J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Aug;20(4):670-673. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.670.
A Novel Missense Mutation of Doublecortin: Mutation Analysis of Korean Patients with Subcortical Band Heterotopia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. mclee@chonnam.ac.kr
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, Gwangju Christian Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1712752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.4.670
Abstract
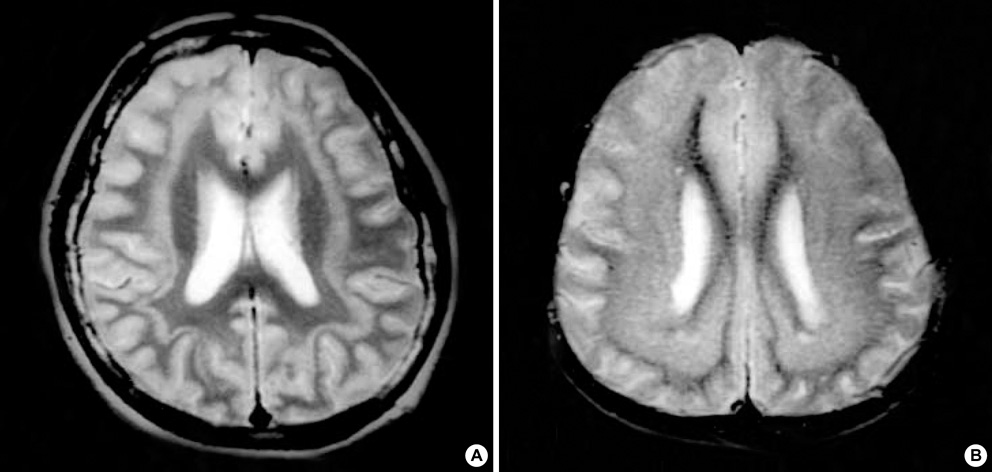
- The neuronal migration disorders, X-linked lissencephaly syndrome (XLIS) and subcortical band heterotopia (SBH), also called "double cortex", have been linked to missense, nonsense, aberrant splicing, deletion, and insertion mutations in doublecortin (DCX) in families and sporadic cases. Most DCX mutations identified to date are located in two evolutionarily conserved domains. We performed mutation analysis of DCX in two Korean patients with SBH. The SBH patients had mild to moderate developmental delays, drug-resistant generalized seizures, and diffuse thick SBH upon brain MRI. Sequence analysis of the DCX coding region in Patient 1 revealed a c.386 C>T change in exon 3. The sequence variation results in a serine to leucine amino acid change at position 129 (S129L), which has not been found in other family members of Patient 1 or in a large panel of 120 control X-chromosomes. We report here a novel c.386 C>T mutation of DCX that is responsible for SBH.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aigner L, Fluegel D, Dietrich J, Ploetz S, Winkler J. Isolated lissencephaly sequence and double-cortex syndrome in a German family with a novel doublecortin mutation. Neuropediatrics. 2000. 31:195–198.
Article2. des Portes V, Pinard JM, Billuart P, Vinet MC, Koulakoff A, Carrie A, Gelot A, Dupuis E, Motte J, Berwald-Netter Y, Catala M, Kahn A, Beldjord C, Chelly J. A novel CNS gene required for neuronal migration and involved in X-linked subcortical laminar heterotopia and lissencephaly syndrome. Cell. 1998. 92:51–61.
Article3. Gleeson JG, Allen KM, Fox JW, Lamperti ED, Berkovic S, Scheffer I, Cooper EC, Dobyns WB, Minnerath SR, Ross ME, Walsh CA. Doublecortin, a brain-specific gene mutated in human X-linked lissencephaly and double cortex syndrome, encodes a putative signaling protein. Cell. 1998. 92:63–72.
Article4. Gleeson JG, Luo RF, Grant PE, Guerrini R, Huttenlocher PR, Berg MJ, Ricci S, Cusmai R, Wheless JW, Berkovic S, Scheffer I, Dobyns WB, Walsh CA. Genetic and neuroradiological heterogeneity of double cortex syndrome. Ann Neurol. 2000. 47:265–269.
Article5. Gleeson JG, Minnerath S, Kuzniecky RI, Dobyns WB, Young ID, Ross ME, Walsh CA. Somatic and germline mosaic mutations in the doublecortin gene are associated with variable phenotypes. Am J Hum Genet. 2000. 67:574–581.
Article6. Kato M, Kanai M, Soma O, Takusa Y, Kimura T, Numakura C, Matsuki T, Nakamura S, Hayasaka K. Mutation of the doublecortin gene in male patients with double cortex syndrome: somatic mosaicism detected by hair root analysis. Ann Neurol. 2001. 50:547–551.
Article7. Matsumoto N, Leventer RJ, Kuc JA, Mewborn SK, Dudlicek LL, Ramocki MB, Pilz DT, Mills PL, Das S, Ross ME, Ledbetter DH, Dobyns WB. Mutation analysis of the DCX gene and genotype/phenotype correlation in subcortical band heterotopia. Eur J Hum Genet. 2001. 9:5–12.
Article8. Pilz DT, Kuc J, Matsumoto N, Bodurtha J, Bernadi B, Tassinari CA, Dobyns WB, Ledbetter DH. Subcortical band heterotopia in rare affected males can be caused by missense mutations in DCX (XLIS) or LIS1. Hum Mol Genet. 1999. 8:1757–1760.
Article9. Sapir T, Horesh D, Caspi M, Atlas R, Burgess HA, Wolf SG, Francis F, Chelly J, Elbaum M, Pietrokovski S, Reiner O. Doublecortin mutations cluster in evolutionarily conserved functional domains. Hum Mol Genet. 2000. 9:703–712.
Article10. Gleeson JG, Minnerath SR, Fox JW, Allen KM, Luo RF, Hong SE, Berg MJ, Kuzniecky R, Reitnauer PJ, Borgatti R, Mira AP, Guerrini R, Holmes GL, Rooney CM, Berkovic S, Scheffer I, Cooper EC, Ricci S, Cusmai R, Crawford TO, Leroy R, Andermann E, Wheless JW, Dobyns WB, Ross ME, Walsh CA. Characterization of mutations in the gene doublecortin in patients with double cortex syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1999. 45:146–153.11. Aigner L, Uyanik G, Couillard-Despres S, Ploetz S, Wolff G, Morris-Rosendahl D, Martin P, Eckel U, Spranger S, Otte J, Woerle H, Holthausen H, Apheshiotis N, Fluegel D, Winkler J. Somatic mosaicism and variable penetrance in doublecortin-associated migration disorders. Neurology. 2003. 60:329–332.
Article12. Demelas L, Serra G, Conti M, Achene A, Mastropaolo C, Matsumoto N, Dudlicek LL, Mills PL, Dobyns WB, Ledbetter DH, Das S. Incomplete penetrance with normal MRI in a woman with germline mutation of the DCX gene. Neurology. 2001. 57:327–330.
Article13. Poolos NP, Das S, Clark GD, Lardizabal D, Noebels JL, Wyllie E, Dobyns WB. Males with epilepsy, complete subcortical band heterotopia, and somatic mosaicism for DCX. Neurology. 2002. 58:1559–1562.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Possible Role of a Missense Mutation of p.P167S on NOTCH3 Gene Associated with Cerebral Autosomal Dominant Arteriopathy with Subcortical Infarcts and Leukoencephalopathy
- A Novel Mutation in the XLRS1 Gene in a Korean Family with X-linked Retinoschisis
- Periventricular nodular heterotopia in a child with a mild Mowat–Wilson phenotype caused by a novel missense mutation of ZEB2
- Neonatal Hemimegalencephaly Accompanying Band Heterotopia: Sonographic Finding and Correlation with MR Finding
- Epidermolytic Ichthyosis: Hot Spot Mutation in KRT10 Gene Mutation