Tuberc Respir Dis.
2007 Jan;62(1):71-73. 10.4046/trd.2007.62.1.71.
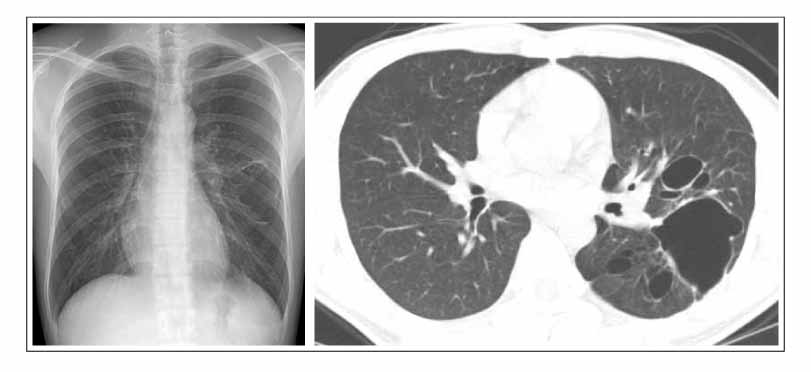
Multicystic Pulmonary Parenchymal Lesions in a Young Adult with Hemoptysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Department of Medicine, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. wjkoh@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Thoracic Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1518493
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2007.62.1.71
Abstract
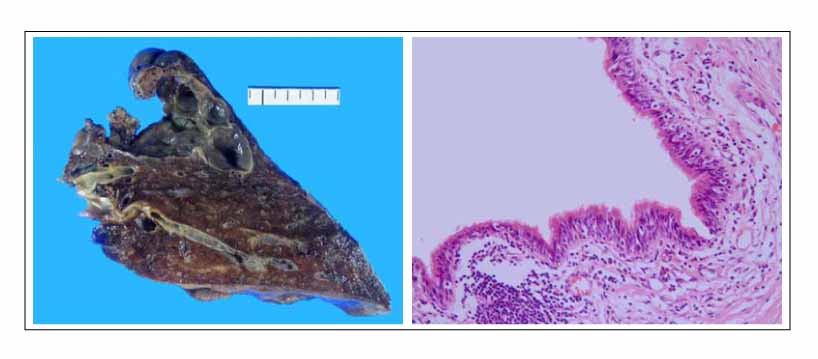
- Bronchogenic cysts are commonly located in the mediastinum or lung parenchyma, and arise from the abnormal budding of the primitive tracheobronchial tube. Cough and pain are the most common symptoms. Bronchogenic cysts appear as spherical or oval masses with smooth outlines and are usually unilocular and noncalcified. We report a young adult with a bronchogenic cyst presenting as multicystic pulmonary parenchymal lesions. This case is very unusual because a multicystic intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst is very rare in adults.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Suen HC, Mathisen DJ, Grillo HC, LeBlanc J, McLoud TC, Moncure AC, et al. Surgical management and radiological characteristics of bronchogenic cysts. Ann Thorac Surg. 1993. 55:476–481.2. Sarper A, Ayten A, Golbasi I, Demircan A, Isin E. Bronchogenic cyst. Tex Heart Inst J. 2003. 30:105–108.3. Nakata H, Nakayama C, Kimoto T, Nakayama T, Tsukamoto Y, Nobe T, et al. Computed tomography of mediastinal bronchogenic cysts. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1982. 6:733–738.4. Naidich D, Zerhouni E, Siegelman S. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance of the thorax. 1991. New York: Raven press;120–123.5. Yoon YC, Lee KS, Kim TS, Kim J, Shim YM, Han J. Intrapulmonary bronchogenic cyst: CT and pathologic findings in five adult patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:167–170.6. Aktogu S, Yuncu G, Halilcolar H, Ermete S, Buduneli T. Bronchogenic cysts: clinicopathological presentation and treatment. Eur Respir J. 1996. 9:2017–2021.7. Kim YW, Lee SH, Hong SC, Lee HH, Park SJ, Lee GJ, et al. A case report of a bronchogenic cyst misconceived to lung cancer. Tuberc Respir Dis. 2003. 55:526–530.8. St-Georges R, Deslauriers J, Duranceau A, Vaillancourt R, Deschamps C, Beauchamp G, et al. Clinical spectrum of bronchogenic cysts of the mediastinum and lung in the adult. Ann Thorac Surg. 1991. 52:6–13.9. Patel SR, Meeker DP, Biscotti CV, Kirby TJ, Rice TW. Presentation and management of bronchogenic cysts in the adult. Chest. 1994. 106:79–85.10. Ramenofsky ML, Leape LL, McCauley RG. Bronchogenic cyst. J Pediatr Surg. 1979. 14:219–224.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Parenchymal Pulmonary Endometriosis
- Three Cases of Parenchymal Pulmonary Endometriosis
- A Case of Parenchymal Pulmonary Endometriosis Diagnosed by Cytology of Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid
- A case of catamenial hemoptysis
- Isolated Unilateral Pulmonary Artery Hypoplasia with Accompanying Pulmonary Parenchymal Findings on CT: A Case Report