Lab Med Online.
2014 Jul;4(3):125-131. 10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.125.
Clinical Significance of Clonal Rearrangement of the Immunoglobulin Gene in the Bone Marrow of Patients with B-cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Busan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. liring@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1706848
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/lmo.2014.4.3.125
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
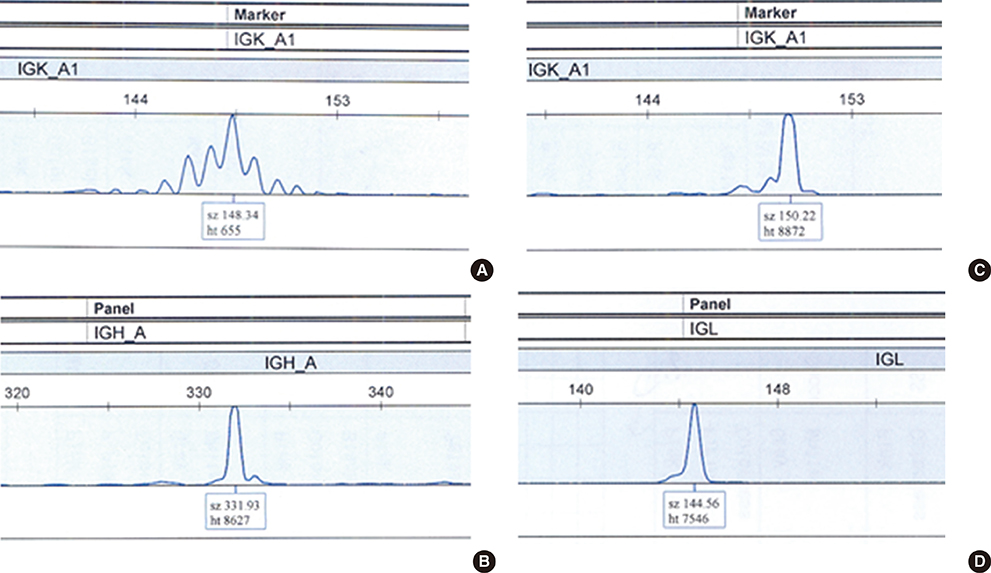
In the early stages of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), it can be difficult to recognize minimal morphological changes in the bone marrow (BM). In particular, when the quality of the BM biopsy is poor, determining BM involvement is limited to microscopic findings on BM aspiration. In this study, we compared the results of clonal immunoglobulin (IG) gene rearrangements with BM morphology results in B-cell NHL patients who underwent BM analysis as a staging workup and evaluated the usefulness of the clonal IG gene rearrangements for staging.
METHODS
Forty two B-cell NHL patients were analyzed. Clonal rearrangements of the IG heavy chain (IGH), kappa light chain (IGK) and lambda light chain (IGL) genes were detected using the IdentiClone(TM) Clonality assay (InVivoScribe Technologies, USA). Clinical characteristics and outcomes were evaluated based on the detection of monoclonal IG gene rearrangements.
RESULTS
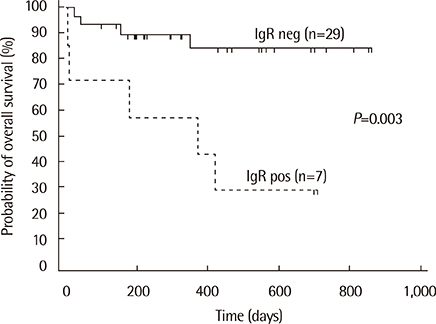
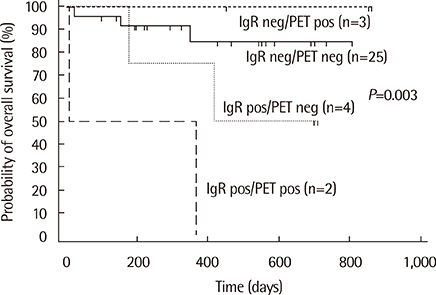
Monoclonal IG gene rearrangements were found in 9 of 42 patients (21.4%). Microscopic BM involvement was found in only 2 of 42 patients (4.8%). The monoclonality rate of IG genes in BM was correlated with clinical stage and the international prognostic index (P<0.01). Patients with monoclonal IG gene rearrangements in BM had a significantly higher relapse rate (P=0.014) and poorer overall survival at 2 yr (P<0.01).
CONCLUSIONS
Clonality analysis of BM in B-cell NHL can contribute to identification of patients with occult BM involvement with a significantly poorer overall survival despite normal BM histology.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnostic Accuracy and Prognostic Relevance of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Rearrangement and 18F-FDG-PET/CT Compared With Unilateral Bone Marrow Trephination for Detecting Bone Marrow Involvement in Patients With Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Mihee Kim, Seo-Yeon Ahn, Jae-Sook Ahn, Ga-Young Song, Sung-Hoon Jung, Je-Jung Lee, Hyeoung-Joon Kim, Jun Hyung Lee, Myung-Geun Shin, Sang Yun Song, Deok-Hwan Yang
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;37(1):e2. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2022.37.e2.
Reference
-
1. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H, et al. WHO Classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: IARC Press;2008.2. van Dongen JJ, Langerak AW, Bruggemann M, Evans PA, Hummel M, Lavender FL, et al. Design and standardization of PCR primers and protocols for detection of clonal immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene recombinations in suspect lymphoproliferations: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia. 2003; 17:2257–2317.
Article3. Mitterbauer-Hohendanner G, Mannhalter C, Winkler K, Mitterbauer M, Skrabs C, Chott A, et al. Prognostic significance of molecular staging by PCR-amplification of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Leukemia. 2004; 18:1102–1107.
Article4. Chute DJ, Cousar JB, Mahadevan MS, Siegrist KA, Silverman LM, Stoler MH. Detection of immunoglobulin heavy chain gene rearrangements in classic hodgkin lymphoma using commercially available BIOMED-2 primers. Diagn Mol Pathol. 2008; 17:65–72.
Article5. The International Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Prognostic Factors Project. A predictive model for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:987–994.6. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:579–586.
Article7. Oh HR, Lee MJ, Park G, Moon DS, Park YJ, Jang SJ. A case of lambda-expressing pulmonary MALT lymphoma with dual clonal rearrangements of kappa and lambda immunoglobulin light chain gene. Korean J Lab Med. 2009; 29:256–261.
Article8. Langerak AW, Molina TJ, Lavender FL, Pearson D, Flohr T, Sambade C, et al. Polymerase chain reaction-based clonality testing in tissue samples with reactive lymphoproliferations: usefulness and pitfalls. A report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BMH4-CT98-3936. Leukemia. 2007; 21:222–229.
Article9. Macintyre E, Willerford D, Morris SW. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma: Molecular Features of B Cell Lymphoma. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2000; 180–204.
Article10. Zwicky CS, Maddocks AB, Andersen N, Gribben JG. Eradication of polymerase chain reaction detectable immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma is associated with decreased relapse after autologous bone marrow transplantation. Blood. 1996; 88:3314–3322.
Article11. Langerak AW, Groenen PJ, Bruggemann M, Beldjord K, Bellan C, Bonello L, et al. EuroClonality/BIOMED-2 guidelines for interpretation and reporting of Ig/TCR clonality testing in suspected lymphoproliferations. Leukemia. 2012; 26:2159–2171.
Article12. Halldorsdottir AM, Zehnbauer BA, Burack WR. Application of BIOMED-2 clonality assays to formalin-fixed paraffin embedded follicular lymphoma specimens: superior performance of the IGK assays compared to IGH for suboptimal specimens. Leuk Lymphoma. 2007; 48:1338–1343.
Article13. Payne K, Wright P, Grant JW, Huang Y, Hamoudi R, Bacon CM, et al. BIOMED-2 PCR assays for IGK gene rearrangements are essential for B-cell clonality analysis in follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2011; 155:84–92.
Article14. van Krieken JH, Langerak AW, Macintyre EA, Kneba M, Hodges E, Sanz RG, et al. Improved reliability of lymphoma diagnostics via PCR-based clonality testing: report of the BIOMED-2 Concerted Action BHM4-CT98-3936. Leukemia. 2007; 21:201–206.
Article15. Sung JY, Kang SY, Kim SH, Kwon JE, Ko YH. Analysis of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement: comparison between BIOMED-2 multiplex PCR and conventional nested PCR. Lab Med Online. 2011; 1:195–201.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangement analysis in malignant lymphoid neoplasms
- A Case of Nasal-type T/NK-cell Lymphoma Resembling Cellulitis
- Application of Gene Rearrangement Analysis for Diagnosis of Malignant Lymphoma
- Utility of an immunoglobulin gene rearrangement assay based on multiplex PCR in detecting bone marrow involvement in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Primary Cutaneous B Cell Lymphoma