Ann Lab Med.
2013 Jul;33(4):288-292. 10.3343/alm.2013.33.4.288.
Rapid Determination of Chimerism Status Using Dihydrorhodamine Assay in a Patient with X-linked Chronic Granulomatous Disease Following Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. eskang@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1707238
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2013.33.4.288
Abstract
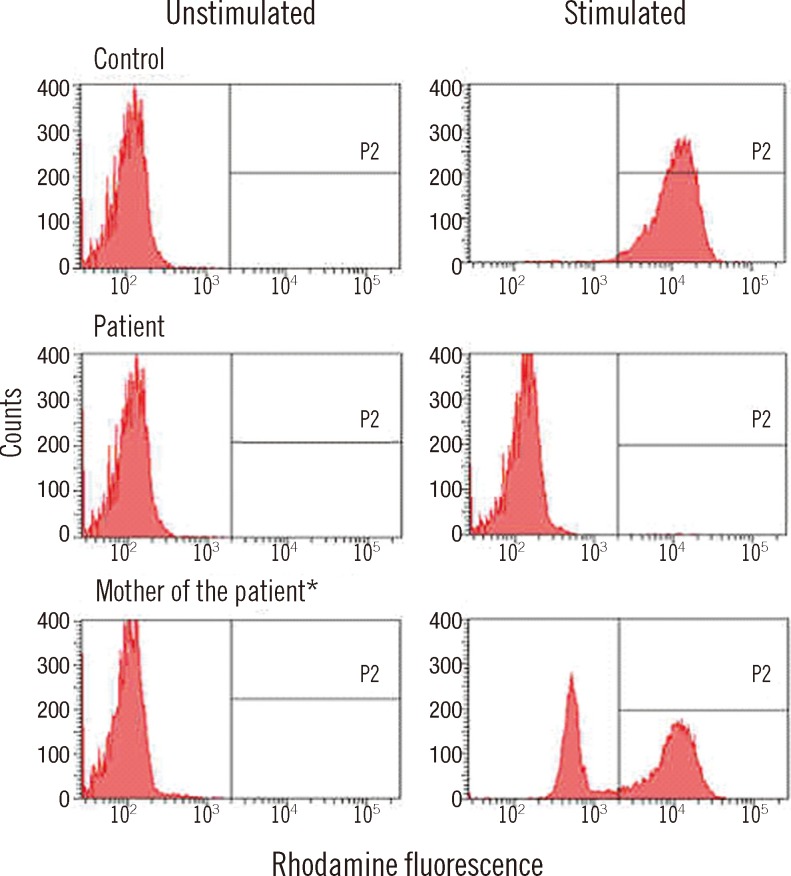
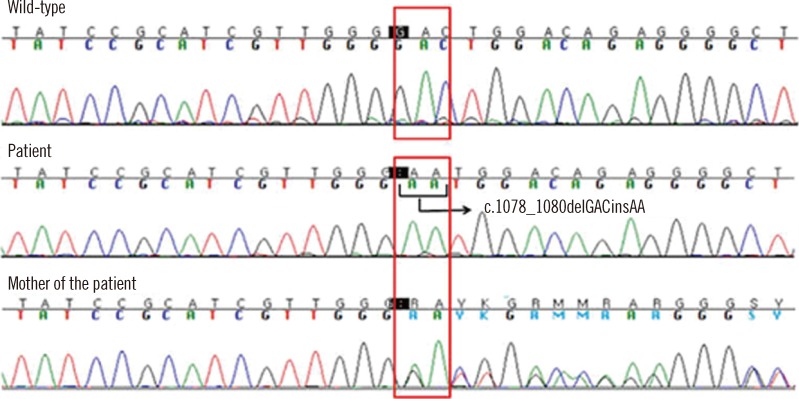
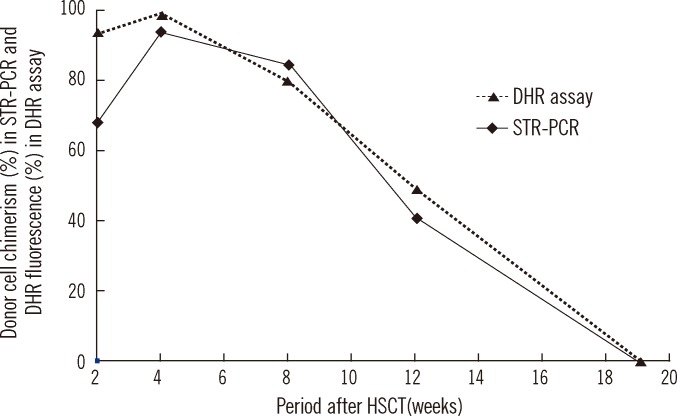
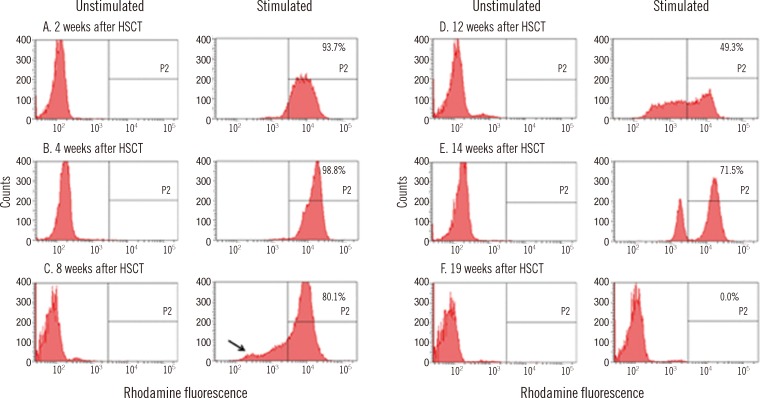
- Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD) is a rare genetic disease, which is caused by defects in the NADPH oxidase complex (gp91phox, p22phox, p40phox, p47phox, and p67phox) of phagocytes. This defect results in impaired production of superoxide anions and other reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are necessary for killing bacterial and fungal microorganisms and leads to recurrent, life-threatening bacterial and fungal infections and granulomatous inflammation. The dihydrorhodamine (DHR) flow cytometry assay is a useful diagnostic tool for CGD that can detect absent or reduced NADPH oxidase activity in stimulated phagocytes. We report a patient with X-linked CGD carrying a novel mutation of the CYBB gene whose chimerism status following hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been rapidly determined using the DHR assay. The level of DHR activity correlates well with short tandem repeat PCR analysis. Considering the advantages of this simple, rapid, and cost-effective procedure, serial measurement of DHR assay would facilitate the rapid determination of a patient's engraftment status, as a supplementary monitoring tool of chimerism status following HSCT.
MeSH Terms
-
Base Sequence
*Chimerism
DNA Mutational Analysis
Flow Cytometry
Granulomatous Disease, Chronic/*diagnosis/*enzymology/genetics/surgery
*Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Homozygote
Humans
Infant, Newborn
Male
Membrane Glycoproteins/chemistry/*genetics
Mutation
NADPH Oxidase/chemistry/*genetics
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Rhodamines/chemistry/metabolism
Membrane Glycoproteins
Rhodamines
NADPH Oxidase
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Flow Cytometry for the Diagnosis of Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: A Single Center Experience
Won Kyung Kwon, SooIn Choi, Hee-jin Kim, Hee Jae Huh, Ji-Man Kang, Yae-Jean Kim, Keon Hee Yoo, Kangmo Ahn, Hye Kyung Cho, Kyong Ran Peck, Ja-Hyun Jang, Chang-Seok Ki, Eun-Suk Kang
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2020;12(2):292-305. doi: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.292.Novel Markers of Early Neutrophilic and Monocytic Engraftment after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Jimin Kahng, Seung-Ah Yahng, Jae Wook Lee, Yonggoo Kim, Myungshin Kim, Eun-Jee Oh, Yeon-Joon Park, Jong Wook Lee, Bin Cho, Kyungja Han
Ann Lab Med. 2014;34(2):92-97. doi: 10.3343/alm.2014.34.2.92.
Reference
-
1. Winkelstein JA, Marino MC, Johnston RB Jr, Boyle J, Curnutte J, Gallin JI, et al. Chronic granulomatous disease. Report on a national registry of 368 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 2000; 79:155–169. PMID: 10844935.
Article2. Matute JD, Arias AA, Wright NA, Wrobel I, Waterhouse CC, Li XJ, et al. A new genetic subgroup of chronic granulomatous disease with autosomal recessive mutations in p40 phox and selective defects in neutrophil NADPH oxidase activity. Blood. 2009; 114:3309–3315. PMID: 19692703.3. Kuhns DB, Alvord WG, Heller T, Feld JJ, Pike KM, Marciano BE, et al. Residual NADPH oxidase and survival in chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:2600–2610. PMID: 21190454.
Article4. Roos D, Kuhns DB, Maddalena A, Roesler J, Lopez JA, Ariga T, et al. Hematologically important mutations: X-linked chronic granulomatous disease (third update). Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2010; 45:246–265. PMID: 20729109.
Article5. Vowells SJ, Sekhsaria S, Malech HL, Shalit M, Fleisher TA. Flow cytometric analysis of the granulocyte respiratory burst: a comparison study of fluorescent probes. J Immunol Methods. 1995; 178:89–97. PMID: 7829869.
Article6. Smith JA, Weidemann MJ. Further characterization of the neutrophil oxidative burst by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1993; 162:261–268. PMID: 8315293.
Article7. Jirapongsananuruk O, Malech HL, Kuhns DB, Niemela JE, Brown MR, Anderson-Cohen M, et al. Diagnostic paradigm for evaluation of male patients with chronic granulomatous disease, based on the dihydrorhodamine 123 assay. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:374–379. PMID: 12589359.
Article8. Elbim C, Lizard G. Flow cytometric investigation of neutrophil oxidative burst and apoptosis in physiological and pathological situations. Cytometry A. 2009; 75:475–481. PMID: 19358285.
Article9. Olsson LM, Nerstedt A, Lindqvist AK, Johansson SC, Medstrand P, Olofsson P, et al. Copy number variation of the gene NCF1 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2012; 16:71–78. PMID: 21728841.10. Roos D, de Boer M, Borregard N, Bjerrum OW, Valerius NH, Seger RA, et al. Chronic granulomatous disease with partial deficiency of cytochrome b558 and incomplete respiratory burst: variants of the X-linked, cytochrome b558-negative form of the disease. J Leukoc Biol. 1992; 51:164–171. PMID: 1431553.11. van Eeden SF, Klut ME, Walker BA, Hogg JC. The use of flow cytometry to measure neutrophil function. J Immunol Methods. 1999; 232:23–43. PMID: 10618507.
Article12. Kang EM, Marciano BE, DeRavin S, Zarember KA, Holland SM, Malech HL. Chronic granulomatous disease: overview and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1319–1326. PMID: 21497887.
Article13. Martinez CA, Shah S, Shearer WT, Rosenblatt HM, Paul ME, Chinen J, et al. Excellent survival after sibling or unrelated donor stem cell transplantation for chronic granulomatous disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129:176–183. PMID: 22078471.
Article14. Ringdén O, Remberger M, Svahn BM, Barkholt L, Mattsson J, Aschan J, et al. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for inherited disorders: experience in a single center. Transplantation. 2006; 81:718–725. PMID: 16534474.
Article15. Thiede C. Diagnostic chimerism analysis after allogeneic stem cell transplantation: new methods and markers. Am J Pharmacogenomics. 2004; 4:177–187. PMID: 15174899.16. Lawler M, McCann SR, Marsh JC, Ljungman P, Hows J, Vandenberghe E, et al. Serial chimerism analyses indicate that mixed haemopoietic chimerism influences the probability of graft rejection and disease recurrence following allogeneic stem cell transplantation (SCT) for severe aplastic anaemia (SAA): indication for routine assessment of chimerism post SCT for SAA. Br J Haematol. 2009; 144:933–945. PMID: 19183198.
Article17. Koldehoff M, Steckel NK, Hlinka M, Beelen DW, Elmaagacli AH. Quantitative analysis of chimerism after allogeneic stem cell transplantation by real-time polymerase chain reaction with single nucleotide polymorphisms, standard tandem repeats, and Y-chromosome-specific sequences. Am J Hematol. 2006; 81:735–746. PMID: 16838323.18. Schichman SA, Suess P, Vertino AM, Gray PS. Comparison of short tandem repeat and variable number tandem repeat genetic markers for quantitative determination of allogeneic bone marrow transplant engraftment. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002; 29:243–248. PMID: 11859397.
Article19. Matsuda K, Yamauchi K, Tozuka M, Suzuki T, Sugano M, Hidaka E, et al. Monitoring of hematopoietic chimerism by short tandem repeats, and the effect of CD selection on its sensitivity. Clin Chem. 2004; 50:2411–2414. PMID: 15563497.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- What should we consider in mixed chimerism after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation?
- Lineage-specific chimerism analysis in nucleated cells, T cells and natural killer cells after myeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Mixed chimerism after hemopoietic stem cell transplantation
- The Strategies for the Prevention of Chronic GVHD in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
- Clinical Significance of Mixed Chimerism after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation