Yonsei Med J.
2013 Mar;54(2):330-335. 10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.330.
Anti-Allodynic Effects of Levodopa in Neuropathic Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anaesthesiology and Pain Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. demoon@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Anesthesia, St. Michael's Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada.
- KMID: 1503893
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.2.330
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Levodopa is the most effective anti-Parkinsonian agent. It has also been known to exhibit analgesic properties in laboratory and clinical settings. However, studies evaluating its effects on neuropathic pain are limited. The aim of the present study was to examine the anti-allodynic effects of levodopa in neuropathic rats.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Sprague-Dawley male rats underwent the surgical procedure for L5 and L6 spinal nerves ligation. Sixty neuropathic rats were randomly divided into 6 groups for the oral administration of distilled water and levodopa at 10, 30, 50, 70, and 100 mg/kg, respectively. We co-administered carbidopa with levodopa to prevent peripheral synthesis of dopamine from levodopa, and observed tactile, cold, and heat allodynia pre-administration, and at 15, 30, 60, 90, 120, 150, 180, and 240 min after drug administration. We also measured locomotor function of neuropathic rats using rotarod test to examine whether levodopa caused side effects or not.
RESULTS
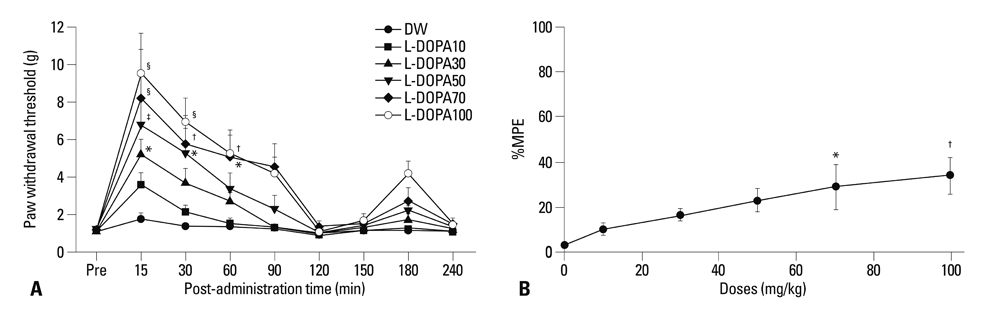
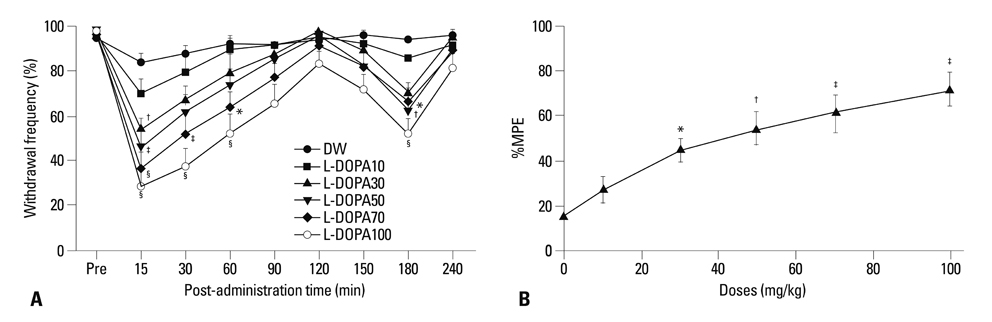
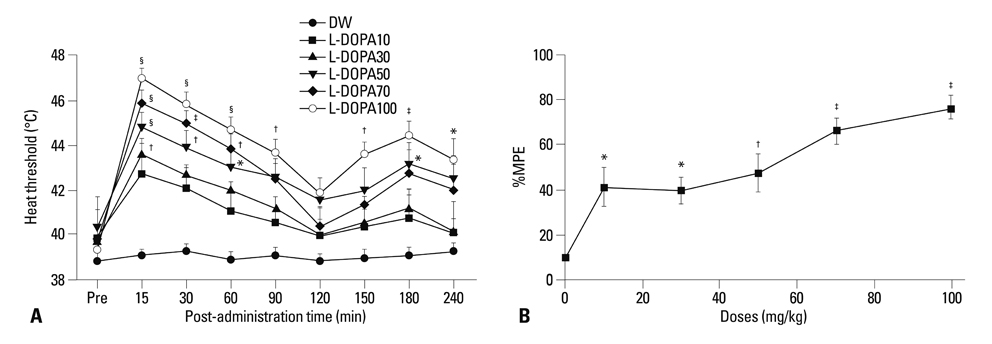
Distilled water group didn't show any difference in all allodynia. For the levodopa groups (10-100 mg/kg), tactile and heat withdrawal thresholds were increased, and cold withdrawal frequency was decreased dose-dependently (p<0.01). In addition, levodopa induced biphasic analgesia. Different dosage of levodopa did not impact on the rotarod time (p>0.05).
CONCLUSION
Levodopa reversed tactile, cold and heat allodynia in neuropathic rat without any side effects.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Carbidopa/administration & dosage/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Dopamine Agents/administration & dosage/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Hyperalgesia/*drug therapy
Levodopa/administration & dosage/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Male
Neuralgia/*drug therapy
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Rotarod Performance Test
Dopamine Agents
Levodopa
Carbidopa
Figure
Reference
-
1. Park HJ, Moon DE. Pharmacologic management of chronic pain. Korean J Pain. 2010. 23:99–108.2. Mercuri NB, Bernardi G. The 'magic' of L-dopa: why is it the gold standard Parkinson's disease therapy? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005. 26:341–344.
Article3. Conti CF, de Oliveira MM, Andriolo RB, Saconato H, Atallah AN, Valbuza JS, et al. Levodopa for idiopathic restless legs syndrome: evidence-based review. Mov Disord. 2007. 22:1943–1951.
Article4. Nixon DW. Letter: use of L-dopa to relieve pain from bone metastases. N Engl J Med. 1975. 292:647.5. Ertas M, Sagduyu A, Arac N, Uludag B, Ertekin C. Use of levodopa to relieve pain from painful symmetrical diabetic polyneuropathy. Pain. 1998. 75:257–259.
Article6. Kernbaum S, Hauchecorne J. Administration of levodopa for relief of herpes zoster pain. JAMA. 1981. 246:132–134.
Article7. Paalzow GH. L-dopa induces opposing effects on pain in intact rats: (-)-sulpiride, SCH 23390 or alpha-methyl-DL-p-tyrosine methylester hydrochloride reveals profound hyperalgesia in large antinociceptive doses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992. 263:470–479.8. Shimizu T, Iwata S, Morioka H, Masuyama T, Fukuda T, Nomoto M. Antinociceptive mechanism of L-DOPA. Pain. 2004. 110:246–249.
Article9. Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. Efficacy of pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: an update and effect related to mechanism of drug action. Pain. 1999. 83:389–400.
Article10. Cobacho N, De la Calle JL, González-Escalada JR, Paíno CL. Levodopa analgesia in experimental neuropathic pain. Brain Res Bull. 2010. 83:304–309.
Article11. Thompson EB, Galysh FT. Quantitative assessment of anesthetic-induced cardiac sensitization to epinephrine. Anesth Analg. 1973. 52:800–806.
Article12. Park HJ, Joo HS, Chang HW, Lee JY, Hong SH, Lee Y, et al. Attenuation of neuropathy-induced allodynia following intraplantar injection of pregabalin. Can J Anaesth. 2010. 57:664–671.
Article13. Kim SH, Chung JM. An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain. 1992. 50:355–363.
Article14. Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 1994. 53:55–63.
Article15. Choi Y, Yoon YW, Na HS, Kim SH, Chung JM. Behavioral signs of ongoing pain and cold allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 1994. 59:369–376.
Article16. Almási R, Pethö G, Bölcskei K, Szolcsányi J. Effect of resiniferatoxin on the noxious heat threshold temperature in the rat: a novel heat allodynia model sensitive to analgesics. Br J Pharmacol. 2003. 139:49–58.
Article17. Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain. 1988. 33:87–107.
Article18. Björklund A, Skagerberg G. Evidence for a major spinal cord projection from the diencephalic A11 dopamine cell group in the rat using transmitter-specific fluorescent retrograde tracing. Brain Res. 1979. 177:170–175.
Article19. Skagerberg G, Lindvall O. Organization of diencephalic dopamine neurones projecting to the spinal cord in the rat. Brain Res. 1985. 342:340–351.
Article20. Holstege JC, Van Dijken H, Buijs RM, Goedknegt H, Gosens T, Bongers CM. Distribution of dopamine immunoreactivity in the rat, cat and monkey spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1996. 376:631–652.
Article21. Qu S, Ondo WG, Zhang X, Xie WJ, Pan TH, Le WD. Projections of diencephalic dopamine neurons into the spinal cord in mice. Exp Brain Res. 2006. 168:152–156.
Article22. Fleetwood-Walker SM, Hope PJ, Mitchell R. Antinociceptive actions of descending dopaminergic tracts on cat and rat dorsal horn somatosensory neurones. J Physiol. 1988. 399:335–348.
Article23. Gao X, Zhang Y, Wu G. Effects of dopaminergic agents on carrageenan hyperalgesia after intrathecal administration to rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2001. 418:73–77.
Article24. Jensen TS, Yaksh TL. Effects of an intrathecal dopamine agonist, apomorphine, on thermal and chemical evoked noxious responses in rats. Brain Res. 1984. 296:285–293.
Article25. Tamae A, Nakatsuka T, Koga K, Kato G, Furue H, Katafuchi T, et al. Direct inhibition of substantia gelatinosa neurones in the rat spinal cord by activation of dopamine D2-like receptors. J Physiol. 2005. 568(Pt 1):243–253.
Article26. Yokoyama C, Okamura H, Nakajima T, Taguchi J, Ibata Y. Autoradiographic distribution of [3H]YM-09151-2, a high-affinity and selective antagonist ligand for the dopamine D2 receptor group, in the rat brain and spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1994. 344:121–136.
Article27. Ansah OB, Leite-Almeida H, Wei H, Pertovaara A. Striatal dopamine D2 receptors attenuate neuropathic hypersensitivity in the rat. Exp Neurol. 2007. 205:536–546.
Article28. Magnusson JE, Fisher K. The involvement of dopamine in nociception: the role of D(1) and D(2) receptors in the dorsolateral striatum. Brain Res. 2000. 855:260–266.
Article29. Michael-Titus A, Bousselmame R, Costentin J. Stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors induces an analgesia involving an opioidergic but non enkephalinergic link. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990. 187:201–207.
Article30. Pertovaara A, Wei H. Dual influence of the striatum on neuropathic hypersensitivity. Pain. 2008. 137:50–59.
Article31. Sheng HY, Qu CL, Huo FQ, Du JQ, Tang JS. D2-like but not D1-like dopamine receptors are involved in the ventrolateral orbital cortex-induced antinociception: a GABAergic modulation mechanism. Exp Neurol. 2009. 215:128–134.
Article32. Taylor BK, Joshi C, Uppal H. Stimulation of dopamine D2 receptors in the nucleus accumbens inhibits inflammatory pain. Brain Res. 2003. 987:135–143.
Article33. Shimizu T, Iwata S, Miyata A, Fukuda T, Nomoto M. Delayed L-DOPA-induced hyperalgesia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2006. 85:643–647.
Article34. Calabresi P, Di Filippo M, Ghiglieri V, Tambasco N, Picconi B. Levodopa-induced dyskinesias in patients with Parkinson's disease: filling the bench-to-bedside gap. Lancet Neurol. 2010. 9:1106–1117.
Article35. Körner Y, Meindorfner C, Möller JC, Stiasny-Kolster K, Haja D, Cassel W, et al. Predictors of sudden onset of sleep in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2004. 19:1298–1305.
Article36. Moskovitz C, Moses H 3rd, Klawans HL. Levodopa-induced psychosis: a kindling phenomenon. Am J Psychiatry. 1978. 135:669–675.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Synergistic anti-allodynic effect between intraperitoneal thalidomide and morphine on rat spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain
- Intrathecal Gabapentin Increases Interleukin-10 Expression and Inhibits Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine in a Rat Model of Neuropathic Pain
- The Synergistic Effect of Intrathecally Administered Dexmedetomidine and Ketorolac on Mechanical Allodynia in Rats with Spinal Nerve Ligation
- The effect of inducing morphine tolerance on anti-allodynic action of gabapentin in spinal nerve-ligated rat
- Glia Dose not Participate in Antinociceptive Effects of Gabapentin in Rats with Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain