Yonsei Med J.
2006 Jun;47(3):333-342. 10.3349/ymj.2006.47.3.333.
Expression of MT-1 MMP, MMP2, MMP9 and TIMP2 mRNAs in Ductal Carcinoma in Situ and Invasive Ductal Carcinoma of the Breast
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, MizMedi Breast Center, MizMedi Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jungwh96@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 3Department of Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1715851
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2006.47.3.333
Abstract
- We investigated the expression of membrane type-1 (MT1)-MMP, MMP2, MMP9 and TIMP2 mRNAs and their roles in ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) and T1 and T2 invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. We further compared these two types of carcinomas for differences in microvessel density, and expression of angiogenic factors and CD44std. MT1-MMP, MMP2, MMP9 and TIMP2 mRNA were expressed in both DCIS and invasive ductal carcinomas. Expression rates of MT1-MMP, MMP2, MMP9 and TIMP2 mRNAs were not statistically different between DCIS and invasive ductal carcinomas, nor did they differ statistically when grouped by tumor size, histologic grade or nuclear grade of invasive ductal carcinoma. Microvessel density and expression of VEGF and TGF-beta were not statistically different between DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma. CD44std expression was significantly increased in DCIS compared to invasive ductal carcinoma (p < 0.05) and it was also significantly increased in lower clinical stage, histologic grade and nuclear grade of invasive ductal carcinoma (p < 0.05). Axillary node metastasis was significantly correlated with MT1-MMP mRNA, VEGF and TGF-beta expression (p < 0.05) and MT1-MMP mRNA was positively correlated with VEGF expression and TIMP2 mRNA (p < 0.05). In summary, patterns of MMP mRNA expression in DCIS and invasive ductal carcinoma suggest that the invasive potential of breast carcinoma is already achieved before morphologically overt invasive growth is observed. As MT1-MMP mRNA expression is significantly correlated with axillary nodal metastasis, it may be useful as a prognostic indicator of invasive ductal carcinoma. Considering the positive correlation of MT1-MMP mRNA and TIMP2mRNA expression, our finding supports a role for TIMP2 in tumor growth, as well as the utility of CD44std as a prognostic indicator of breast cancer.
MeSH Terms
-
Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinase-2/genetics
RNA, Messenger/metabolism
Matrix Metalloproteinases, Membrane-Associated
Matrix Metalloproteinases/*genetics
Matrix Metalloproteinase 9/genetics
Matrix Metalloproteinase 2/genetics
Matrix Metalloproteinase 1/genetics
Humans
Gene Expression Regulation, Neoplastic
Gene Expression Regulation, Enzymologic
Female
Carcinoma, Ductal, Breast/genetics/*physiopathology
Carcinoma in Situ/genetics/*physiopathology
Breast Neoplasms/genetics/*physiopathology
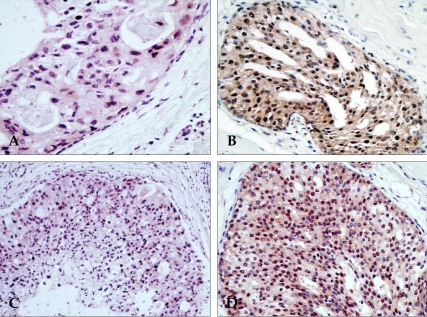
Figure
Reference
-
1. Toi M, Ishigaki S, Tominaga T. Metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1998; 52:113–124. PMID: 10066076.
Article2. Talvensaari-Mattila A, Pääkkö P, Höyhtyä M, Blanco-Sequeiros G, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 immunoreactive protein: a marker of aggressiveness in breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1998; 83:1153–1162. PMID: 9740080.3. Talvensaari-Mattila A, Pääkkö P, Blanco-Sequeiro G, Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T. Matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP2) is associated with the risk for a relapse in postmenopausal patients with node-positive breast carcinoma treated with antiestrogen adjuvant therapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2001; 65:55–61. PMID: 11245340.
Article4. Scorilas A, Karameris A, Arnogiannaki N, Ardavanis A, Bassilopoulos P, Trangas T, et al. Overexpression of matrix-metalloproteinase-9 in human breast cancer: a potential favorable indicator in node-negative patients. Br J Cancer. 2001; 84:1488–1496. PMID: 11384099.5. Liabakk NB, Talbot I, Smith RA, Wilkinson K, Ballewill F. Matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) type IV collagenase in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:190–196. PMID: 8548762.6. Pyke C, Ralfkier E, Huhtala P, Hurskainen T, Dano K, Tryggvason K. Localization of messenger RNA for Mr 72,000 and 92,000 type IV collagenase in human skin cancers by in situ hybridization. Cancer Res. 1992; 52:1336–1341. PMID: 1310643.7. Kodate M, Kasai T, Hashimoto H, Yabumoto K, Iwata Y, Manobe H. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase (gelatinase) in T1 adenocarcinoma of the lung. Pathol Int. 1997; 47:461–469. PMID: 9234385.
Article8. Sato H, Takano T, Kinoshita T, Imai K, Okada Y, Stetler-Stevenson WG, et al. Cell surface binding and activation of gelatinase A induced by expression of membrane-type-1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP). FEBS Lett. 1996; 385:238–240. PMID: 8647259.
Article9. Schneider J, Pollan M, Ruibal A, Jimenez E, Lucas AR, Nunez MI, et al. Histologic grade and CD44 are independent predictors of axillary lymph node invasion in early (T1) breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 1999; 20:319–330. PMID: 10567878.
Article10. Lyzak JS, Yaremko ML, Recant W, Baunoch DA, Joseph L. Role of CD44 in nonpalpable T1a and T1b breast cancer. Hum Pathol. 1997; 28:772–778. PMID: 9224743.
Article11. Joensuu H, Klemi PJ, Toikkanen S, Jalkanen S. Glycoprotein CD44 expression and its association with survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 1993; 143:867–874. PMID: 8362982.12. Yu Q, Stamenkovic I. Cell surface-localized matrix metalloproteinase-9 proteolytically activates TGF-beta and promotes tumor invasion and angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:163–176. PMID: 10652271.13. Black MM, Speer FD. Nuclear structure in cancer tissues. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1957; 105:97–102. PMID: 13442910.14. Elston CW, Ellis IO. Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. The value of histologic grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 1991; 19:403–410. PMID: 1757079.15. Brummer O, Athar S, Riethdorf L, Loning T, Herbst H. Matrix-metalloproteinases 1,2, and 3 and their tissue inhibitors 1 and 2 in benign and malignant breast lesions: an in situ hybridization study. Virchows Arch. 1999; 435:566–573. PMID: 10628798.16. Nielsen BS, Schested M, Kjeldsen L, Borregaard N, Rygaard J, Danon K. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in vascular pericytes in human breast cancer. Lab Invest. 1997; 77:345–355. PMID: 9354769.17. Duffy MJ, Blaser J, Duggan C, McDermott E, O'Higgins N, Fennelly JJ, et al. Assay of matrix metalloproteinase types 8 and 9 by ELISA in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 1995; 71:1025–1028. PMID: 7734294.18. Pacheo MM, Mourao M, Mantovani EB, Nishimoto IN, Brentani MM. Expression of gelatinase A and B, stromelysin-3 and matrilysin genes in breast carcinomas: clinico-pathological correlations. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1998; 16:577–585. PMID: 9932604.19. Rha SY, Yang WI, Kim JH, Roh JK, Min JS, Lee KS, et al. Different expression patterns of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 1998; 5:875–879. PMID: 9625836.
Article20. Ishigaki S, Toi M, Ueno T, Matsumoto H, Muta M, Koike M, et al. Significance of membrane-type-1-matrix metalloproteinase expression in breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1999; 90:516–522. PMID: 10391091.21. Jones JL, Glynn P, Walker RA. Expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, their inhibitors and the activator MT1-MMP in primary breast carcinoma. J Pathol. 1999; 189:161–168. PMID: 10547569.22. Nakanishi K, Kawai T, Sato H, Aida S, Kasamatsu H, Aurues T, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 (MMP-2) and of membrane-type-1-matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in transitional cell carcinoma of the upper urinary tract. Hum Pathol. 2000; 31:193–200. PMID: 10685633.23. Gilles C, Polette M, Piette J, Munaut C, Thompson EW, Birembaut P, et al. High level of MT-MMP expression is associated with invasiveness of cervical cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1996; 65:209–213. PMID: 8567119.
Article24. Polette M, Nawrocki B, Gilles C, Sato H, Seiki M, Tournier JM, et al. MT-MMP expression and localization in human lung and breast cancers. Virchows Arch. 1996; 428:29–35. PMID: 8646366.25. Ueno H, Nakamura H, Inoue M, Imai K, Noguchi M, Sato H, et al. Expression and tissue localization of membrane-types 1, 2, and 3 matrix metalloproteinases in human invasive breast carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997; 57:2055–2060. PMID: 9158005.26. Liotta LA, Stetler-Steverson WG. Tumor invasion and metastasis. an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cancer Res. 1991; 51:5054s–5059s. PMID: 1884381.27. Curran S, Murray GI. Matrix metalloproteinase in tumour invasion and metastasis. J Pathol. 1999; 189:300–308. PMID: 10547590.28. Massi D, Franchi A, Ketabchi S, Paglierani M, Pimpinelli N, Santucci M. Expression and prognostic significance of matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in primary neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin. Hum Pathol. 2003; 34:80–88. PMID: 12605370.
Article29. Kaufmann M, Heider K, Sinn HP, von Minckwitz G, Ponta H, Herrlich P. CD44 variant exon epitopes in primary breast cancer and length of survival. Lancet. 1995; 345:615–619. PMID: 7534855.
Article30. Ristamaki R, Joensuu H, Soderstrom KO, Jalkanen S. CD44v6 expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: an association with low histologic grade and poor prognosis. J Pathol. 1995; 176:259–267. PMID: 7545748.31. Kainz C, Kohlberger P, Sliutz G, Temfer C, Heinzl H, Reinthaller A, et al. Splice variants of CD44 in human cervical cancer stage IB to IIB. Gynecol Oncol. 1995; 57:383–387. PMID: 7539775.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma of the Breast Associated with Mixed Lobular and Ductal Carcinoma In Situ: A Case Report
- Expression of MMP-2, MT1-MMP, and TIMP-2 mRNA in Breast Carcinomas
- An Unusual Presentation of Extensive Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Accompanying Invasive Ductal Carcinoma on MRI: A Case Report
- Apocrine Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast Presented Mass with Morphological Change on Follow-Up Ultrasound: A Report of Case
- c-erbB-2 Oncoprotein Expression in Ductal Carcinoma in situ and Paget's Disease of the Breast