J Korean Med Sci.
2007 Apr;22(2):283-289. 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.283.
Promotive Effect of Minoxidil Combined with All-trans Retinoic Acid (tretinoin) on Human Hair Growth in Vitro
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Laboratory of Cutaneous Aging and Hair Research, Clinical Research Institute, Seoul National University Hospital, Institute of Dermatological Science, Seoul National University, Seo
- KMID: 1713189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2007.22.2.283
Abstract
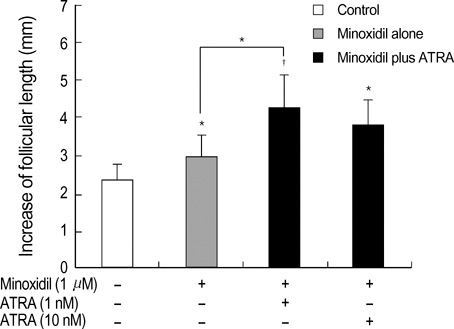
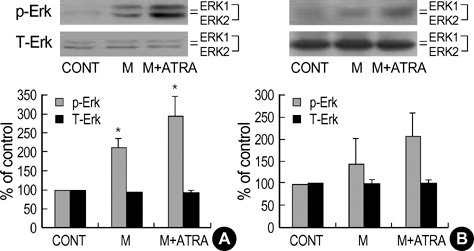
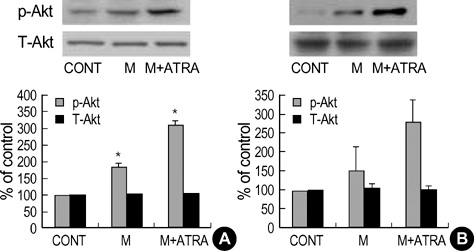
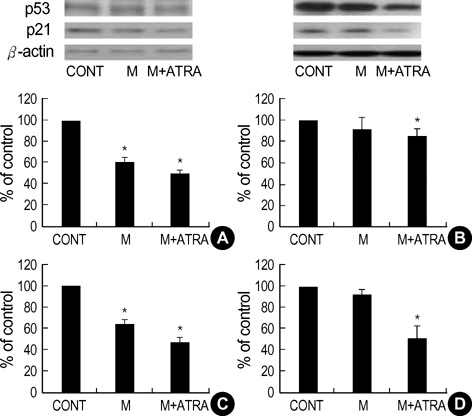
- Minoxidil induces hair growth in male pattern baldness and prolongs the anagen phase. All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) has been reported to act synergistically with minoxidil in vivo: they can enhance more dense hair regrowth than either compound alone. We evaluated the effect of minoxidil combined with ATRA on hair growth in vitro. The effect of co-treatment of minoxidil and ATRA on hair growth was studied in hair follicle organ culture. In cultured human dermal papilla cells (DPCs) and normal human epidermal keratinocytes, the expressions of Erk, Akt, Bcl-2, Bax, P53 and P21 were evaluated by immunoblot analysis. Minoxidil plus ATRA additively promoted hair growth in vitro, compared with minoxidil alone. In addition, minoxidil plus ATRA elevated phosphorylated Erk, phosphorylated Akt and the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax, but decreased the expressions of P53 and P21 more effectively than by minoxidil alone. Our results suggest that minoxidil plus ATRA would additively enhance hair growth by mediating dual functions: 1) the prolongation of cell survival by activating the Erk and Akt signaling pathways, and 2) the prevention of apoptosis of DPCs and epithelial cells by increasing the ratio of Bcl-2/Bax and downregulating the expressions of P53 and P21.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Role of Arachidonic Acid in Promoting Hair Growth
Semchin Munkhbayar, Sunhyae Jang, A-Ri Cho, Soon-Jin Choi, Chang Yup Shin, Hee Chul Eun, Kyu Han Kim, Ohsang Kwon
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(1):55-64. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.1.55.Acute Stress-Induced Changes in Follicular Dermal Papilla Cells and Mobilization of Mast Cells: Implications for Hair Growth
Hyoseung Shin, Soon-Jin Choi, A-Ri Cho, Dong Young Kim, Kyu Han Kim, Ohsang Kwon
Ann Dermatol. 2016;28(5):600-606. doi: 10.5021/ad.2016.28.5.600.
Reference
-
1. Tanigaki-Obana N, Ito M. Effects of cepharanthine and minoxidil on proliferation, differentiation and keratinization of cultured cells from the murine hair apparatus. Arch Dermatol Res. 1992. 284:290–296.
Article2. Lee WS, Ahn HJ, Kim YH. The effect of coapplication of capsaicin and minoxidil on the murine hair growth. Korean J Dermatol. 2003. 41:451–460.3. Messenger AG, Rundegren J. Minoxidil: mechanisms of action on hair growth. Br J Dermatol. 2004. 150:186–194.
Article4. Morris RJ, Liu Y, Marles L, Yang Z, Trempus C, Li S, Lin JS, Sawicki JA, Cotsarelis G. Capturing and profiling adult hair follicle stem cells. Nat Biotechnol. 2004. 22:411–417.
Article5. Bergfeld WF. Retinoids and hair growth. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1998. 39:S86–S89.
Article6. Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ. Molecular mechanisms of retinoid actions in skin. FASEB J. 1996. 10:1002–1013.
Article7. Bazzano G, Terezakis N, Attia H, Bazzano A, Dover R, Fenton D, Mandir N, Celleno L, Tamburro M, Jaconi S. Effect of retinoids on follicular cells. J Invest Dermatol. 1993. 101:138S–142S.
Article8. Bazzano GS, Terezakis N, Galen W. Topical tretinoin for hair growth promotion. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986. 15:880–883. 890–893.
Article9. Ferry JJ, Forbes KK, VanderLugt JT, Szpunar GJ. Influence of tretinoin on the percutaneous absorption of minoxidil from an aqueous topical solution. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1990. 47:439–446.
Article10. Han JH, Kwon OS, Chung JH, Cho KH, Eun HC, Kim KH. Effect of minoxidil on proliferation and apoptosis in dermal papilla cells of human hair follicle. J Dermatol Sci. 2004. 34:91–98.
Article11. Messenger AG. The culture of dermal papilla cells from human hair follicles. Br J Dermatol. 1984. 110:685–689.
Article12. Philpott MP, Green MR, Kealey T. Human hair growth in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1990. 97:463–471.
Article13. Randall VA, Thornton MJ, Redfern CP. Dermal papilla cells from human hair follicles express mRNA for retinoic acid receptors in culture. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991. 642:457–458.
Article14. Boyera N, Galey I, Bernard BA. Biphasic effects of minoxidil on the proliferation and differentiation of normal human keratinocytes. Skin Pharmacol. 1997. 10:206–220.
Article15. Boyce ST, Ham RG. Calcium-regulated differentiation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes in chemically defined clonal culture and serum-free serial culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1983. 81:33s–40s.
Article16. Mosmann T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983. 65:55–63.
Article17. Kim R, Tanabe K, Emi M, Uchida Y, Inoue H, Toge T. Inducing cancer cell death by targeting transcription factors. Anticancer Drugs. 2003. 14:3–11.
Article18. Skov MJ, Quigley JW, Bucks DA. Topical delivery system for tretinoin: research and clinical implications. J Pharm Sci. 1997. 86:1138–1143.
Article19. You YO, Lee G, Min BM. Retinoic acid extends the in vitro life span of normal human oral keratinocytes by decreasing p16 (INK4A) expression and maintaining telomerase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000. 268:268–274.20. Robinson MJ, Cobb MH. Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1997. 9:180–186.
Article21. Bost F, Caron L, Marchetti I, Dani C, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Binetruy B. Retinoic acid activation of the ERK pathway is required for embryonic stem cell commitment into the adipocyte lineage. Biochem J. 2002. 361:621–627.
Article22. Chung JH, Kang S, Varani J, Lin J, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ. Decreased extracellular-signal-regulated kinase and increased stress-activated MAP kinase activities in aged human skin in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 2000. 115:177–182.
Article23. Chang F, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Blalock WL, Franklin R, McCubrey JA. Regulation of cell cycle progression and apoptosis by the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway [Review]. Int J Oncol. 2003. 22:469–480.24. Ahmad S, Singh N, Glazer RI. Role of AKT1 in 17beta-estradiol- and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-dependent proliferation and prevention of apoptosis in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1999. 58:425–430.25. Tang Y, Zhou H, Chen A, Pittman RN, Field J. The Akt proto-oncogene links Ras to Pak and cell survival signals. J Biol Chem. 2000. 275:9106–9109.
Article26. Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Lee JT, Shelton JG, Navolanic PM, Blalock WL, Franklin RA, McCubrey JA. Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia. 2003. 17:590–603.
Article27. Cory S, Huang DC, Adams JM. The Bcl-2 family: roles in cell survival and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 2003. 22:8590–8607.
Article28. McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Blalock WL, Lee JT, Moye PW, Chang F, Pearce M, Shelton JG, White MK, Franklin RA, Pohnert SC. Synergistic effects of pi3k/akt on abrogation of cytokine-dependency induced by oncogenic raf. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2001. 41:289–323.
Article29. Stenn KS, Lawrence L, Veis D, Korsmeyer S, Seiberg M. Expression of the bcl-2 protooncogene in the cycling adult mouse hair follicle. J Invest Dermatol. 1994. 103:107–111.
Article30. Lindner G, Botchkarev VA, Botchkareva NV, Ling G, van der Veen C, Paus R. Analysis of apoptosis during hair follicle regression (catagen). Am J Pathol. 1997. 151:1601–1617.31. Ferraris C, Cooklis M, Polakowska RR, Haake AR. Induction of apoptosis through the PKC pathway in cultured dermal papilla fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1997. 234:37–46.
Article32. Adams JM, Cory S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 1998. 281:1322–1326.
Article33. Chung JJ, Cho S, Kwon YK, Kim DH, Kim K. Activation of retinoic acid receptor gamma induces proliferation of immortalized hippocampal progenitor cells. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2000. 83:52–62.34. Reed JC, Miyashita T, Takayama S, Wang HG, Sato T, Krajewski S, Aime-Sempe C, Bodrug S, Kitada S, Hanada M. BCL-2 family proteins: regulators of cell death involved in the pathogenesis of cancer and resistance to therapy. J Cell Biochem. 1996. 60:23–32.
Article35. Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1997. 389:300–305.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of TNF-alpha and Minoxidil on Human Hair Growth in Vitro
- The Effect of Retinoids in Medulloblastoma Cell Culture
- Effect of All-trans-retinoic Acid on the Growth and cAMP Level in Cultured Normal Human Melanocytes Stimulated by a-MSH
- The Effect of All-trans and 13-cis-retinoic Acid in Medulloblastoma and Glioblastoma Cell Culture
- Growth Effect of Minoxidil and Minoxidil Sulfate on Cultured Human Keratinocytes and Outer Root Sheath Cells