Clin Orthop Surg.
2013 Jun;5(2):124-128. 10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.124.
The Outcome and Complications of the Locked Plating Management for the Periprosthetic Distal Femur Fractures after a Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of the Adult Joint Reconstructive Surgery, Parvathy Hospital, Chennai, India. gavaskar.ortho@gmail.com
- 2Dhruv Clinics, Chennai, India.
- KMID: 1705533
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2013.5.2.124
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
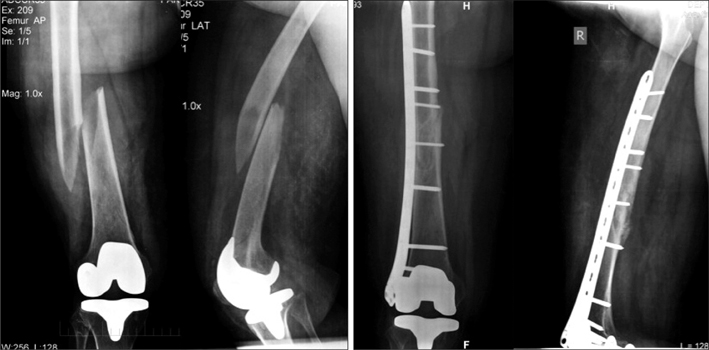
The osteosynthesis of the periprosthetic fractures following a total knee arthroplasty (TKA) can be technically difficult with the relatively small satisfactory outcomes and the high complication rates. The purpose of the study is to analyze the mid-term radiological and functional outcomes following the locked plating of the distal femur periprosthetic fractures after a TKA.
METHODS
Records of 20 patients with a periprosthetic distal femur fracture following TKA treated by the locked plate osteosynthesis were retrospectively evaluated. The union rate, complications and functional outcome measures were analyzed.
RESULTS
Successful union was achieved in 18 of the 19 patients available for the follow-up. The mean follow-up was 39 +/- 10 months. Significant reductions (p < 0.05) in the range of motion and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC) scores were evident in the follow-up. Secondary procedures were required in 5 patients to address the delay in union and the reduced knee range of motion. The osteosynthesis failed in 1 patient who underwent a revision TKA.
CONCLUSIONS
The satisfactory union rates can be achieved with the locked plate osteosynthesis in the periprosthetic distal femur fractures after TKA. Prolonged rehabilitation coupled with the un-modifiable risk factors can decrease the activity and satisfaction levels, which can significantly alter the functional outcome.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Arthroplasty, Replacement, Knee/*adverse effects
Female
Femoral Fractures/*etiology/radiography
Fracture Fixation, Internal/*adverse effects
Humans
Male
Osteoporosis/epidemiology
Periprosthetic Fractures/*etiology/radiography
Postoperative Complications/etiology
Range of Motion, Articular
Retrospective Studies
Risk Factors
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Berry DJ. Epidemiology: hip and knee. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999. 30(2):183–190.2. Hohl M. Rockwood CA, Green DP, editors. Fractures about the knee. Fractures in adults. 1984. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott;1429–1444.3. Merkel KD, Johnson EW Jr. Supracondylar fracture of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1986. 68(1):29–43.
Article4. McAuley JP, Sanchez FL. Knee: role and results of allografts. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999. 30(2):293–303.5. Moran MC, Brick GW, Sledge CB, Dysart SH, Chien EP. Supracondylar femoral fracture following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. (324):196–209.
Article6. Felix NA, Stuart MJ, Hanssen AD. Periprosthetic fractures of the tibia associated with total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997. (345):113–124.
Article7. Chalidis BE, Tsiridis E, Tragas AA, Stavrou Z, Giannoudis PV. Management of periprosthetic patellar fractures: a systematic review of literature. Injury. 2007. 38(6):714–724.8. Chen F, Mont MA, Bachner RS. Management of ipsilateral supracondylar femur fractures following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1994. 9(5):521–526.
Article9. Herrera DA, Kregor PJ, Cole PA, Levy BA, Jonsson A, Zlowodzki M. Treatment of acute distal femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty: systematic review of 415 cases (1981-2006). Acta Orthop. 2008. 79(1):22–27.
Article10. Rorabeck CH, Taylor JW. Classification of periprosthetic fractures complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999. 30(2):209–214.
Article11. Meek RM, Norwood T, Smith R, Brenkel IJ, Howie CR. The risk of peri-prosthetic fracture after primary and revision total hip and knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011. 93(1):96–101.
Article12. Culp RW, Schmidt RG, Hanks G, Mak A, Esterhai JL Jr, Heppenstall RB. Supracondylar fracture of the femur following prosthetic knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987. (222):212–222.
Article13. Gliatis J, Megas P, Panagiotopoulos E, Lambiris E. Midterm results of treatment with a retrograde nail for supracondylar periprosthetic fractures of the femur following total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2005. 19(3):164–170.
Article14. Han HS, Oh KW, Kang SB. Retrograde intramedullary nailing for periprosthetic supracondylar fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2009. 1(4):201–206.
Article15. Chettiar K, Jackson MP, Brewin J, Dass D, Butler-Manuel PA. Supracondylar periprosthetic femoral fractures following total knee arthroplasty: treatment with a retrograde intramedullary nail. Int Orthop. 2009. 33(4):981–985.
Article16. Large TM, Kellam JF, Bosse MJ, Sims SH, Althausen P, Masonis JL. Locked plating of supracondylar periprosthetic femur fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2008. 23:6 Suppl 1. 115–120.
Article17. Kim JJ, Kim E, Kim KY. Predicting the rotationally neutral state of the femur by comparing the shape of the contralateral lesser trochanter. Orthopedics. 2001. 24(11):1069–1070.
Article18. Buckley R, Mohanty K, Malish D. Lower limb malrotation following MIPO technique of distal femoral and proximal tibial fractures. Injury. 2011. 42(2):194–199.
Article19. Kolb W, Guhlmann H, Windisch C, Marx F, Koller H, Kolb K. Fixation of periprosthetic femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty with the less invasive stabilization system: a midterm follow-up study. J Trauma. 2010. 69(3):670–676.
Article20. Streubel PN, Gardner MJ, Morshed S, Collinge CA, Gallagher B, Ricci WM. Are extreme distal periprosthetic supracondylar fractures of the femur too distal to fix using a lateral locked plate? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010. 92(4):527–534.
Article21. Hou Z, Bowen TR, Irgit K, et al. Locked plating of periprosthetic femur fractures above total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2012. 26(7):427–432.
Article22. Ricci WM, Loftus T, Cox C, Borrelli J. Locked plates combined with minimally invasive insertion technique for the treatment of periprosthetic supracondylar femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma. 2006. 20(3):190–196.
Article23. Sisto DJ, Lachiewicz PF, Insall JN. Treatment of supracondylar fractures following prosthetic arthroplasty of the knee. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985. (196):265–272.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Locked Plating in Elderly Patients with Distal Femur Fracture: How to Avoid Complications?
- Periprosthetic Fracture after Locked Plating in the Osteoporotic Long Bone Fracture
- Periprosthetic Fractures Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Revision Arthroplasty Using a MUTARS® Prosthesis in Comminuted Periprosthetic Fracture of the Distal Femur
- Periprosthetic Fractures following Total Knee Arthroplasty