J Rheum Dis.
2012 Apr;19(2):104-107. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.2.104.
A Cases of Adult Onset Still's Disease with Hemolytic Anemia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Pusan, Korea. wtchung@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2223109
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.2.104
Abstract
- Adult onset Still's disease (AOSD) is a systemic inflammatory disorder of unknown etiology. AOSD is characterized by fever, arthralgia, salmon-colored skin rash, hepatosplenomegaly and its laboratory abnormalities include leukocytosis, elevated liver enzyme, negative autoantibody, and hyperferritinemia. The clinical course varied and severe complicated conditions, such as hemophagocytic syndrome, and disseminated intravascular coagulation, occurred occasionally. Such a complication is accompanied with hemolytic anemia and lead to be a fatal course. We report the first case of AOSD with hemolytic anemia, which improved with high dose steroid therapy.
MeSH Terms
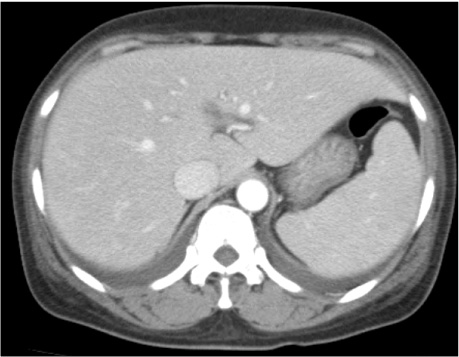
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H, et al. Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still's disease. J Rheumatol. 1992. 19:424–430.2. Bywaters EG. Still's disease in the adult. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971. 30:121–133.3. Pouchot J, Sampalis JS, Beaudet F, Carette S, Décary F, Salusinsky-Sternbach M, et al. Adult Still's disease: manifestations, disease course, and outcome in 62 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991. 70:118–136.4. Efthimiou P, Paik PK, Bielory L. Diagnosis and management of adult onset Still's disease. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006. 65:564–572.5. Kumakura S, Ishikura H, Umegae N, Yamagata S, Kobayashi S. Autoimmune-associated hemophagocytic syndrome. Am J Med. 1997. 102:113–115.6. Bagnari V, Colina M, Ciancio G, Govoni M, Trotta F. Adult-onset Still's disease. Rheumatol Int. 2010. 30:855–862.7. Mert A, Ozaras R, Tabak F, Bilir M, Ozturk R, Ozdogan H, et al. Fever of unknown origin: a review of 20 patients with adult-onset Still's disease. Clin Rheumatol. 2003. 22:89–93.8. Wouters JM, van der Veen J, van de Putte LB, de Rooij DJ. Adult onset Still's disease and viral infections. Ann Rheum Dis. 1988. 47:764–767.9. Omagari K, Matsunaga Y, Yamashita H, Nishiyama H, Hazama H, Oda H, et al. Successful treatment with cyclosporin in adult-onset Still disease manifesting as acute hepatitis with marked hyperferritinemia. Am J Med Sci. 2003. 326:148–151.10. Kötter I, Wacker A, Koch S, Henes J, Richter C, Engel A, et al. Anakinra in patients with treatment-resistant adult-onset Still's disease: four case reports with serial cytokine measurements and a review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2007. 37:189–197.11. van de Putte LB, Wouters JM. Adult-onset Still's disease. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1991. 5:263–275.12. Masson C, Le Loët X, Lioté F, Renou P, Dubost JJ, Boissier MC, et al. Adult Still's disease. Part II. Management, outcome, and prognostic factors. Rev Rhum Engl Ed. 1995. 62:758–765.13. Coombs RRA, Mourant AE, Race RR. A new test for the detection of weak and incomplete Rh agglutinins. Br J Exp Pathol. 1945. 26:255–266.14. Karasawa M. Autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Nihon Rinsho. 2008. 66:520–523.15. Pirofsky B. Clinical aspects of autoimmune hemolytic anemia. Semin Hematol. 1976. 13:251–265.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia in Ulcerative Colitis
- Severe Late-onset Anemia Associated with Rhesus D Alloimmunization
- A case of Wilson disease associated with hemolytic anemia and cholelithiasis
- Two Cases of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemic
- A new paradigm in the diagnosis of hereditary hemolytic anemia