC5AC mRNA expression was decreased by MbetaCD and this decrease occurred IL-1-receptor-specifically. Moreover, we have shown that MbetaCD suppressed the activation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAPK in cells activated with IL-1beta. This result suggests that MbetaCD-mediated suppression of IL-1beta-induced MUC5AC mRNA operated via the ERK- and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway.
CONCLUSION
Cholesterol depletion in NCI-H292 cell membrane may be considered an anti-hypersecretory method since it effectively inhibits mucus secretion of respiratory epithelial cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brown DA, London E. Functions of lipid rafts in biological membranes. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1998. 14:111–136.
Article2. Burger K, Gimpl G, Fahrenholz F. Regulation of receptor function by cholesterol. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2000. 57:1577–1592.
Article3. Simons K, Toomre D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000. 1:31–39.
Article4. Edidin M. The state of lipid rafts: from model membranes to cells. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2003. 32:257–283.
Article5. Simons K, Ikonen E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature. 1997. 387:569–572.
Article6. Pike LJ. Lipid rafts: bringing order to chaos. J Lipid Res. 2003. 44:655–667.
Article7. Hovenberg HW, Davies JR, Herrmann A, Lindén CJ, Carlstedt I. MUC5AC, but not MUC2, is a prominent mucin in respiratory secretions. Glycoconj J. 1996. 13:839–847.
Article8. Thornton DJ, Howard M, Khan N, Sheehan JK. Identification of two glycoforms of the MUC5B mucin in human respiratory mucus. Evidence for a cysteine-rich sequence repeated within the molecule. J Biol Chem. 1997. 272:9561–9566.
Article9. Wickström C, Davies JR, Eriksen GV, Veerman EC, Carlstedt I. MUC5B is a major gel-forming, oligomeric mucin from human salivary gland, respiratory tract and endocervix: identification of glycoforms and C-terminal cleavage. Biochem J. 1998. 334(Pt 3):685–693.
Article10. Song KS, Lee WJ, Chung KC, Koo JS, Yang EJ, Choi JY, et al. Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis factor-alpha induce MUC5AC overexpression through a mechanism involving ERK/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases-MSK1-CREB activation in human airway epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:23243–23250.
Article11. Kim JH, Chang JH, Yoon JH, Kwon SH, Bae JH, Kim KS. [6]-Gingerol suppresses interleukin-1 beta-induced MUC5AC gene expression in human airway epithelial cells. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2009. 23:385–391.
Article12. Lambert S, Ameels H, Gniadecki R, Hérin M, Poumay Y. Internalization of EGF receptor following lipid rafts disruption in keratinocytes is delayed and dependent on p38 MAPK activation. J Cell Physiol. 2008. 217:834–845.
Article13. Calleros L, Lasa M, Toro MJ, Chiloeches A. Low cell cholesterol levels increase NFkappaB activity through a p38 MAPK-dependent mechanism. Cell Signal. 2006. 18:2292–2301.
Article14. Kim S, Han J, Lee DH, Cho KH, Kim KH, Chung JH. Cholesterol, a Major Component of Caveolae, Down-regulates Matrix Metalloproteinase-1 Expression through ERK/JNK Pathway in Cultured Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Ann Dermatol. 2010. 22:379–388.
Article15. Muppidi JR, Siegel RM. Ligand-independent redistribution of Fas (CD95) into lipid rafts mediates clonotypic T cell death. Nat Immunol. 2004. 5:182–189.
Article16. Garofalo T, Misasi R, Mattei V, Giammarioli AM, Malorni W, Pontieri GM, et al. Association of the death-inducing signaling complex with microdomains after triggering through CD95/Fas. Evidence for caspase-8-ganglioside interaction in T cells. J Biol Chem. 2003. 278:8309–8315.
Article17. Gniadecki R. Depletion of membrane cholesterol causes ligand-independent activation of Fas and apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 320:165–169.
Article18. Lambert S, Vind-Kezunovic D, Karvinen S, Gniadecki R. Ligand-independent activation of the EGFR by lipid raft disruption. J Invest Dermatol. 2006. 126:954–962.
Article19. Bang B, Gniadecki R, Gajkowska B. Disruption of lipid rafts causes apoptotic cell death in HaCaT keratinocytes. Exp Dermatol. 2005. 14:266–272.
Article20. Maxfield FR, Tabas I. Role of cholesterol and lipid organization in disease. Nature. 2005. 438:612–621.
Article21. Jans R, Atanasova G, Jadot M, Poumay Y. Cholesterol depletion upregulates involucrin expression in epidermal keratinocytes through activation of p38. J Invest Dermatol. 2004. 123:564–573.
Article22. Cuschieri J. Implications of lipid raft disintegration: enhanced anti-inflammatory macrophage phenotype. Surgery. 2004. 136:169–175.
Article23. Chen X, Resh MD. Cholesterol depletion from the plasma membrane triggers ligand-independent activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 2002. 277:49631–49637.
Article24. Zuo W, Chen YG. Specific activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by transforming growth factor-beta receptors in lipid rafts is required for epithelial cell plasticity. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. 20:1020–1029.
Article25. Lee JH, Wang LC, Yu HH, Lin YT, Yang YH, Chiang BL. Type I IL-1 receptor (IL-1RI) as potential new therapeutic target for bronchial asthma. Mediators Inflamm. 2010. 2010:567351.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Berberine Suppresses Interleukin-1beta-Induced MUC5AC Gene Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Suppression of IL-1beta-induced MUC5AC Gene Expression by Ginkgo biloba Extract(EGb 761) in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Galangin Regulates Mucin 5AC Gene Expression via the Nuclear Factor-κB Inhibitor α/Nuclear Factor-κB p65 Pathway in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
- Effects of Homogentisic Acid and Natural Products Derived from Pinellia ternata on Secretion, Production and Gene Expression of MUC5AC Mucin from Cultured Airway Epithelial Cells
- Eriodictyol Inhibits the Production and Gene Expression of MUC5AC Mucin via the IκBα-NF-κB p65 Signaling Pathway in Airway Epithelial Cells