Korean J Ophthalmol.
2013 Feb;27(1):39-43. 10.3341/kjo.2013.27.1.39.
Relationship of Hypertropia and Excyclotorsion in Superior Oblique Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Kim's Eye Hospital, Konyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. ungsookim@kimeye.com
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Bundang Jesaeng General Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 1501794
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.1.39
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the correlation between hypertropia and excyclotorsion in acquired superior oblique palsy (SOP).
METHODS
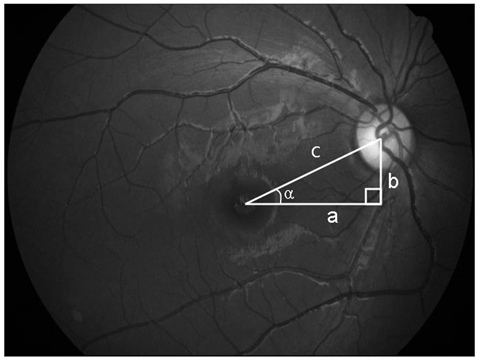
Thirty-one patients with acquired unilateral SOP were recruited for this study. The torsional angle of each patient was assessed via one objective method (fundus photography) and two subjective methods (double Maddox rod test and major amblyoscope). The patient population was divided into two groups (concordance group, n = 19 and discordance group, n = 12) according to the correspondence between the hypertropic eye (paralytic eye) and the more extorted eye (non-fixating eye), which was evaluated by fundus photography.
RESULTS
The mean value of objective torsion was 5.09degrees +/- 3.84degrees. The subjective excyclotorsion degrees were 5.18degrees +/- 4.11degrees and 3.65degrees +/- 1.93degrees as measured by double Maddox rod test and major amblyoscope, respectively. Hypertropia and the excyclotorsional angle did not differ significantly between the groups (p = 0.257). Although no correlation was found in the discordance group, the concordance group showed a significant and positive correlation between hypertropia and excyclotorsion (p = 0.011).
CONCLUSIONS
Torsional deviation was not related to hypertropia. However, in the concordance patients in whom the hypertropic eye showed excyclotorsion, a significant positive correlation was found between hypertropia and excyclotorsion.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Child
Diagnostic Techniques, Ophthalmological
Eye Movements
Female
Follow-Up Studies
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Oculomotor Muscles/*physiopathology
Ophthalmologic Surgical Procedures/*methods
Ophthalmoplegia/*etiology/physiopathology/surgery
Retrospective Studies
Strabismus/*etiology/physiopathology/surgery
Treatment Outcome
Trochlear Nerve Diseases/*complications/physiopathology/surgery
Young Adult
Figure
Reference
-
1. Helveston EM. Diagnosis and management of superior oblique palsy. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1985. 25:69–77.2. Helveston EM, Mora JS, Lipsky SN, et al. Surgical treatment of superior oblique palsy. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc. 1996. 94:315–328.3. Na KS, Lee SY, Lee YC. Ocular torsion in unilateral superior oblique palsy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007. 48:1388–1393.4. Bixenman WW, von Noorden GK. Apparent foveal displacement in normal subjects and in cyclotropia. Ophthalmology. 1982. 89:58–62.5. Von Noorden GK, Murray E, Wong SY. Superior oblique paralysis: a review of 270 cases. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986. 104:1771–1776.6. Ruttum M, von Noorden GK. The Bagolini striated lens test for cyclotropia. Doc Ophthalmol. 1984. 58:131–139.7. Kushner BJ, Kraft SE, Vrabec M. Ocular torsional movements in humans with normal and abnormal ocular motility. Part I. Objective measurements. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984. 21:172–177.8. Souza-Dias C. The diagnosis and treatment of bilateral masked superior oblique palsy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1988. 106:371–373.9. Kraft SP, Scott WE. Masked bilateral superior oblique palsy: clinical features and diagnosis. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1986. 23:264–272.10. Olivier P, von Noorden GK. Excyclotropia of the nonparetic eye in unilateral superior oblique muscle paralysis. Am J Ophthalmol. 1982. 93:30–33.11. Mollan SP, Edwards JH, Price A, et al. Aetiology and outcomes of adult superior oblique palsies: a modern series. Eye (Lond). 2009. 23:640–644.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anterior Transposition of the Inferior Oblique Muscle for Treatment of Hypertropia in Superior Oblique Muscle Palsy
- Analysis of Effect of Inferior Oblique Myectomy in Patients With Inferior Oblique Overaction
- The Effect of Modified Anterior Transposition of the Inferior Oblique Muscle for Hypertropia in Superior Oblique Muscle Palsy with Inferior Oblique Muscle Overaction
- The Relationship of Hypertropia, Inferior Oblique Overaction and Extorsion in Congenital Superior Oblique Palsy
- A Case of Surgery for Congenital Superior Oblique Palsy with Intorsion of Nonparalized Eye