Korean J Radiol.
2013 Jun;14(3):487-492. 10.3348/kjr.2013.14.3.487.
Glioma Grading Capability: Comparisons among Parameters from Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI and ADC Value on DWI
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 120-752, Korea. slee@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Radiology, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 137-701, Korea.
- KMID: 1705464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2013.14.3.487
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Permeability parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI (DCE-MRI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) value on diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) can be quantitative physiologic metrics for gliomas. The transfer constant (Ktrans) has shown efficacy in grading gliomas. Volume fraction of extravascular extracellular space (ve) has been underutilized to grade gliomas. The purpose of this study was to evaluate ve in its ability to grade gliomas and to assess the correlation with other permeability parameters and ADC values.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 33 patients diagnosed with pathologically-confirmed gliomas were examined by 3 T MRI including DCE-MRI and ADC map. A region of interest analyses for permeability parameters from DCE-MRI and ADC were performed on the enhancing solid portion of the tumors. Permeability parameters form DCE-MRI and ADC between low- and high-grade gliomas; the diagnostic performances of presumptive metrics and correlation among those metrics were statistically analyzed.
RESULTS
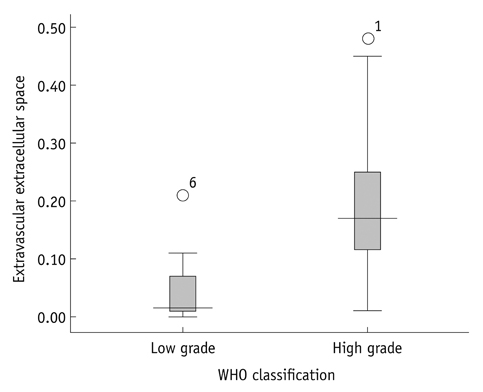
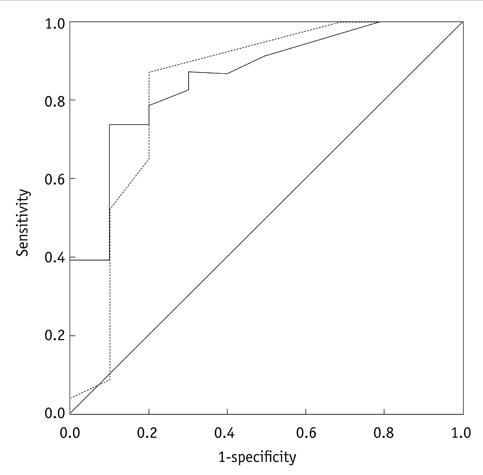
High-grade gliomas showed higher Ktrans (0.050 vs. 0.010 in median value, p = 0.002) and higher ve (0.170 vs. 0.015 in median value, p = 0.001) than low-grade gliomas. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed significance in both Ktrans and ve for glioma grading. However, there was no significant difference in diagnostic performance between Ktrans and ve. ADC value did not correlate with any of the permeability parameters from DCE-MRI.
CONCLUSION
Extravascular extracellular space (ve) appears to be comparable with transfer constant (Ktrans) in differentiating high-grade gliomas from low-grade gliomas. ADC value does not show correlation with any permeability parameters from DCE-MRI.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Aged
Brain Neoplasms/metabolism/*pathology
Contrast Media/*diagnostic use
Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging/*methods
Extracellular Space/metabolism
Female
Glioma/metabolism/*pathology
Humans
Magnetic Resonance Imaging/methods
Male
Middle Aged
Neoplasm Grading
Permeability
ROC Curve
Sensitivity and Specificity
Contrast Media
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Historical Overview, Technical Developments, and Clinical Applications
Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, Chang-Woo Ryu, Zang-Hee Cho
Prog Med Phys. 2020;31(3):35-53. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.3.35.
Reference
-
1. Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, et al. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007. 114:97–109.2. Law M, Yang S, Babb JS, Knopp EA, Golfinos JG, Zagzag D, et al. Comparison of cerebral blood volume and vascular permeability from dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced perfusion MR imaging with glioma grade. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004. 25:746–755.3. Cha S. Update on brain tumor imaging: from anatomy to physiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:475–487.4. Mills SJ, Patankar TA, Haroon HA, Balériaux D, Swindell R, Jackson A. Do cerebral blood volume and contrast transfer coefficient predict prognosis in human glioma? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:853–858.5. Hamstra DA, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD. Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: a biomarker for treatment response in oncology. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:4104–4109.6. O'Connor JP, Jackson A, Asselin MC, Buckley DL, Parker GJ, Jayson GC. Quantitative imaging biomarkers in the clinical development of targeted therapeutics: current and future perspectives. Lancet Oncol. 2008. 9:766–776.7. Waldman AD, Jackson A, Price SJ, Clark CA, Booth TC, Auer DP, et al. Quantitative imaging biomarkers in neuro-oncology. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2009. 6:445–454.8. Harrer JU, Parker GJ, Haroon HA, Buckley DL, Embelton K, Roberts C, et al. Comparative study of methods for determining vascular permeability and blood volume in human gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2004. 20:748–757.9. Sourbron S, Ingrisch M, Siefert A, Reiser M, Herrmann K. Quantification of cerebral blood flow, cerebral blood volume, and blood-brain-barrier leakage with DCE-MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009. 62:205–217.10. Lacerda S, Law M. Magnetic resonance perfusion and permeability imaging in brain tumors. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2009. 19:527–557.11. Thompson G, Mills SJ, Stivaros SM, Jackson A. Imaging of brain tumors: perfusion/permeability. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2010. 20:337–353.12. Cha S, Yang L, Johnson G, Lai A, Chen MH, Tihan T, et al. Comparison of microvascular permeability measurements, K(trans), determined with conventional steady-state T1-weighted and first-pass T2*-weighted MR imaging methods in gliomas and meningiomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:409–417.13. Jia Z, Geng D, Xie T, Zhang J, Liu Y. Quantitative analysis of neovascular permeability in glioma by dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging. J Clin Neurosci. 2012. 19:820–823.14. Awasthi R, Rathore RK, Soni P, Sahoo P, Awasthi A, Husain N, et al. Discriminant analysis to classify glioma grading using dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI and immunohistochemical markers. Neuroradiology. 2012. 54:205–213.15. Mills SJ, Soh C, Rose CJ, Cheung S, Zhao S, Parker GJ, et al. Candidate biomarkers of extravascular extracellular space: a direct comparison of apparent diffusion coefficient and dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging--derived measurement of the volume of the extravascular extracellular space in glioblastoma multiforme. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. 31:549–553.16. Sugahara T, Korogi Y, Kochi M, Ikushima I, Shigematu Y, Hirai T, et al. Usefulness of diffusion-weighted MRI with echo-planar technique in the evaluation of cellularity in gliomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999. 9:53–60.17. Guo AC, Cummings TJ, Dash RC, Provenzale JM. Lymphomas and high-grade astrocytomas: comparison of water diffusibility and histologic characteristics. Radiology. 2002. 224:177–183.18. Tofts PS, Brix G, Buckley DL, Evelhoch JL, Henderson E, Knopp MV, et al. Estimating kinetic parameters from dynamic contrast-enhanced T(1)-weighted MRI of a diffusable tracer: standardized quantities and symbols. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999. 10:223–232.19. Lüdemann L, Grieger W, Wurm R, Budzisch M, Hamm B, Zimmer C. Comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI with WHO tumor grading for gliomas. Eur Radiol. 2001. 11:1231–1241.20. Pike MM, Stoops CN, Langford CP, Akella NS, Nabors LB, Gillespie GY. High-resolution longitudinal assessment of flow and permeability in mouse glioma vasculature: Sequential small molecule and SPIO dynamic contrast agent MRI. Magn Reson Med. 2009. 61:615–625.21. Burnet NG, Lynch AG, Jefferies SJ, Price SJ, Jones PH, Antoun NM, et al. High grade glioma: imaging combined with pathological grade defines management and predicts prognosis. Radiother Oncol. 2007. 85:371–378.22. Mills SJ, Soh C, O'Connor JP, Rose CJ, Buonaccorsi G, Cheung S, et al. Enhancing fraction in glioma and its relationship to the tumoral vascular microenvironment: a dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. 31:726–731.23. Rumboldt Z, Camacho DL, Lake D, Welsh CT, Castillo M. Apparent diffusion coefficients for differentiation of cerebellar tumors in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006. 27:1362–1369.24. Norris DG. The effects of microscopic tissue parameters on the diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging experiment. NMR Biomed. 2001. 14:77–93.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Discriminating Tumor Deposits From Metastatic Lymph Nodes in Rectal Cancer: A Pilot Study Utilizing Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRI
- Diffusion-weighted and Dynamic Contrast-enhanced MRI of Metastatic Bone Tumors: Correlation of the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient, K(trans) and ve values
- Diagnosis of Infectious Spondylitis Using Non-Contrast Enhanced MRI With Axial Diffusion-Weighted Images: Comparison With Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI
- The Role of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and the Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) Values for Breast Tumors
- Treatment Response Evaluation of Breast Cancer after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy and Usefulness of the Imaging Parameters of MRI and PET/CT