J Bacteriol Virol.
2013 Dec;43(4):328-336. 10.4167/jbv.2013.43.4.328.
Analysis of the Expression Pattern of microRNA of KSHV in KSHV-infected Human Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology and Immunology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Yongdu-dong, Jung-gu, Daejeon, Korea. smyoo@eulji.ac.kr
- KMID: 1502001
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2013.43.4.328
Abstract
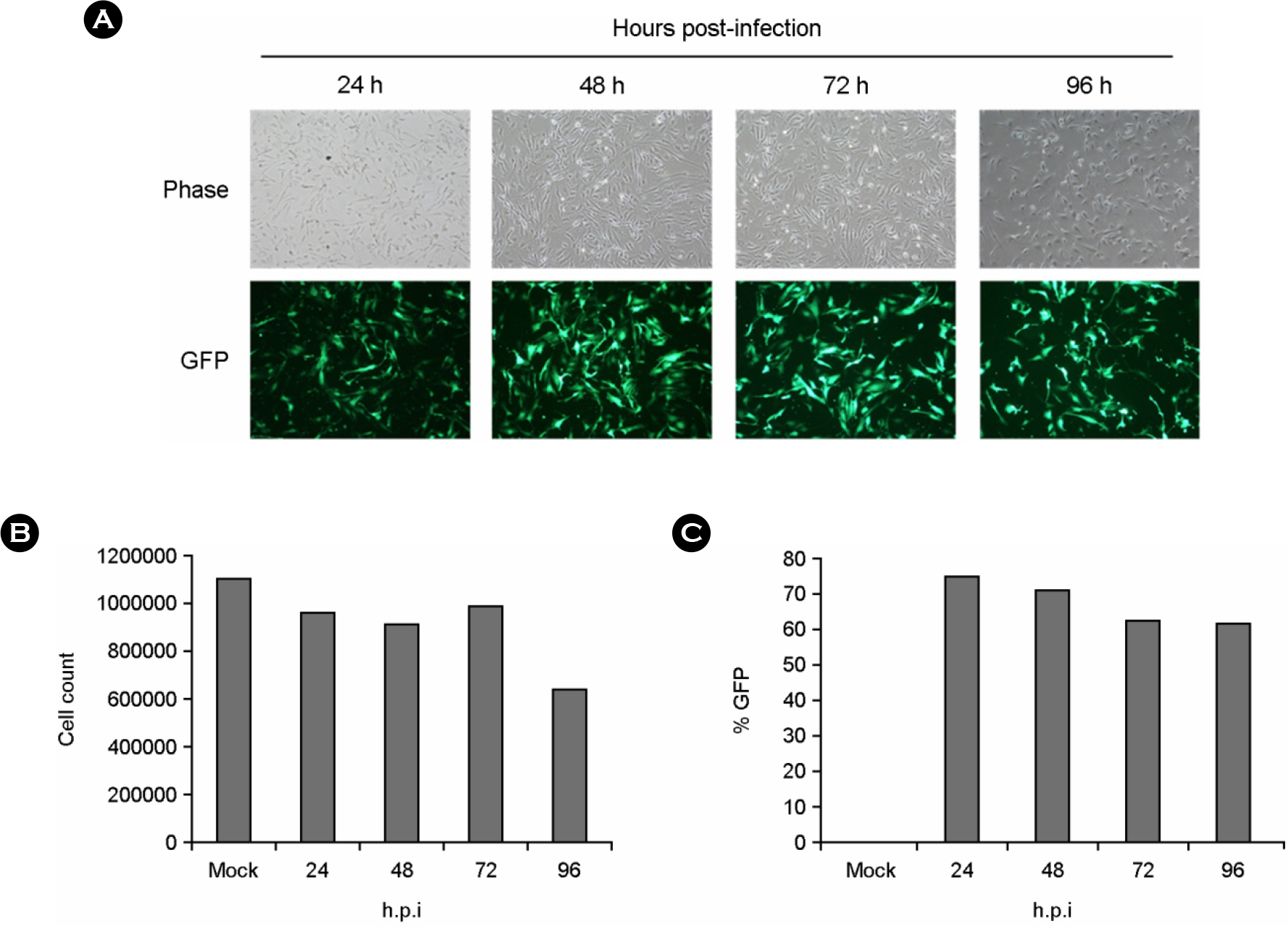
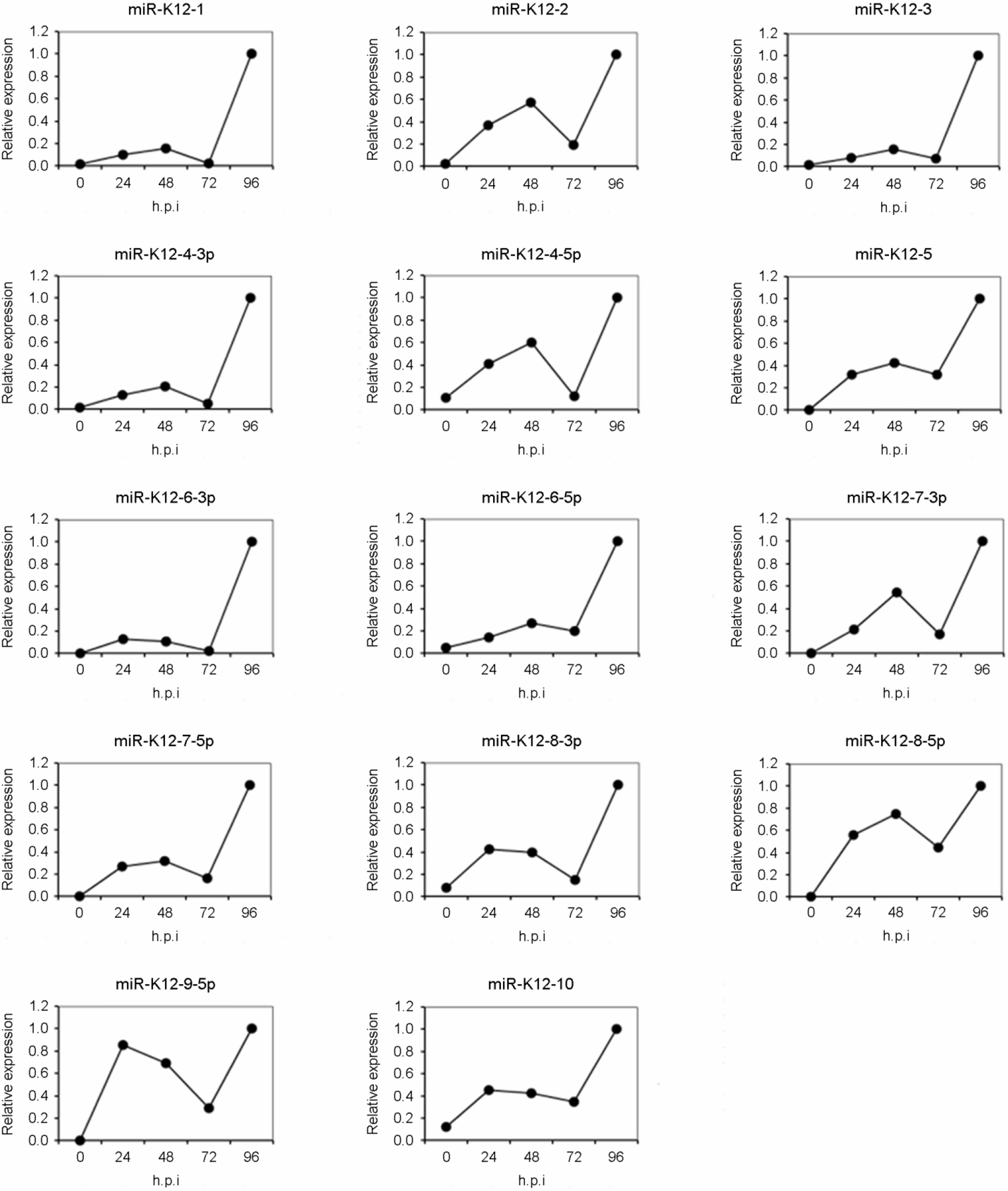
- Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (KSHV) is subdivided into gamma-herpesvirus and causes Kaposi's sarcoma in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected patients. A defining feature of herpesviral biology is the presence of two alternative genetic lifestyles - a latent infection and a lytic replicative cycle. Almost all herpesviruses examined so far have been shown to express viral miRNAs in latently and/or productively infected cells. KSHV encodes an array of 15 distinct miRNAs, all of which are expressed at readily detectable levels in latently KSHV infected cells. The expression of an array of these viral miRNAs in KSHV-infected cells suggests that down-regulation of host cell mRNAs by miRNA-mediated RNA interference may represent a critical step in the establishment and/or maintenance of latent infections by KSHV. To investigate KSHV miRNAs that are expressed in KSHV-infected cells, KSHV-infected human umbilical cord vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and BCBL-1 cells were used and their miRNAs were analyzed by a modified real-time PCR method. Some KSHV miRNAs were detected in KSHV-infected HUVECs and their expression was affected by genetic life cycles. In addition, KSHV miRNAs were also detected in BCBL-1 and their expression was not related to treatment of sodium butyrate. These results indicate that KSHV infection in cells inducing KSHV miRNAs expression would be increased upon entry into latent replication.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1). Lodish HF. Molecular cell biology. 6th ed.New York: WH Freeman & Co;2007.2). Lai E. Micro RNAs are complementary to 3′ UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional regulation. Nat Genet. 2002; 30:363–4.
Article3). Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–97.4). Ji JD, Kim TH. Rheumatoid Arthritis and microRNA. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2010; 17:230–7.
Article5). Boss IW, Renne R. Viral miRNAs: tools for immune evasion. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2010; 13:540–5.
Article6). Cullen BR. Viral and cellular messenger RNA targets of viral microRNAs. Nature. 2009; 457:421–5.
Article7). Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell. 2009; 136:215–33.
Article8). Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN, Sonenberg N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 2008; 9:102–14.
Article9). Qin Z, Kearney P, Plaisance K, Parsons CH. Pivotal advance: Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)-encoded microRNA specifically induce IL-6 and IL-10 secretion by macrophages and monocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 2010; 87:25–34.
Article10). Nachmani D, Stern-Ginossar N, Sarid R, Mandelboim O. Diverse herpesvirus microRNAs target the stress-induced immune ligand MICB to escape recognition by natural killer cells. Cell Host Microbe. 2009; 5:376–85.
Article11). Seo GJ, Fink LH, O'Hara B, Atwood WJ, Sullivan CS. Evolutionarily conserved function of a viral microRNA. J Virol. 2008; 82:9823–8.
Article12). Stern-Ginossar N, Elefant N, Zimmermann A, Wolf DG, Saleh N, Biton M, et al. Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA. Science. 2007; 317:376–81.
Article13). Sullivan CS, Grundhoff AT, Tevethia S, Pipas JM, Ganem D. SV40-encoded microRNAs regulate viral gene expression and reduce susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 2005; 435:682–6.
Article14). Xia T, O'Hara A, Araujo I, Barreto J, Carvalho E, Sapucaia JB, et al. EBV microRNAs in primary lymphomas and targeting of CXCL-11 by ebv-mir-BHRF1-3. Cancer Res. 2008; 68:1436–42.
Article15). Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995; 332:1186–91.
Article16). Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles DM, et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994; 266:1865–9.17). Soulier J, Grollet L, Oksenhendler E, Cacoub P, Cazals-Hatem D, Babinet P, et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood. 1995; 86:1276–80.18). Blasig C, Zietz C, Haar B, Neipel F, Esser S, Brockmeyer NH, et al. Monocytes in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions are productively infected by human herpesvirus 8. J Virol. 1997; 71:7963–8.
Article19). Davis MA, Stürzl M, Blasig C, Schreier A, Guo HG, Reitz M, et al. Expression of human herpesvirus 8-encoded cyclin D in Kaposi's sarcoma spindle cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1997; 89:1868–74.
Article20). Dupin N, Fisher C, Kellam P, Ariad S, Tulliez M, Franck N, et al. Distribution of human herpesvirus-8 latently infected cells in Kaposi's sarcoma, multicentric Castleman's disease, and primary effusion lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999; 96:4546–51.
Article21). Kirshner JR, Staskus K, Haase A, Lagunoff M, Ganem D. Expression of the open reading frame 74 (G-protein-coupled receptor) gene of Kaposi's sarcoma (KS)-associated herpesvirus: implications for KS pathogenesis. J Virol. 1999; 73:6006–14.
Article22). Orenstein JM, Alkan S, Blauvelt A, Jeang KT, Weinstein MD, Ganem D, et al. Visualization of human herpesvirus type 8 in Kaposi's sarcoma by light and transmission electron microscopy. AIDS. 1997; 11:F35–45.
Article23). Stürzl M, Blasig C, Schreier A, Neipel F, Hohenadl C, Cornali E, et al. Expression of HHV-8 latency-associated T0.7 RNA in spindle cells and endothelial cells of AIDS-associated, classical and African Kaposi's sarcoma. Int J Cancer. 1997; 72:68–71.
Article24). Stürzl M, Hohenadl C, Zietz C, Castanos-Velez E, Wunderlich A, Ascherl G, et al. Expression of K13/v-FLIP gene of human herpesvirus 8 and apoptosis in Kaposi's sarcoma spindle cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1999; 91:1725–33.25). Ziegelbauer JM, Sullivan CS, Ganem D. Tandem array-based expression screens identify host mRNA targets of virus-encoded microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2009; 41:130–4.
Article26). Samols MA, Skalsky RL, Maldonado AM, Riva A, Lopez MC, Baker HV, et al. Identification of cellular genes targeted by KSHV-encoded microRNAs. PLoS Pathog. 2007; 11(3):e65.
Article27). Bellare P, Ganem D. Regulation of KSHV lytic switch protein expression by a virus-encoded microRNA: an evolutionary adaptation that fine-tunes lytic reactivation. Cell Host Microbe. 2009; 6:570–5.
Article28). Lei X, Bai Z, Ye F, Huang Y, Gao SJ. Regulation of herpesvirus lifecycle by viral microRNAs. Virulence. 2010; 1:433–5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical significance of kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus(KSHV) infection in patients of multiple myeloma
- An in-silico approach to design potential siRNAs against the ORF57 of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus
- Kaposi Sarcoma Herpes Virus-associated Hemophagocytic Syndrome Complicated by Multicentric Castleman Disease and Kaposi Sarcoma in a HIV-negative Immunocompetent Patient: An Autopsy Case
- Clinicopathologic study of Castleman's disease in Korea
- MicroRNA profiling of tacrolimus-stimulated Jurkat human T lympocytes