Korean J Ophthalmol.
2006 Mar;20(1):62-64. 10.3341/kjo.2006.20.1.62.
A Novel Mutation in the XLRS1 Gene in a Korean Family with X-linked Retinoschisis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Institute of Vision Research, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hjkoh@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Biochemistry, Sejong University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1099074
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2006.20.1.62
Abstract
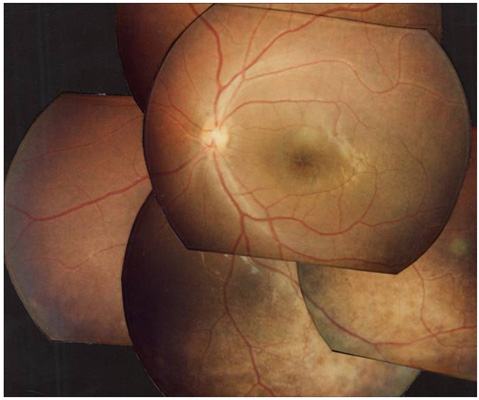
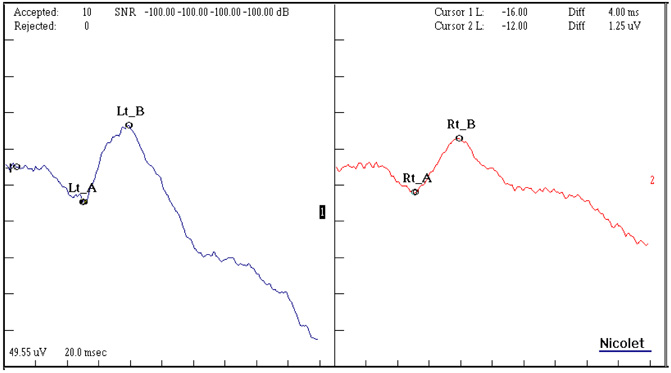
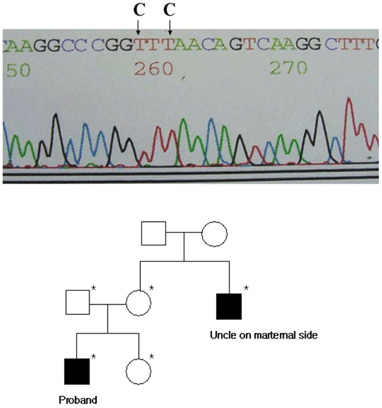
- PURPOSE: To report a novel missense mutation in the XLRS1 gene in a Korean family with X-linked retinoschisis. METHODS: Observation case report of a family with a proband with X-linked retinoschisis underwent complete ophthalmologic examination. Genomic DNA was excluded from the family's blood and all exons of the XLRS1 gene were amplified by polymerase chain reaction and analyzed using a direct sequencing method. RESULTS: A novel Leu103Phe missense mutation was identified. CONCLUSIONS: A novel Leu103Phe mutation is an additional missense mutation which is responsible for the pathogenesis of X-linked retinoschisis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. George NDL, Yates JRW, Moore AT. X-linked retinoschisis. Br J Ophthalmol. 1995. 79:697–702.2. Sauer CG, Gehrig A, Warneke-Wittstock R, et al. Positional cloning of the gene associated with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Nature genetics. 1997. 17:164–170.3. The retinoschisis consortium. Functional implications of the spectrum of mutations found in 234 cases with X-linked juvenile retinoschisis (XLRS). Human Molecular Genetics. 1998. 7:1185–1192.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A novel mutation in XLRS1 gene in X-linked juvenile retinoschisis
- Bilateral Juvenile Retinoschisis in four Brothers of a Family
- X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth Patient with a Novel Cys168Arg Missense Mutation in the Connexin32 Gene
- Long-term Results of Vision and Fundus Findings in X-linked Juvenile Retinoschisis
- A family with X-linked Cornelia de Lange syndrome due to a novel SMC1A missense mutation identified by multi-gene panel sequencing