Korean J Radiol.
2013 Aug;14(4):673-676. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.673.
Inflammatory Pseudotumor in the Mediastinum: Imaging with 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon 443-721, Korea. suesj202@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Chest Surgery, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 135-720, Korea.
- KMID: 1715773
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.4.673
Abstract
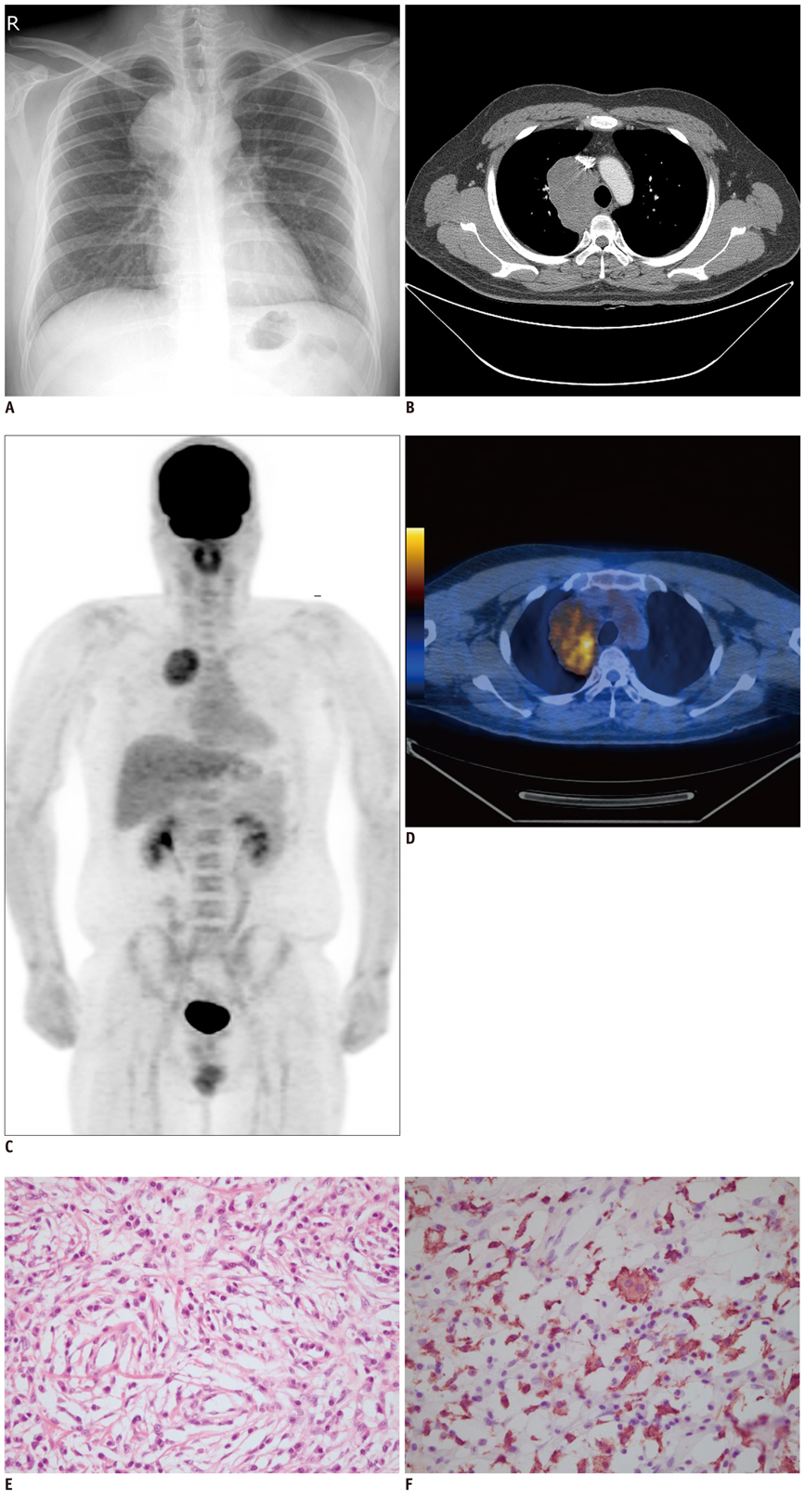
- Mediastinal inflammatory pseudotumor is a rare benign disease with its capability for local invasion and rapid growth. We present a case of middle-mediastinal inflammatory pseudotumor and report its contrast-enhanced chest computed tomography, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography and pathologic findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Patnana M, Sevrukov AB, Elsayes KM, Viswanathan C, Lubner M, Menias CO. Inflammatory pseudotumor: the great mimicker. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012; 198:W217–W227.2. Alongi F, Bolognesi A, Gajate AM, Motta M, Landoni C, Berardi G, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of mediastinum treated with tomotherapy and monitored with FDG-PET/CT: case report and literature review. Tumori. 2010; 96:322–326.3. Chen CH, Lin RL, Liu HC, Chen CH, Hung TT, Huang WC. Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor mimicking anterior mediastinal malignancy. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008; 86:1362–1364.4. Narla LD, Newman B, Spottswood SS, Narla S, Kolli R. Inflammatory pseudotumor. Radiographics. 2003; 23:719–729.5. Yoon KH, Ha HK, Lee JS, Suh JH, Kim MH, Kim PN, et al. Inflammatory pseudotumor of the liver in patients with recurrent pyogenic cholangitis: CT-histopathologic correlation. Radiology. 1999; 211:373–379.6. Obrzut SL, Halpern BS, Monchamp T, Grabski K, Watts WJ, Czernin J. The role of 2-deoxy-2-[(18)F]fluoro-D-glucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography in monitoring the immunosuppressive therapy response of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor. Mol Imaging Biol. 2004; 6:126–130.7. Choi BH, Yoon SH, Lee S, Jo KS, Song HS, An YS, et al. Primary malignant fibrous histiocytoma in mediastinum: imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2012; 46:304–307.8. Chang JM, Lee HJ, Goo JM, Lee HY, Lee JJ, Chung JK, et al. False positive and false negative FDG-PET scans in various thoracic diseases. Korean J Radiol. 2006; 7:57–69.9. Burdick MJ, Jolles PR, Grimes MM, Henry DA. Mediastinal hibernoma simulates a malignant lesion on dual time point FDG imaging. Lung Cancer. 2008; 59:391–394.10. Kaira K, Abe M, Nakagawa K, Ohde Y, Okumura T, Takahashi T, et al. 18F-FDG uptake on PET in primary mediastinal non-thymic neoplasm: a clinicopathological study. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:2423–2429.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma in Mediastinum: Imaging with 18F-FDG PET/CT
- Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Second Primary Cancer
- Esophageal Leiomyoma with intense FDG uptake on 18F-FDG PET/CT
- Dual Time Point 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging Identifies Bilateral Renal Tuberculosis in an Immunocompromised Patient with an Unknown Primary Malignancy
- 18F-FDG PET-CT-Negative Recurrent High-Grade Anaplastic Astrocytoma Detected by 18F-FDOPA PET-CT