J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Dec;21(6):1021-1027. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.1021.
GSTM1 and GSTP1 Polymorphisms as Potential Factors for Modifying the Effect of Smoking on Inflammatory Response
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 28 Yongon-dong, Chongno-gu, Seoul, Korea. ychong1@snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Preventive Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Center for Cancer Prevention and Detection, National Cancer Center Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 6Institute of Environmental Medicine, SNUMRC, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1713112
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.6.1021
Abstract
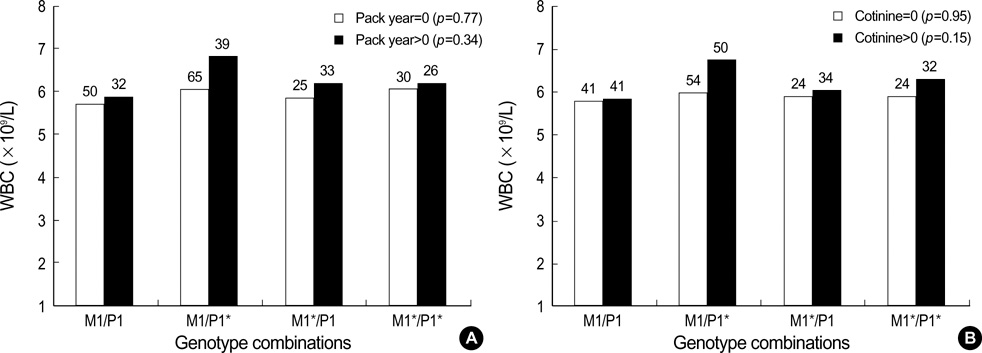
- Inflammation has been known to be an important underlying condition for development of various diseases including cancer. The aims of this study were to investigate whether tobacco smoke exposure increases the level of inflammation biomarkers and the GSTM1 and GSTP1 gene polymorphisms are associated with inflam matory response due to tobacco smoke exposure. We measured urinary cotinine level in 300 healthy university students. Total serum TNF-alpha levels and blood WBC counts were determined to evaluate inflammatory response. Allelic loss of the GSTM1 and the GSTP1 (Ile105Val) polymorphism were determined by PCR and RFLP. Tobacco smoke exposure was found to be associated with increase of both TNF-alpha level and WBC count. Particularly, smokers with combination of GSTM1 null and GSTP1 AG or GG genotypes showed higher TNF-alpha level than those with the other genotype combinations (p=0.07). This result suggests that smoking may induce inflammation measured as TNF-alpha level or WBC count and combinations of the GSTM1 and GSTP1 polymorphisms may modify the effect of smoking on serum TNF-alpha level.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/blood
Students
Smoking/*epidemiology/*genetics/immunology
Risk Factors
Risk Assessment/*methods
Prevalence
Polymorphism, Single Nucleotide/genetics
Male
Korea/epidemiology
Inflammation/*epidemiology/*genetics/immunology
Humans
Glutathione Transferase/*genetics
Glutathione S-Transferase pi/*genetics
Genetic Predisposition to Disease/epidemiology/genetics
Female
Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kaysen GA. Inflammation: cause of vascular disease and malnutrition in dialysis patients. Semin Nephrol. 2004. 24:431–436.
Article2. Busse WW, Lemanske RF Jr. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2001. 344:350–362.
Article3. Balkwill F, Mantovani A. Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet. 2001. 357:539–545.
Article4. Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002. 420:860–867.
Article5. Gupta RA, Dubois RN. Colorectal cancer prevention and treatment by inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2. Nature Rev Cancer. 2001. 1:11–21.
Article6. Kuschner WG, D'Alessandro A, Wong H, Blanc PD. Dose-dependent cigarette smoking-related inflammatory responses in healthy adults. Eur Respir J. 1996. 9:1989–1994.
Article7. Smith KR, Uyeminami DL, Kodavanti UP, Crapo JD, Chang LY, Pinkerton KE. Inhibition of tobacco smoke-induced lung inflammation by a catalytic antioxidant. Free Radic Biol Med. 2002. 33:1106–1114.8. Rusznak C, Sapsford RJ, Devalia JL, Shah SS, Hewitt EL, Lamont AG, Davies RJ, Lozewicz S. Interaction of cigarette smoke and house dust mite allergens on inflammatory mediator release from primary cultures of human bronchial epithelial cells. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001. 31:226–238.
Article9. Aggarwal BB. Tumour necrosis factors receptor associated signalling molecules and their role in activation of apoptosis, JNK and NF-kappaB. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000. 59:i6–i16.10. Komori A, Yatsunami J, Suganuma M, Okabe S, Abe S, Sakai A, Sasaki K, Fujiki H. Tumor necrosis factor acts as a tumor promoter in BALB/3T3 cell transformation. Cancer Res. 1993. 53:1982–1985.11. Pikarsky E, Porat RM, Stein I, Abramovitch R, Amit S, Kasem S, Gutkovich-Pyest E, Urieli-Shoval S, Galun E, Ben-Neriah Y. NF-kappaB functions as a tumour promoter in inflammation-associated cancer. Nature. 2004. 431:461–466.12. Szlosarek PW, Balkwill FR. Tumor necrosis factor a: a potential target for the therapy of solid tumors. Lancet Oncol. 2003. 4:565–573.13. Abrahamsson J, Carlsson B, Mellander L. Tumor necrosis factoralpha in malignant disease. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993. 15:364–369.14. Yano K, Grove JS, Chen R, Rodriguez BL, Curb JD, Tracy RP. Plasma fibrinogen as a predictor of total and cause-specific mortality in elderly Japanese-American men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2001. 21:1065–1070.
Article15. Schmidt MI, Duncan BB, Sharrett AR, Lindberg G, Savage PJ, Offenbacher S, Azambuja MI, Tracy RP, Heiss G. Markers of inflammation and prediction of diabetes mellitus in adults (Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study): a cohort study. Lancet. 1999. 353:1649–1652.
Article16. Churg A, Dai J, Tai H, Xie C, Wright JL. Tumor necrosis factor-α is central to acute cigarette smoke-induced inflammation and connective tissue breakdown. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002. 166:849–854.
Article17. Smith G, Stanley LA, Sim E, Strange RC, Wolf CR. Metabolic polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility. Cancer Surv. 1995. 25:27–65.18. Rushmore TH, Pickett CB. Glutathione S-transferases, structure, regulation and therapeutic implications. J Biol Chem. 1993. 268:11475–11478.
Article19. He JQ, Connett JE, Anthonisen NR, Pare PD, Sandford AJ. Glutathione S-transferase variants and their interaction with smoking on lung function. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004. 170:388–394.
Article20. Hayes JD, Pulford DJ. The glutathione S-transferase supergene family: Regulation of GST and the contribution of the isoenzymes to cancer chemoprotection and drug resistance. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1995. 30:445–600.21. Saarikoski ST, Voho A, Reinikainen M, Anttila S, Karjalainen A, Malaveille C, Vainio H, Husgafvel-Pursiainen K, Hirvonen A. Combined effect of polymorphic GST genes on individual susceptibility to lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 1998. 77:516–521.22. Seidegard J, Pero RW, Markowitz MM, Roush G, Miller DG, Beattie EJ. Isoenzyme(s) of glutathione S-transferase (class mu) as a marker for the susceptibility to lung cancer. A follow-up study. Carcinogenesis. 1990. 11:33–36.23. Palli D, Saieva C, Gemma S, Masala G, Gomez-Miguel MJ, Luzzi I, D'Errico M, Matullo G, Ozzola G, Manetti R, Nesi G, Sera F, Zanna I, Dogliotti E, Testai E. GSTT1 and GSTM1 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer in a high-risk italian population. Int J Cancer. 2005. 115:284–289.24. Zimniak P, Nanduri B, Pikula S, Bandorowicz-Pikula J, Singhal SS, Srivastava SK, Awasthi S, Awasthi YC. Naturally occurring human glutathione S-transferase GSTP1-1 isoforms with isoleucine and valine in position 104 differ in enzymic properties. Eur J Biochem. 1994. 224:893–899.
Article25. Keatings VM, Collins PD, Scott DM, Barnes PJ. Difference in interleukin-8 and TNFα in induced sputum from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or asthma. Am J Respir Crit Med. 1996. 153:530–534.26. Cejas P, Casado E, Belda-Iniesta C, De Castro J, Espinosa E, Redondo A, Sereno M, Garcia-Cabezas MA, Vara JA, Dominguez-Caceres A, Perona R, Gonzalez-Baron M. Implication of oxidative stress and cell membrane lipid peroxidation in human cancer (Spain). Cancer Causes Control. 2004. 15:707–719.27. Hakim IA, Harris RB, Chow HH, Dean M, Brown S, Ali IU. Effect of a 4-month tea intervention on oxidative DNA damage among heavy smokers: role of glutathione S-transferase genotypes. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004. 13:242–249.28. Hayes JD, Strange RC. Potential contribution of the glutathione S-transferase supergene family to resistence to oxidative stress. Free Radic Res. 1995. 22:193–207.29. Barnes PJ. Reactive oxygen species and airway inflammation. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990. 9:235–243.
Article30. Ryberg D, Skaug V, Hewer A, Phillips DH, Harries LW, Wolf CR, Ogreid D, Ulvik A, Vu P, Haugen A. Genotypes of glutathione S-transferase M1 and P1 and their significance for lung DNA adduct levels and caner risk. Carcinogenesis. 1997. 18:1285–1289.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- GST (GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1) polymorphisms in the genetic susceptibility of Turkish patients to cervical cancer
- Impact of Glutathione S-Transferase M1 and T1 Gene Polymorphisms on the Smoking-Related Coronary Artery Disease
- The Association between Pneumoconiosis and Genetic Polymorphism of GSTM1, GSTT1, GSTP1, NAT2, CYP2E1 and CYP1A1
- GSTM1, GSTT1 and GSTP1 Polymorphisms in the Korean Population
- Effects of Smoking and Polymorphisms of Glutathione S-Transferase M1 and T1 as Risk Factors on the Development of Bladder Cancer