J Korean Soc Endocrinol.
2006 Apr;21(2):116-124. 10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.116.
Expression of 4-1BB and 4-1BBL in Graves'Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ulsan University Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea.
- 2Biomedical Research Center, Ulsan University Hospital, Korea.
- KMID: 1511950
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2006.21.2.116
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: 4-1BB mediated costimulatory signal is a recently identified immunotherapeutic strategy for treating autoimmune diseases without depressing the immune response. In this study, we investigated the expression of 4-1BB and 4-1BBL on the peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and we assessed whether the serum levels of soluble (s) 4-1BB and s4-1BBL in the patients with Graves' disease (GD) and compared them with normal subjects.
METHODS
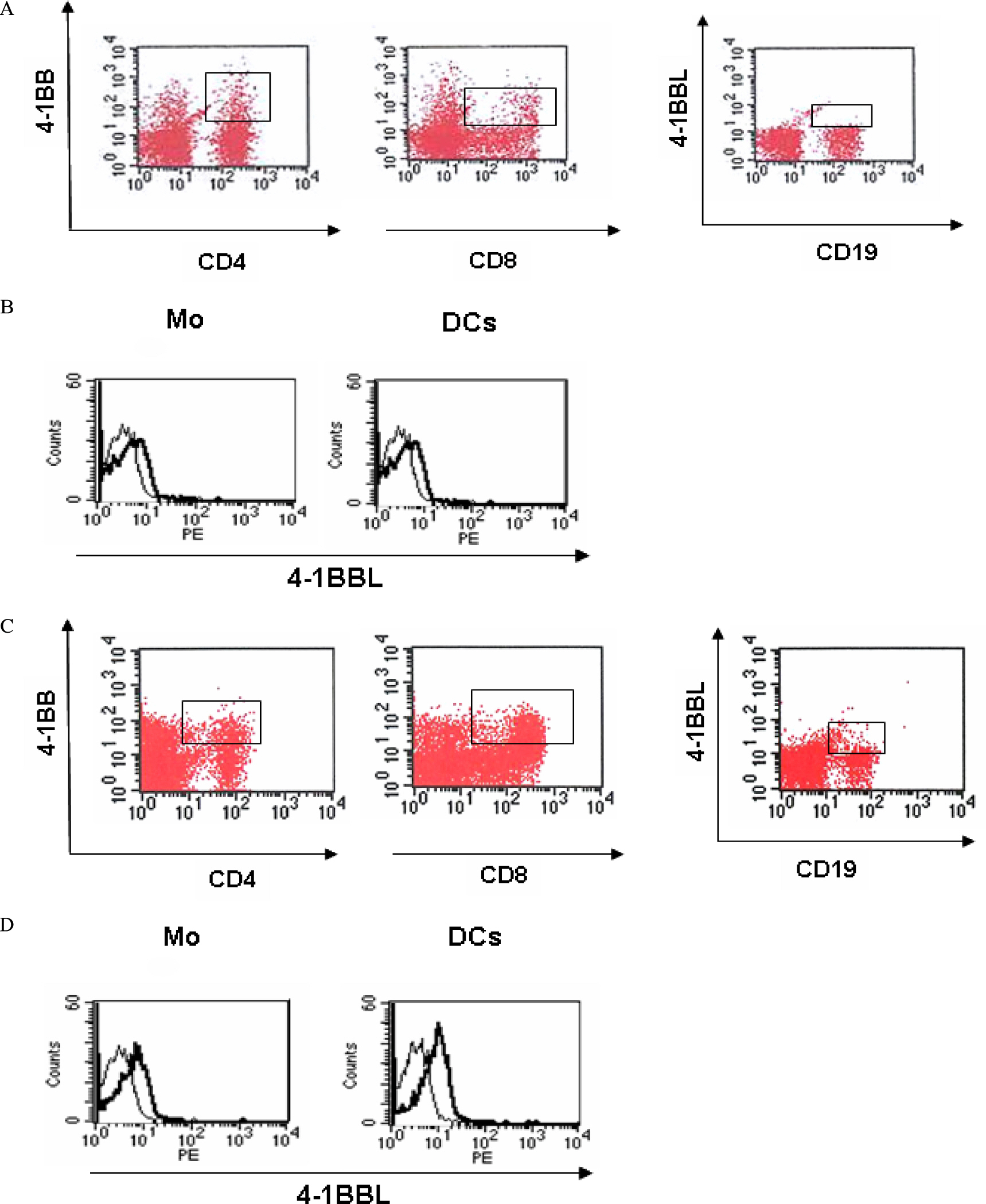
Expression of 4-1BB and 4-1BBL on PBMC of GD patients was determined by flow cytometry. The concentrations of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL were assessed in the sera of GD patients by performing ELISA.
RESULTS
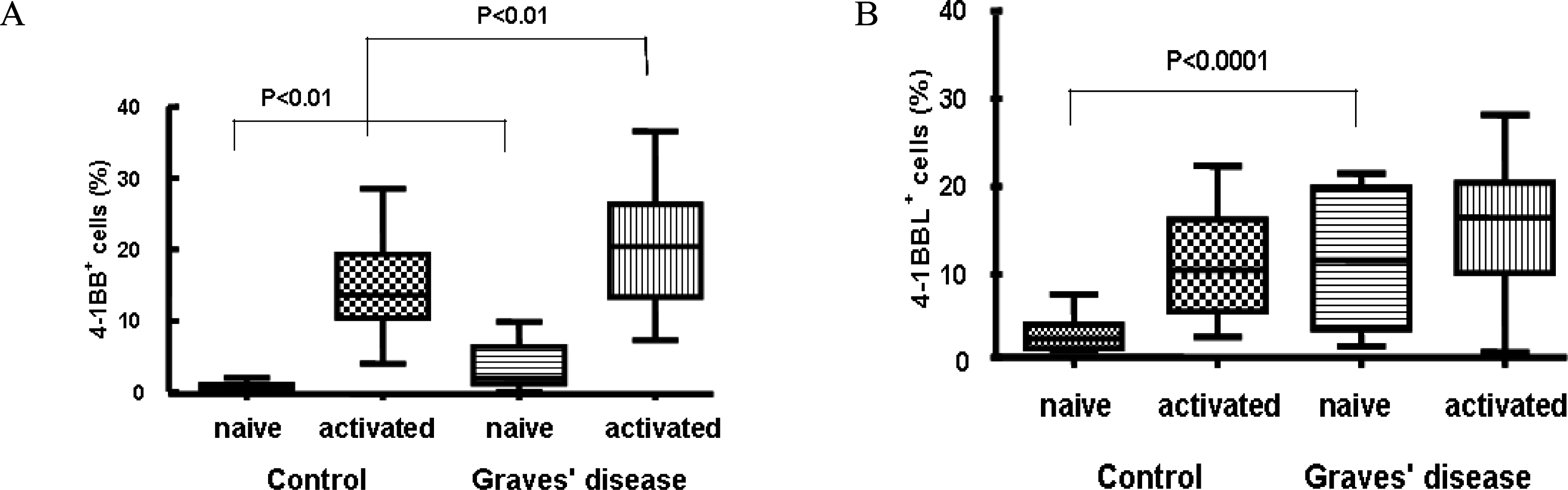
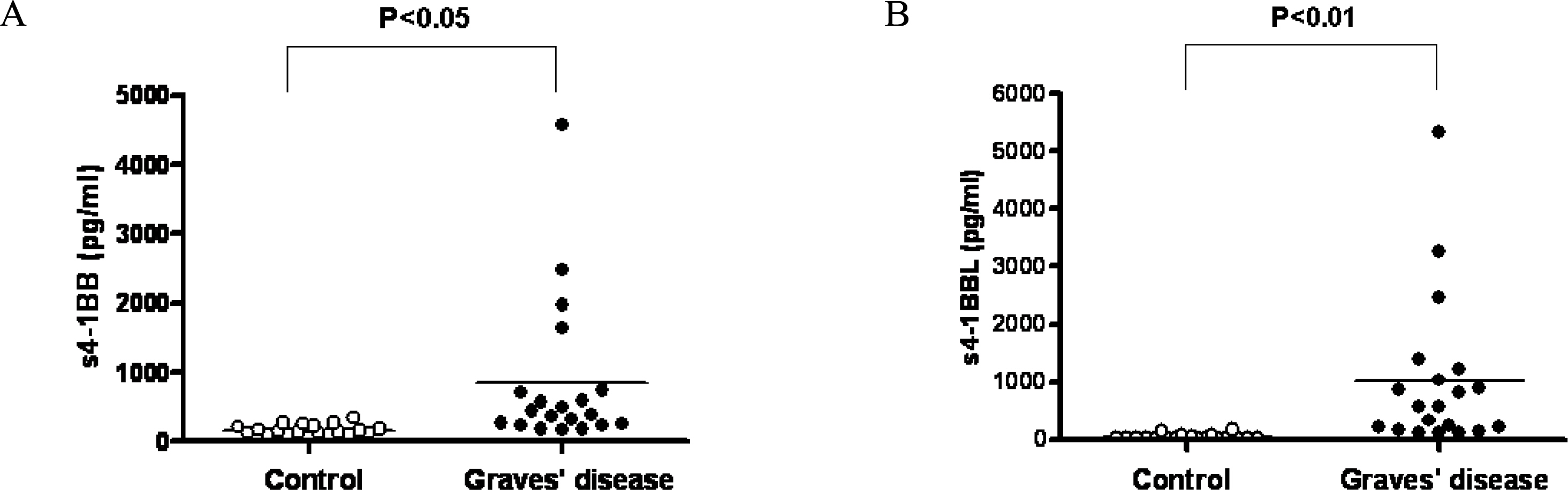
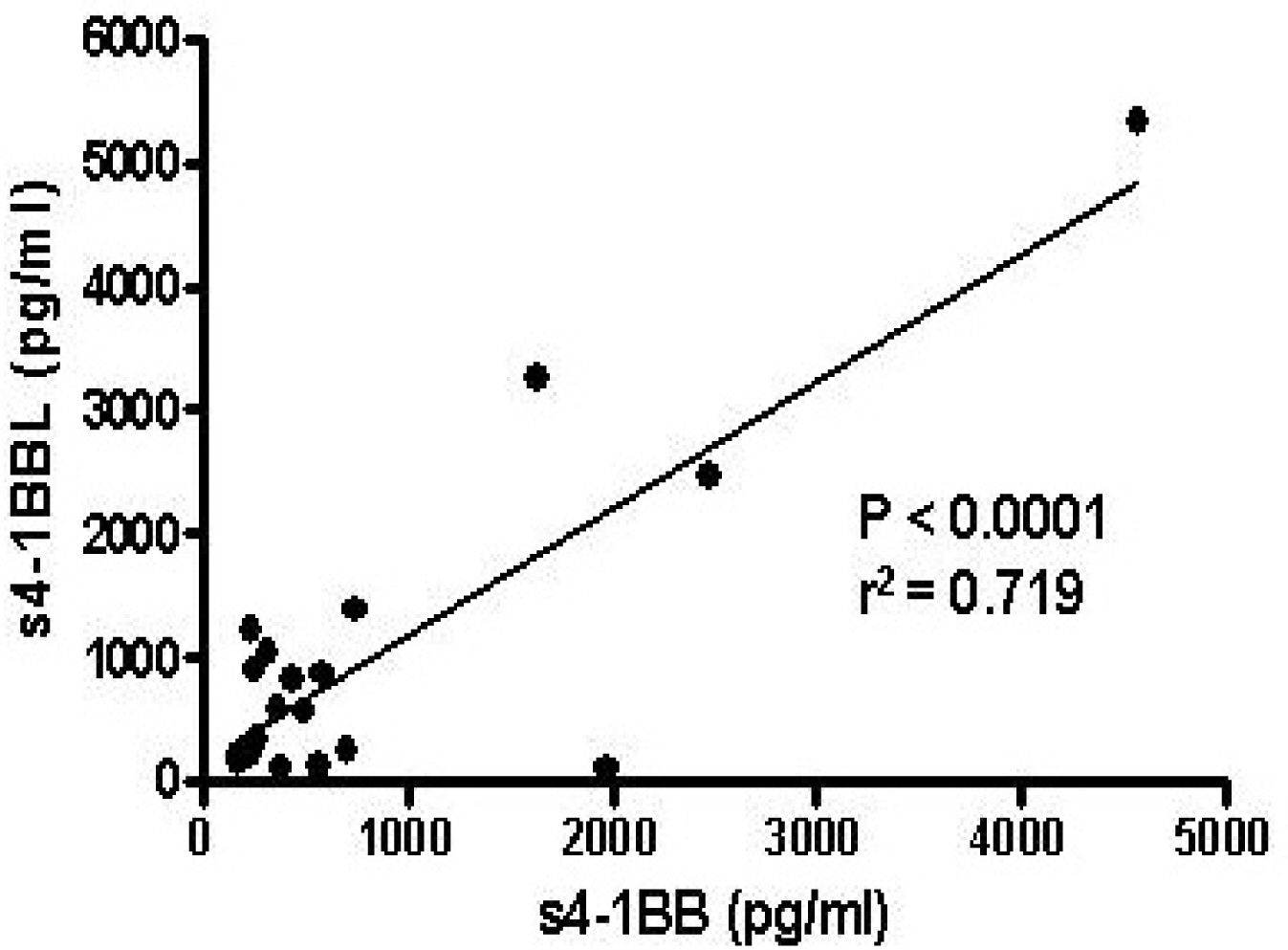
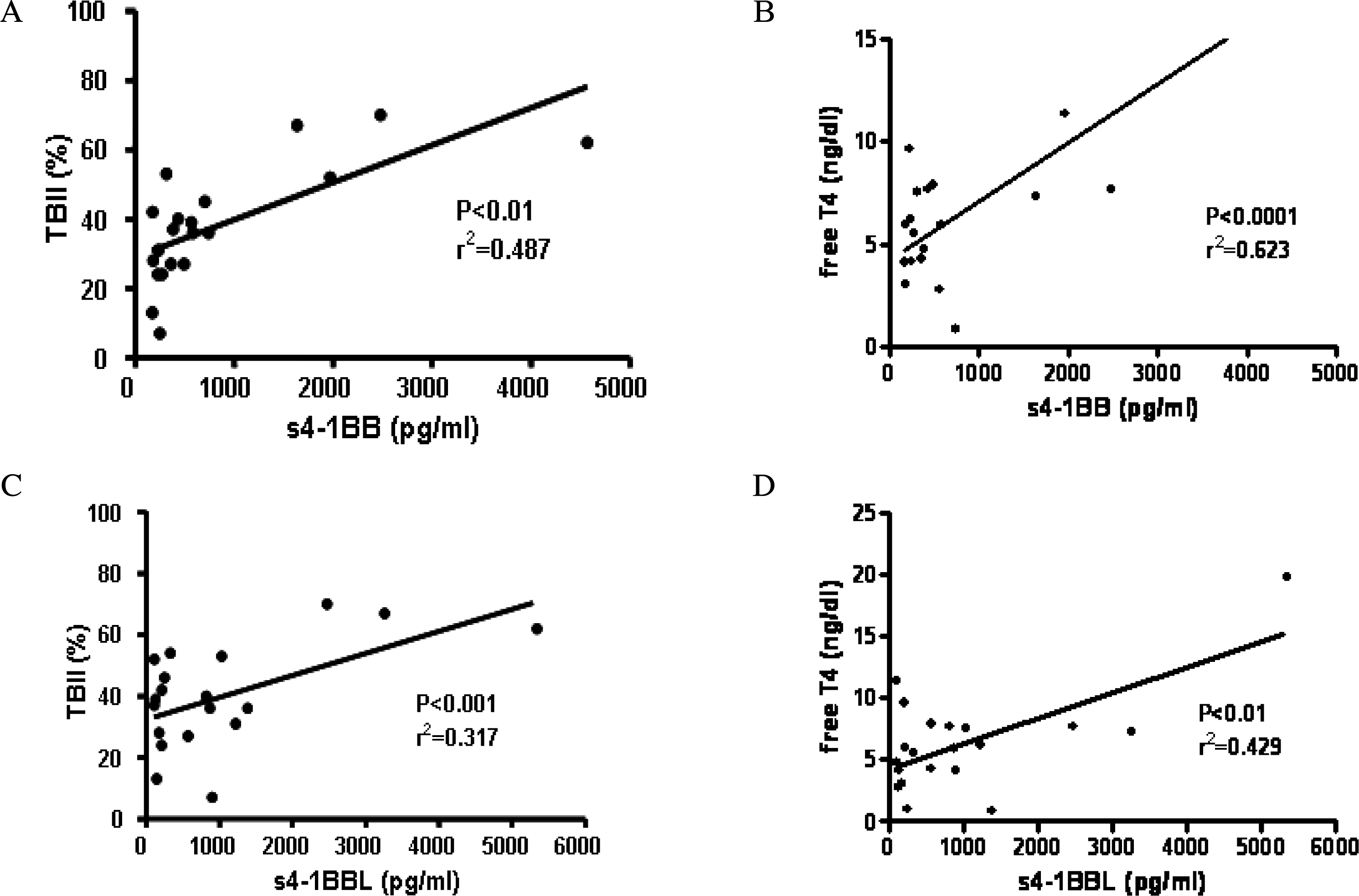
4-1BB was constitutively expressed on naive CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of the GD patients and this was increased by stimulation. 4-1BBL was also expressed on the antigen-presenting cells such as CD19+ B cells, monocytes and dendritic cells in GD patients. The serum levels of s4-1BB and s4-1BBL were significantly higher in GD patients than those in controls, and these levels were significantly correlated with the serum levels of thyroid-binding inhibitory immunoglobulin and free T4.
CONCLUSION
These results indicate that effector T cells of GD patients can be activated through the 4-1BB-mediated costimulatory signal. Elevated s4-1BB and s4-1BBL levels in the sera of GD patients may affect modulation of the clinical course in GD patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mathis D, Benoist C. Back to central tolerance. Immunity. 2004; 20:509–516.
Article2. Heufelder AE. Pathogenesis of ophthalmopathy in autoimmune thyroid disease. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2000; 1:87–95.3. Weetman AP. Autoimmune thyroid disease: propagation and progression. Eur J Endocrinol. 2003; 148:1–9.
Article4. Salmaso C, Olive D, Pesce G, Bagnasco M. Costimulatory molecules and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Autoimmunity. 2002; 35:159–167.
Article5. Croft M. Costimulation of T cells by OX40, 4-1BB, and CD27. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003; 14:265–273.
Article6. Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Tschopp J. The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci. 2002; 27:19–26.
Article7. Kwon B, Yu KY, Ni J, Yu GL, Jang IK, Kim YJ, Xing L, Liu D, Wang SX, Kwon BS. Identification of a novel activation-inducible protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily and its ligand. J Biol Chem. 1999; 274:6056–6061.
Article8. Mittler RS, Bailey TS, Klussman K, Trailsmith MD, Hoffmann MK. Anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibodies abrogate T cell-dependent humoral immune responses in vivo through the induction of helper T cell anergy. J Exp Med. 1999; 190:1535–1540.
Article9. Mittler RS, Foell J, McCausland M, Strahotin S, Niu L, Bapat L, Hewes LB. Anti-CD137 antibodies in the treatment of autoimmune disease and cancer. Immunol Res. 2004; 29:197–208.
Article10. Foell J, Strahotin S, O’Neil SP, McCausland MM, Suwyn C, Haber M, Chander PN, Bapat AS, Yan XJ, Chiorazzi M, Hoffmann MK, Mittler RS. CD137 costimulatory T cell receptor engagement reverses acute disease in lupus-prone NZB x NZW F1 mice. J Clin Invest. 2003; 111:1505–1518.11. Sun Y, Lin X, Chen HM, Wu Q, Subudhi SK, Chen L, Fu XY. Administration of agonistic anti-4-1BB monoclonal antibody leads to the amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2002; 168:1457–1465.
Article12. Seo SK, Choi JH, Kim YH, Kang WJ, Park HY, Suh JH, Choi BK, Vinay DS, Kwon BS. 4-1BB-mediated immunotherapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Med. 2004; 10:1088–1094.
Article13. Chistiakov DA, Turakulov RI. CTLA-4 and its role in autoimmune thyroid disease. J Mol Endocrinol. 2003; 31:21–36.
Article14. Anand A, Dean GS, Quereshi K, Isenberg DA, Lydyard PM. Characterization of CD3+CD4-CD8-(double negative) T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: activation markers. Lupus. 2002; 11:493–500.15. Brunner-Weinzierl MC, Hoff H, Burmester GR. Multiple functions for CD28 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 during different phases of T cell responses: implications for arthritis and autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Res Ther. 2004; 6:45–54.16. Nakamoto Y, Niki M, Watanabe M, Iwatani Y. Increase in immunoglobulin G3-secreting cells in intractable Graves’ disease. Thyroid. 2003; 13:325–331.
Article17. Watanabe M, Yamamoto N, Matsuzuka F, Miyauchi A, Iwatani Y. Decrease of CD154 intensity on peripheral CD4+ T cells in autoimmune thyroid disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 2004; 136:555–558.
Article18. Metkar SS, Naresh KN, Manna PP, Srinivas V, Advani SH, Nadkarni JJ. Circulating levels of TNF alpha and TNF receptor superfamily members in lymphoid neoplasia. Am J Hematol. 2000; 65:105–110.19. Setareh M, Schwarz H, Lotz M. A mRNA variant encoding a soluble form of 4-1BB, a member of the murine NGF/TNF receptor family. Gene. 1995; 164:311–315.
Article20. Michel J, Schwarz H. Expression of soluble CD137 correlates with activation-induced cell death of lymphocytes. Cytokine. 2000; 12:742–746.
Article21. Salih HR, Schmetzer HM, Burke C, Starling GC, Dunn R, Pelka-Fleischer R, Nuessler V, Kiener PA. Soluble CD137 (4-1BB) ligand is released following leukocyte activation and is found in sera of patients with hematological malignancies. J Immunol. 2001; 167:4059–4066.
Article22. Salih HR, Nuessler V, Denzlinger C, Starling GC, Kiener PA, Schmetzer HM. Serum levels of CD137 ligand and CD178 are prognostic factors for progression of myelodysplastic syndrome. Leuk Lymphoma. 2004; 45:301–308.
Article23. Michel J, Langstein J, Hofstadter F, Schwarz H. A soluble form of CD137 (ILA/4-1BB), a member of the TNF receptor family, is released by activated lymphocytes and is detectable in sera of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Immunol. 1998; 28:290–295.
Article24. Jung HW, Choi SW, Choi JI, Kwon BS. Serum concentrations of soluble 4-1BB and4-1BB ligand correlated with the disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Med. 2004; 36:13–22.25. Yamada-Okabe T, Satoh Y, Yamada-Okabe H. Thyroid hormone induces the expression of 4-1BB and activation of caspases in a thyroid hormone receptor-dependent manner. Eur J Biochem. 2003; 270:3064–3073.
Article26. Seko Y, Sugishita K, Sato O, Takagi A, Tada Y, Matsuo H, Yagita H, Okumura K, Nagai R. Expression of costimulatory molecules (4-1BBL and Fas) and major histocompatibility class I chain-related A (MICA) in aortic tissue with Takayasu’s arteritis. J Vasc Res. 2004; 41:84–90.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serum concentrations of soluble 4-1BB and 4-1BB ligand correlated with the disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis
- Expression of 4-1BB and 4-1BBL in thymocytes during thymus regeneration
- The Change of Immunoactivity of Dendritic Cells Induced by Mouse 4-1BBL Recombinant Adenovirus
- Serum Neopterin Concentration in Children with Graves' Disease
- Euthyroid Graves' Ophthalmopathy with Negative Autoantibodies