Yonsei Med J.
2006 Feb;47(1):55-62. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.55.
The Combination of TRAIL Treatment and Cancer Cell Selective Expression of TRAIL-Death Receptor DR4 Induces Cell Death in TRAIL-Resistant Cancer Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimkh34@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science of Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1715873
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.1.55
Abstract
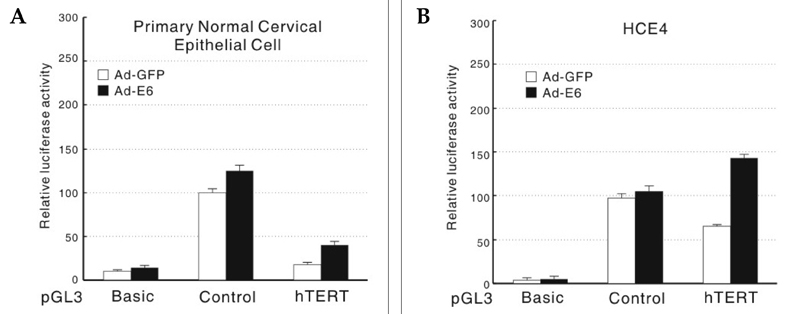
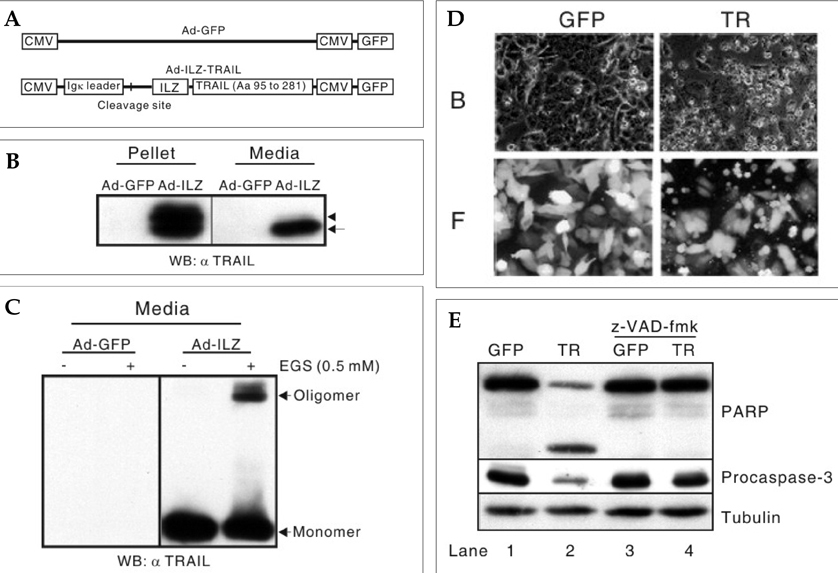
- The human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) promoter can be used for the tumor-specific expression of transgenes in order to induce selective cancer cell death. The hTERT core promoter is active in cancer cells but not in normal cells. To examine whether the combination of TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) treatment and cancer cell-selective expression of the TRAIL-death receptor could induce cell death in TRAIL-resistant cancer cells, we generated a death receptor-4 (DR4)-expressing adenovirus (Ad-hTERT-DR4), in which the expression of DR4 is driven by the hTERT promoter. Upon infection, DR4 expression was slightly increased in cancer cell lines, and cell death was observed in TRAIL-resistant cancer cell lines but not in normal human cells when DR4 infection was combined with TRAIL treatment. We also generated an adenovirus that expresses a secretable isoleucine zipper (ILZ)-fused, extracellular portion of TRAIL (Ad-ILZ-TRAIL). In cells infected with Ad-ILZ-TRAIL, TRAIL was expressed, secreted, oligomerized and biologically active in the induction of apoptosis in TRAIL-sensitive cancer cells. When Ad-hTERT-DR4 infected TRAIL-resistant HCE4 cells and Ad-ILZ-TRAIL infected TRAIL-resistant HCE7 cells were co-cultured, cell deaths were evident 24 h after co-culture. Taken together, our results reveal that the combination of TRAIL and cancer cell-specific expression of DR4 has the potential to overcome the resistance of cancer cells to TRAIL without inducing significant cell death in normal cells.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/genetics/*pharmacology/secretion
Telomerase/genetics
TNF-Related Apoptosis-Inducing Ligand
Receptors, Tumor Necrosis Factor/genetics/*metabolism
Promoter Regions (Genetics)
Neoplasms/genetics/metabolism/pathology
Membrane Glycoproteins/genetics/*pharmacology/secretion
Humans
Drug Resistance, Neoplasm
DNA-Binding Proteins/genetics
Cell Line
Apoptosis Regulatory Proteins/genetics/*pharmacology/secretion
Apoptosis/*drug effects
Antineoplastic Agents/*pharmacology
Adenoviridae/genetics
Figure
Reference
-
1. Klingelhutz AJ, Foster SA, McDougall JK. Telomerase activation by the E6 gene product of human papillomavirus type 16. Nature. 1996. 380:79–82.2. Greider CW, Blackburn EH. Telomeres, telomerase and cancer. Sci Am. 1996. 274:92–97.3. Nugent CI, Lundblad V. The telomerase reverse transcriptase: components and regulation. Genes Dev. 1998. 12:1073–1085.4. Park YM, Choi JY, Byun BH, Cho CH, Kim HS, Kim BS. Telomerase is strongly activated in hepatocellular carcinoma but not in chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis. Exp Mol Med. 1998. 30:35–40.5. Ramakrishnan S, Eppenberger U, Mueller H, Shinkai Y, Narayanan R. Expression profile of the putative catalytic subunit of the telomerase gene. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:622–625.6. Takakura M, Kyo S, Kanaya T, Tanaka M, Inoue M. Expression of human telomerase subunits and correlation with telomerase activity in cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 1998. 58:1558–1561.7. Takakura M, Kyo S, Kanaya T, Hirano H, Takeda J, Yutsudo M, et al. Cloning of human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene promoter and identification of proximal core promoter sequences essential for transcriptional activation in immortalized and cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:551–557.8. Zhao JQ, Hoare SF, McFarlane R, Muir S, Parkinson EK, Black DM, et al. Cloning and characterization of human and mouse telomerase RNA gene promoter sequences. Oncogene. 1998. 16:1345–1350.9. French LE, Tschopp J. The TRAIL to selective tumor death. Nat Med. 1999. 5:146–147.10. Ashkenazi A, Pai RC, Fong S, Leung S, Lawrence DA, Marsters SA, et al. Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand. J Clin Invest. 1999. 104:155–162.11. Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B, Griffith TS, Kubin M, et al. Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 1999. 5:157–163.12. Pan G, O'Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R, Ebner R, Ni J, et al. The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand TRAIL. Science. 1997. 276:111–113.13. Wu GS, Burns TF, McDonald ER 3rd, Jiang W, Meng R, Krantz ID, et al. KILLER/DR5 is a DNA damage-inducible p53-regulated death receptor gene. Nat Genet. 1997. 17:141–143.14. Kim K, Fisher MJ, Xu SQ, El-Deiry WS. Molecular determinants of response to TRAIL in killing of normal and cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res. 2000. 6:335–346.15. Zhang XD, Franco A, Myers K, Gray C, Nguyen T, Hersey P. Relation of TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptor and FLICE-inhibitory protein expression to TRAIL-induced apoptosis of melanoma. Cancer Res. 1999. 59:2747–2753.16. Kim K, Nakagawa H, Fei P, Rustgi AK, El-Deiry WS. Targeting Bcl-xL in esophageal squamous cancer to sensitize to chemotherapy plus TRAIL-induced apoptosis while normal epithelial cells are protected by blockade of caspase 9. Cell Death Differ. 2004. 11:583–587.17. Kim SH, Kim K, Kwagh JG, Dicker DT, Herlyn M, Rustgi AK, et al. Death induction by recombinant native TRAIL and its prevention by a caspase 9 inhibitor in primary human esophageal epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2004. 279:40044–40052.18. He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:2509–2514.19. El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993. 75:817–825.20. Harbury PB, Zhang T, Kim PS, Alber T. A switch between two-, three-, and four-stranded coiled coils in GCN4 leucine zipper mutants. Science. 1993. 262:1401–1407.21. Ozoren N, Kim K, Burns TF, Dicker DT, Moscioni AD, El-Deiry WS. The caspase 9 inhibitor Z-LEHD-FMK protects human liver cells while permitting death of cancer cells exposed to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:6259–6265.22. Nagane M, Pan G, Weddle JJ, Dixit VM, Cavenee WK, Huang HJ. Increased death receptor 5 expression by chemotherapeutic agents in human gliomas causes synergistic cytotoxicity with tumor necrosis factorrelated apoptosis-inducing ligand in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2000. 60:847–853.23. Chinnaiyan AM, Prasad U, Shankar S, Hamstra DA, Shanaiah M, Chenevert TL, et al. Combined effect of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and ionizing radiation in breast cancer therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000. 97:1754–1759.24. Kim K, Takimoto R, Dicker DT, Chen Y, Gazitt Y, El-Deiry WS. Enhanced TRAIL sensitivity by p53 over-expression in human cancer but not normal cell lines. Int J Oncol. 2001. 18:241–247.25. Gu J, Andreeff M, Roth JA, Fang B. hTERT promoter induces tumor-specific Bax gene expression and cell killing in syngenic mouse tumor model and prevents systemic toxicity. Gene Ther. 2002. 9:30–37.26. Huang X, Lin T, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA, Stephens LC, et al. Combined TRAIL and Bax gene therapy prolonged survival in mice with ovarian cancer xenograft. Gene Ther. 2002. 9:1379–1386.27. Jacob D, Davis J, Zhu H, Zhang L, Teraishi F, Wu S, et al. Suppressing orthotopic pancreatic tumor growth with a fiber-modified adenovector expressing the TRAIL gene from the human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter. Clin Cancer Res. 2004. 10:3535–3541.28. Kagawa S, He C, Gu J, Koch P, Rha SJ, Roth JA, et al. Antitumor activity and bystander effects of the tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) gene. Cancer Res. 2001. 61:3330–3338.29. Lin T, Gu J, Zhang L, Huang X, Stephens LC, Curley SA, et al. Targeted expression of green fluorescent protein/tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand fusion protein from human telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter elicits antitumor activity without toxic effects on primary human hepatocytes. Cancer Res. 2002. 62:3620–3625.30. Lin T, Huang X, Gu J, Zhang L, Roth JA, Xiong M, et al. Long-term tumor-free survival from treatment with the GFP-TRAIL fusion gene expressed from the hTERT promoter in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2002. 21:8020–8028.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Troglitazone Increases the Susceptibility to TRAIL-Induced Apoptosis in Thyroid Cancer Cell Lines
- Cytotoxic Effects of Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Apoptosis-inducing Ligand (TRAIL)and its Molecular Mechanism in Human Gastric Cancer Cells
- Activated stellate cells express the TRAIL receptor-2/death receptor-5 and undergo TRAIL-mediated apoptosis
- Restoration of the TRAIL Resistance with a Low Dose Doxorubicin in Acute Leukemia Cell Lines
- Ad-TRAIL Induces Apoptosis in Chondrocytes in Vitro and Neutralizing Antibody to TRAIL Prevents The Induction of Apoptosis in Vitro and in Vivo