Yonsei Med J.
2016 Nov;57(6):1517-1522. 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1517.
Revision Arthroplasty Using a MUTARS® Prosthesis in Comminuted Periprosthetic Fracture of the Distal Femur
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Seoul, Seoul, Korea. huuy@schmc.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Soonchunhyang University Hospital Cheonan, Cheonan, Korea.
- KMID: 2427174
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1517
Abstract
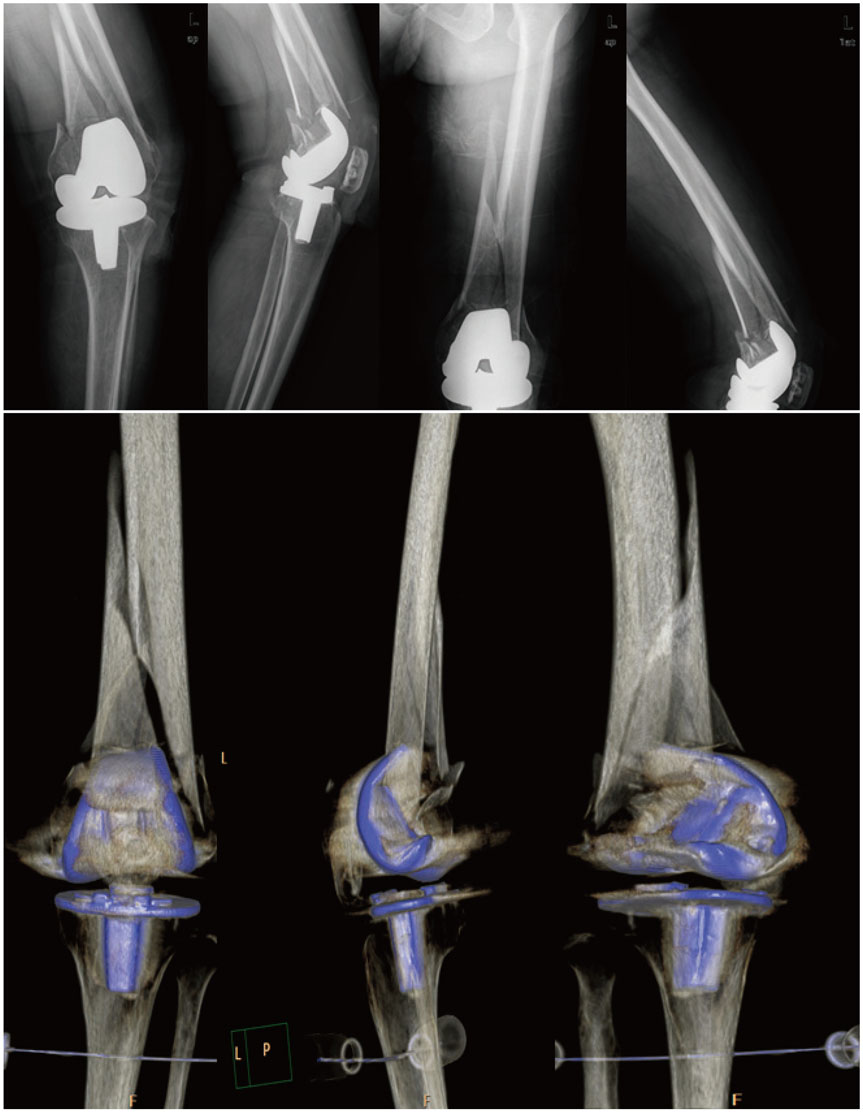
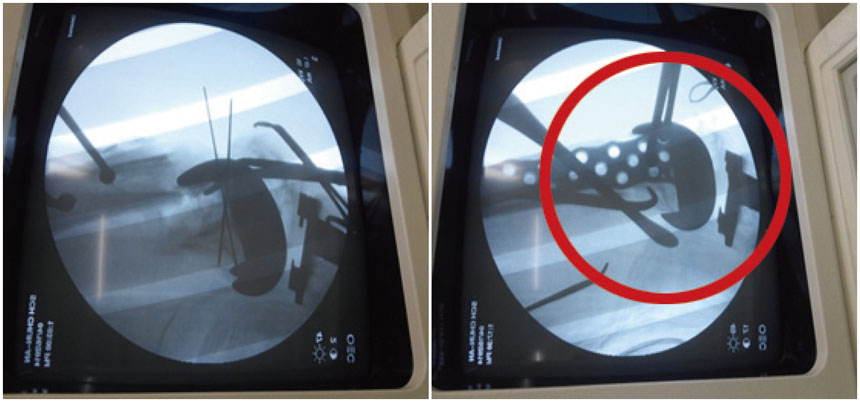
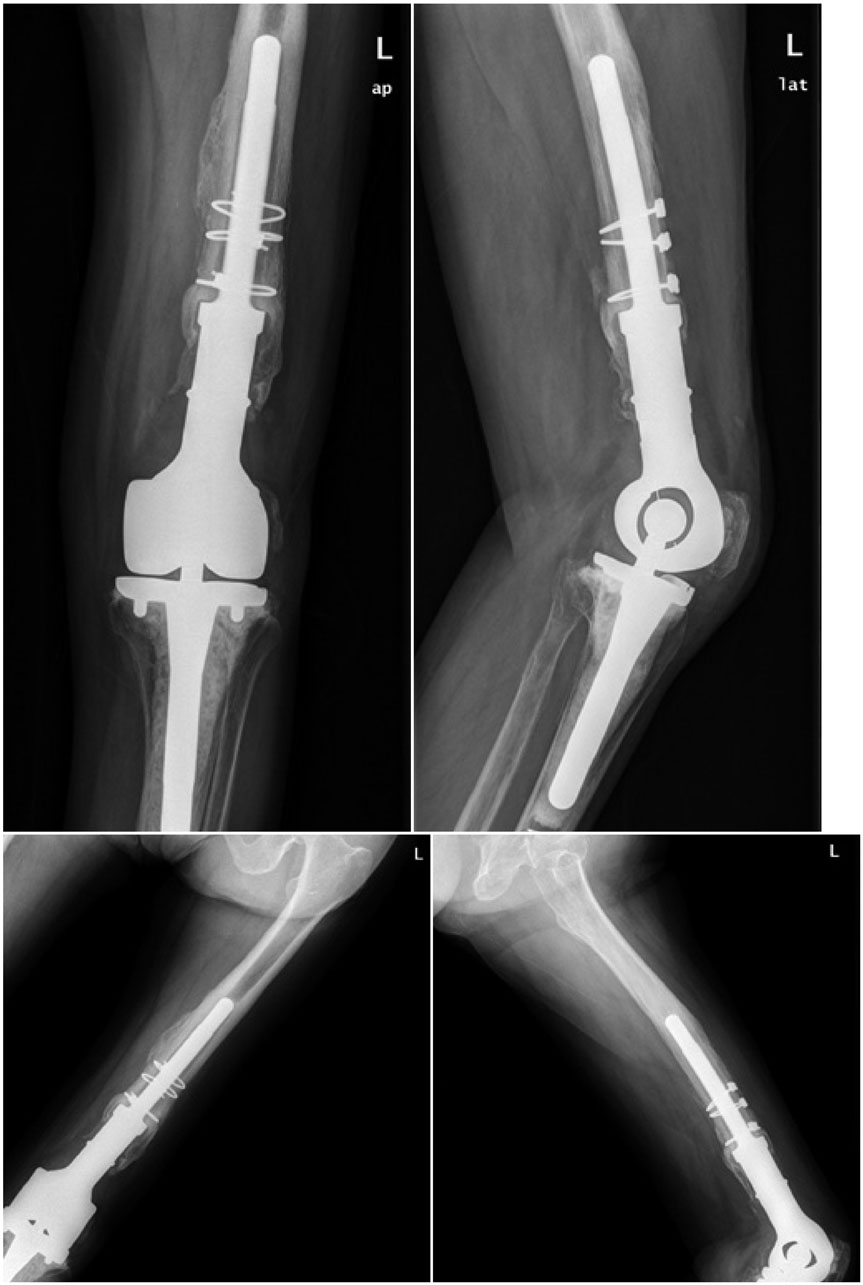
- Periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasty (TKA) are gradually increasing, reflecting extended lifespan, osteoporosis, and the increasing proportion of the elderly during the past decade. Supracondylar periprosthetic femoral fracture is a potential complication after TKA. Generally, open reduction and internal fixation are the conventional option for periprosthetic fracture after TKA. However, the presence of severe comminution with component loosening can cause failure of internal fixation. Although the current concept for periprosthetic fracture is open reduction and internal fixation, we introduce an unusual case of revision arthroplasty using a MUTARS® prosthesis for a comminuted periprosthetic fracture in the distal femur after TKA, with technical tips.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Arthroplasty, Replacement, Knee
Female
Femoral Fractures/*surgery
Femur/surgery
Fracture Fixation, Internal/*methods
Fractures, Comminuted/*surgery
Humans
Male
Open Fracture Reduction/*methods
Osteoporosis/complications
Periprosthetic Fractures/*surgery
*Prostheses and Implants
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ricci WM. Periprosthetic femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015; 29:130–137.
Article2. McGraw P, Kumar A. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Traumatol. 2010; 11:135–141.
Article3. Rorabeck CH. Periprosthetic fractures: a problem on the rise. Orthopedics. 2000; 23:989–990.
Article4. Ayers DC. Supracondylar fracture of the distal femur proximal to a total knee replacement. Instr Course Lect. 1997; 46:197–203.5. Yoo JH, Park SH, Han CD, Oh HC, Park JY, Choi SJ. Radiologic outcomes according to varus deformity in minimally invasive surgery total knee arthroplasty. Yonsei Med J. 2016; 57:225–231.
Article6. Meek RM, Norwood T, Smith R, Brenkel IJ, Howie CR. The risk of peri-prosthetic fracture after primary and revision total hip and knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93:96–101.
Article7. Su ET, DeWal H, Di Cesare PE. Periprosthetic femoral fractures above total knee replacements. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2004; 12:12–20.
Article8. Rorabeck CH, Taylor JW. Classification of periprosthetic fractures complicating total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999; 30:209–214.
Article9. Ji HM, Lee YK, Ha YC, Kim KC, Koo KH. Little impact of antiplatelet agents on venous thromboembolism after hip fracture surgery. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1625–1629.
Article10. Refaat M, Coleman S, Meehan JP, Jamali AA. Periprosthetic supracondylar femur fracture treated with spanning external fixation. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2015; 44:90–93.11. Leonidou A, Moazen M, Lepetsos P, Graham SM, Macheras GA, Tsiridis E. The biomechanical effect of bone quality and fracture topography on locking plate fixation in periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury. 2015; 46:213–217.
Article12. Streubel PN, Gardner MJ, Morshed S, Collinge CA, Gallagher B, Ricci WM. Are extreme distal periprosthetic supracondylar fractures of the femur too distal to fix using a lateral locked plate? J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92:527–534.
Article13. Kolb K, Koller H, Lorenz I, Holz U, Marx F, Grützner P, et al. Operative treatment of distal femoral fractures above total knee arthroplasty with the indirect reduction technique: a long-term follow-up study. Injury. 2009; 40:433–439.
Article14. Jassim SS, McNamara I, Hopgood P. Distal femoral replacement in periprosthetic fracture around total knee arthroplasty. Injury. 2014; 45:550–553.
Article15. Berend KR, Lombardi AV Jr. Distal femoral replacement in nontumor cases with severe bone loss and instability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009; 467:485–492.
Article16. Appleton P, Moran M, Houshian S, Robinson CM. Distal femoral fractures treated by hinged total knee replacement in elderly patients. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2006; 88:1065–1070.
Article17. Saidi K, Ben-Lulu O, Tsuji M, Safir O, Gross AE, Backstein D. Supracondylar periprosthetic fractures of the knee in the elderly patients: a comparison of treatment using allograft-implant composites, standard revision components, distal femoral replacement prosthesis. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29:110–114.
Article18. Moran MC. Treatment of periprosthetic fractures around total hip arthroplasty with an extensively coated femoral component. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11:981–988.
Article19. Kraay MJ, Goldberg VM, Figgie MP, Figgie HE 3rd. Distal femoral replacement with allograft/prosthetic reconstruction for treatment of supracondylar fractures in patients with total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 1992; 7:7–16.
Article20. Seo JG, Moon YW, Kim SM, Park SH. How to minimize rotational conflict between femoral & tibial component in total knee arthroplasty: the use of femoro-tibial axial synchronizer (Linker). Yonsei Med J. 2015; 56:454–459.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty for Spongy Metal Lübeck Hip Prosthesis with Repeated Stem Fracture and Periprosthetic Femur Fractures: A Case Report
- Periprosthetic Fractures Following Total Knee Arthroplasty
- Periprosthetic Femur Fracture due to Unrecognized Surgical Instrument Left in the Medullary Canal : A case report
- Postoperative Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture Associated with Loosening of the Femoral Prosthesis
- Three Staged Revision Arthroplasty Using Structural Allograft in Chronic Periprosthetic Joint Infection Accompanied by Fracture: A Case Report