Infect Chemother.
2015 Jun;47(2):117-119. 10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.117.
Dual Time Point 18F-FDG PET/CT Imaging Identifies Bilateral Renal Tuberculosis in an Immunocompromised Patient with an Unknown Primary Malignancy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine & PET/CT, Amrita Institute of Medical sciences, Amrita Vishwavidyapeetham University, Cochin, India. padmas@aims.amrita.edu
- KMID: 2068996
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2015.47.2.117
Abstract
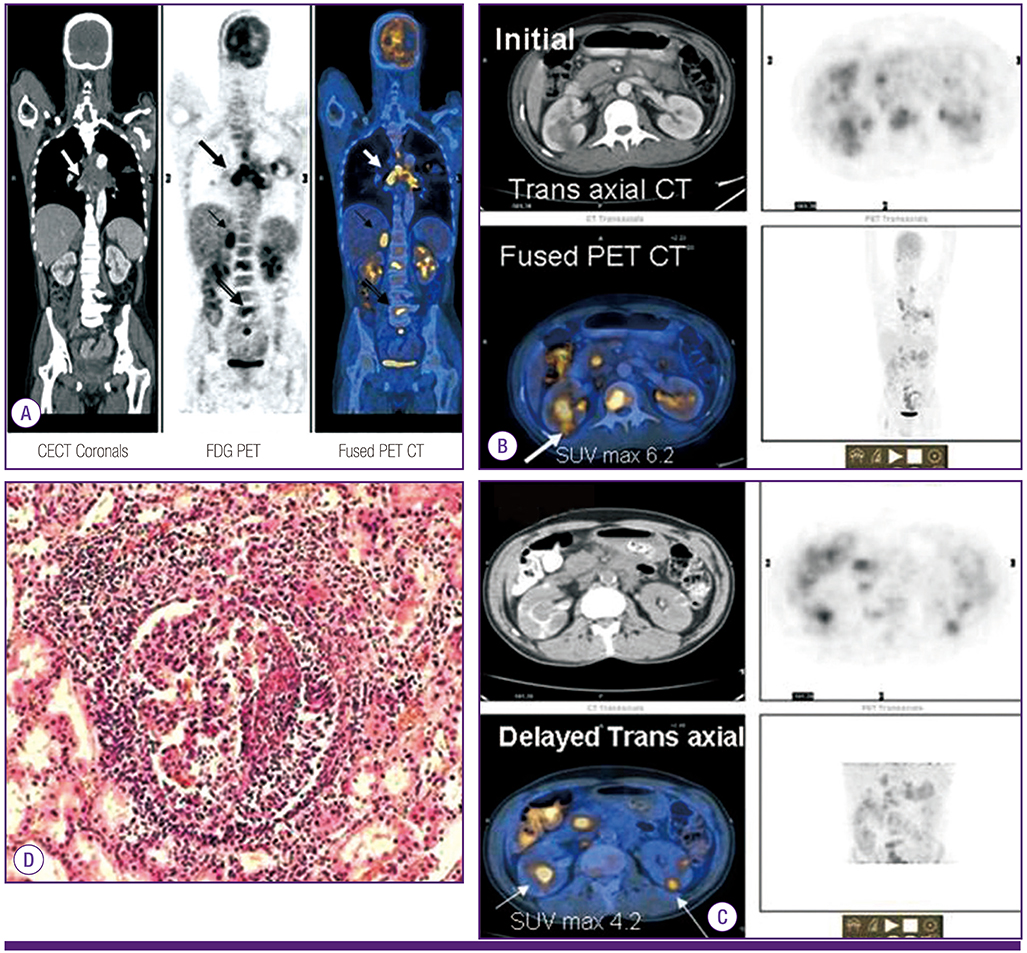
- 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging is an established imaging modality for cancer staging and response assessment. Its role in identifying infective and inflammatory pathologies from malignancy is debated. Dual time - point imaging is a refined technique used to overcome this interpretational dilemma. We present a 59 year old male with an unknown primary malignancy who was referred for a 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging. Images revealed primary lung malignancy with co existing bilateral renal tuberculosis which otherwise would have gone amiss or would have been considered as metastases.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Zhuang H, Pourdehnad M, Lambright ES, Yamamoto AJ, Lanuti M, Li P, Mozley PD, Rossman MD, Albelda SM, Alavi A. Dual time point 18F-FDG PET imaging for differentiating malignant from inflammatory processes. J Nucl Med. 2001; 42:1412–1417.2. Kubota K, Itoh M, Ozaki K, Ono S, Tashiro M, Yamaguchi K, Akaizawa T, Yamada K, Fukuda H. Advantage of delayed whole-body FDG-PET imaging for tumour detection. Eur J Nucl Med. 2001; 28:696–703.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidental Bilateral Renal Oncocytoma in a Patient with Metastatic Carcinoma of Unknown Primary: a Pitfall on 18F-FDG PET/CT
- Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Second Primary Cancer
- The Clinical Role of Dual-Time-Point 18F-FDG PET/CT in Differential Diagnosis of the Thyroid Incidentaloma
- Bilateral Tubo-Ovarian Abscess Mimics Ovarian Cancer on MRI and 18F-FDG PET/CT
- Lung Adenocarcinoma Staged as an Unknown Primary Presenting with Symptomatic Colon Metastases: Staging by 18F-FDG PET/CT