J Korean Rheum Assoc.
2007 Jun;14(2):160-165. 10.4078/jkra.2007.14.2.160.
Two Cases of Adult Onset Still's Disease with Concomitant Hemophagocytic Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jychoe@cu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, The Catholic University of Daegu School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 1526434
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jkra.2007.14.2.160
Abstract
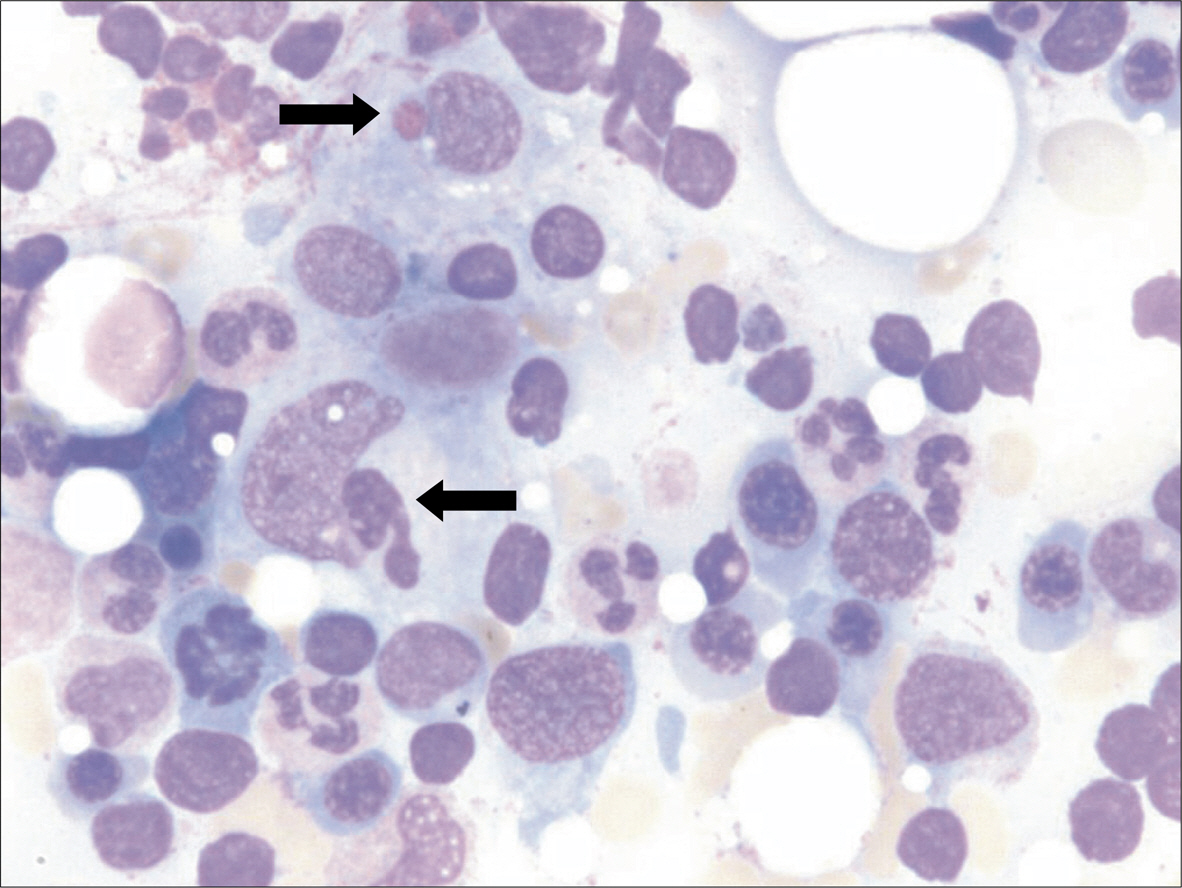
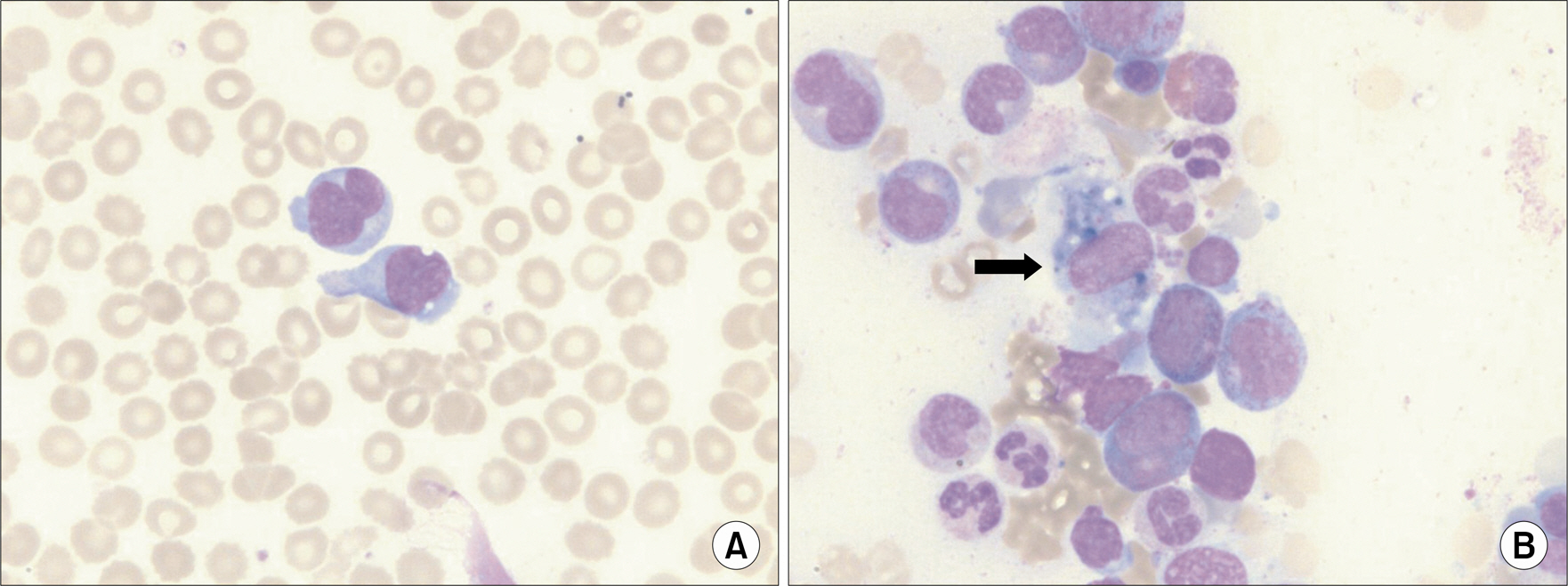
- Adult onset Still's disease is an rare inflammatory disease with the characteristic of fever, skin rash, arthralgia or arthritis, lymphadenopathy, leukocytosis and multiple systemic organ involvement. Its accurate pathogenesis has not been elucidated yet. Its clinical manifestation is also very diverse, from relatively mild symptoms to severe complications such as concomitant infection, liver failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation, myocarditis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, which may lead to death in some cases. Particularly, concomitant hemophagocytic syndrome is rare complication that could induce a fatal outcome. Thus it is important to diagnose early and start treatments. Until now, it has been reported in only one case of adult onset Still's disease in Korea. Here, we report two female cases of adult onset Still's disease with concomitant hemophagocytic syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Magadur-Joly G., Billaud E., Barrier JH., Pennec YL., Masson C., Renou P, et al. Epidemiology of adult Still's disease: estimate of the incidence by a retrospective study in west France. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995. 54:587–90.
Article2). Efthimiou P., Paik PK., Bielory L. Diagnosis and management of adult onset Still's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:564–72.
Article3). Park JH., Bae JH., Choi YS., Lee HS., Jun JB., Jung S, et al. Adult-onset Still's disease with disseminated intravascular coagulation and multiple organ dysfunctions dramatically treated with cyclosporine A. J Korean Med Sci. 2004. 19:137–41.
Article4). Yamaguchi M., Ohta A., Tsunematsu T., Kasukawa R., Mizushima Y., Kashiwagi H, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1992. 19:424–30.5). Kumakura S., Ishikura H., Umegae N., Yamagata S., Kobayashi S. Autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Am J Med. 1997. 102:113–5.
Article6). Amenomori M., Migita K., Miyashita T., Yoshida S., Ito M., Eguchi K, et al. Cytomegalovirus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in a patient with adult onset Still's disease. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005. 23:100–2.7). Egeler RM., Shapiro R., Loechelt B., Filipovich A. Characteristic immune abnormalities in hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1996. 18:340–5.
Article8). Grom AA. Natural killer cell dysfunction: a common pathway in systemic-onset juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, macrophage activation syndrome, and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis? Arthritis Rheum. 2004. 50:689–98.
Article9). Dhote R., Simon J., Papo T., Detournay B., Sailler L., Andre MH, et al. Reactive hemophagocytic syndrome in adult systemic disease: report of twenty-six cases and literature review. Arthritis Rheum. 2003. 49:633–9.
Article10). Kumakura S., Ishikura H., Munemasa S., Adachi T., Murakawa Y., Kobayashi S. Adult onset Still's disease associated hemophagocytosis. J Rheumatol. 1997. 24:1645–8.11). Arlet JB., Le TH., Marinho A., Amoura Z., Wechsler B., Papo T, et al. Reactive haemophagocytic syndrome in adult-onset Still's disease: a report of six patients and a review of the literature. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:1596–601.
Article12). Fautrel B., Sibilia J., Mariette X., Combe B. Club Rhumatismes et Inflammation. Tumour necrosis factor alpha blocking agents in refractory adult Still's disease: an observational study of 20 cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005. 64:262–6.13). Kokkinos A., Iliopoulos A., Greka P., Efthymiou A., Katsilambros N., Sfikakis PP. Successful treatment of refractory adult-onset Still's disease with infliximab. A prospective, non-comparative series of four patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2004. 23:45–9.
Article14). Emmenegger U., Frey U., Reimers A., Fux C., Semela D., Cottagnoud P, et al. Hyperferritinemia as indicator for intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in reactive macrophage activation syndromes. Am J Hematol. 2001. 68:4–10.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Cases of Adult Onset Still's Disease with Hemolytic Anemia
- A Case of Adult Onset Still's Disease Presented with Acute Febrile Hepatitis
- Kikuchi-Fujimoto Disease with Cutaneous Involvement Associated with Hemophagocytic Syndrome
- Two Cases of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis Following Kikuchi's Disease
- A Case of Adult-onset Still's Disease Associated with Leukopenia