J Vet Sci.
2009 Dec;10(4):323-329. 10.4142/jvs.2009.10.4.323.
Evaluation of a competitive ELISA for antibody detection against avian influenza virus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Green Cross Veterinary Products, Youngin 446-569, Korea.
- 2National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service, Anyang 430-757, Korea.
- 3Animal Genetics, Suwon 443-823, Korea. jsoh@naver.com
- 4College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- KMID: 1726905
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2009.10.4.323
Abstract
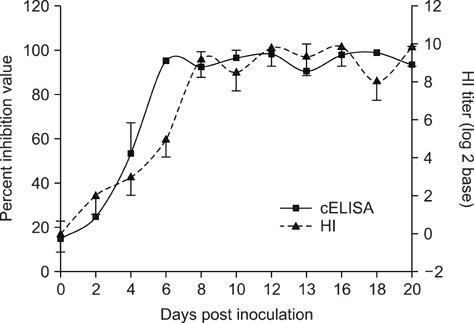
- Active serologic surveillance is necessary to control the spread of the avian influenza virus (AIV). In this study, we evaluated a commercially-available cELISA in terms of its ability to detect AIV antibodies in the sera of 3,358 animals from twelve species. cELISA detected antibodies against reference H1- through H15-subtype AIV strains without cross reactivity. Furthermore, the cELISA was able to detect antibodies produced following a challenge of the AIV H9N2 subtype in chickens, or following vaccination of the AIV H9 or H5 subtypes in chickens, ducks and geese. Next, we tested the sensitivity and specificity of the cELISA with sera from twelve different animal species, and compared these results with those obtained by the hemagglutination-inhibition (HI) test, the "gold standard" in AIV sera surveillance, a second commercially-available cELISA (IZS ELISA), or the agar gel precipitation (AGP) test. Compared with the HI test, the sensitivities and specificities of cELISA were 95% and 96% in chicken, 86% and 88% in duck, 97% and 100% in turkey, 100% and 87% in goose, and 91% and 97% in swine, respectively. The sensitivities and specificities of the cELISA in this study were higher than those of IZS ELISA for the duck, turkey, goose, and grey partridge sera samples. The results of AGP test against duck and turkey sera also showed significant correlation with the results of cELISA (R-value >0.9). In terms of flock sensitivity, the cELISA correlated better with the HI test than with commercially-available indirect ELISAs, with 100% flock sensitivity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Capua I, Alexander DJ. The challenge of avian influenza to the veterinary community. Avian Pathol. 2006. 35:189–205.
Article2. Capua I, Marangon S. The use of vaccination to combat multiple introductions of Notifiable Avian Influenza viruses of the H5 and H7 subtypes between 2000 and 2006 in Italy. Vaccine. 2007. 25:4987–4995.
Article3. Chomel JJ, Thouvenot D, Onno M, Kaiser C, Gourreau JM, Aymard M. Rapid diagnosis of influenza infection of NP antigen using an immunocapture ELISA test. J Virol Methods. 1989. 25:81–91.
Article4. Cox NJ, Newman G, Donis RO, Kawaoka Y. Topley WWC, Wilson SGS, Mahy BWJ, editors. Orthomyxoviruses: influenza. Topley and Wilson's Microbiology and Microbial Infections. 2005. London: Hodder Arnold;634–698.
Article5. Hoffmann E, Stech J, Guan Y, Webster RG, Perez DR. Universal primer set for the full-length amplification of all influenza A viruses. Arch Virol. 2001. 146:2275–2289.
Article6. Jin M, Wang G, Zhang R, Zhao S, Li H, Tan Y, Chen H. Development of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with nucleoprotein as antigen for detection of antibodies to avian influenza virus. Avian Dis. 2004. 48:870–878.
Article7. Julkunen I, Pyhälä R, Hovi T. Enzyme immunoassay, complement fixation and hemagglutination inhibition tests in the diagnosis of influenza A and B virus infections. purified hemagglutinin in subtype-specific diagnosis. J Virol Methods. 1985. 10:75–84.
Article8. Lambrecht B, Steensels M, Van Borm S, Meulemans G, van den Berg T. Development of an M2e-specific enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for differentiating infected from vaccinated animals. Avian Dis. 2007. 51:Suppl. 221–226.
Article9. Li OTW, Barr I, Leung CYH, Chen H, Guan Y, Peiris JSM, Poon LLM. Reliable universal RT-PCR assays for studying influenza polymerase subunit gene sequences from all 16 haemagglutinin subtypes. J Virol Methods. 2007. 142:218–222.
Article10. Meulemans G, Carlier MC, Gonze M, Petit P. Comparison of hemagglutination-inhibition, agar gel precipitin, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for measuring antibodies against influenza viruses in chickens. Avian Dis. 1987. 31:560–563.
Article11. Newton DW, Treanor JJ, Menegus MA. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of influenza virus infections. Am J Manag Care. 2000. 6:Suppl. S265–S275.12. Petric M, Comanor L, Petti CA. Role of the laboratory in diagnosis of influenza during seasonal epidemics and potential pandemics. J Infect Dis. 2006. 194:Suppl 2. S98–S110.
Article13. Prince HE, Leber AL. Comparison of complement fixation and hemagglutination inhibition assays for detecting antibody responses following influenza virus vaccination. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. 10:481–482.
Article14. Shafer AL, Katz JB, Eernisse KA. Development and validation of a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of type A influenza antibodies in avian sera. Avian Dis. 1998. 42:28–34.
Article15. Snyder DB, Marquardt WW, Yancey FS, Savage PK. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of antibody against avian influenza virus. Avian Dis. 1985. 29:136–144.
Article16. Starick E, Römer-Oberdörfer A, Werner O. Type- and subtype-specific RT-PCR assays for avian influenza A viruses (AIV). J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2000. 47:295–301.
Article17. Starick E, Werner O, Schirrmeier H, Köllner B, Riebe R, Mundt E. Establishment of a competitive ELISA (cELISA) system for the detection of influenza a virus nucleoprotein antibodies and its application to field sera from different species. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006. 53:370–375.
Article18. Wu R, Hu S, Xiao Y, Li Z, Shi D, Bi D. Development of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with nucleoprotein as antigen for detection and quantification of antibodies against avian influenza virus. Vet Res Commun. 2007. 31:631–641.
Article19. Zhou EM, Chan M, Heckert RA, Riva J, Cantin MF. Evaluation of a competitive ELISA for detection of antibodies against avian influenza virus nucleoprotein. Avian Dis. 1998. 42:517–522.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Development of Competitive ELISA for Detection of Avian Metapneumovirus Antibodies in Chicken
- Detection of the Avian Influenza Viruses Nonstructural Protein 1 for Distinction between Vaccinated and Infected Chickens Using Synthetic Peptide-Based ELISA
- Avian Influenza
- Control of Avian Influenza: Calls for International Collaboration
- The significance of avian influenza virus mouse-adaptation and its application in characterizing the efficacy of new vaccines and therapeutic agents