J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2007 Oct;48(10):1394-1398. 10.3341/jkos.2007.48.10.1394.
The Relationship of Hypertropia, Inferior Oblique Overaction and Extorsion in Congenital Superior Oblique Palsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. leeyc@cmc.cuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Keimyung University School of Medicine2, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2210994
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2007.48.10.1394
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: To evaluate the correlation among hypertropia, inferior oblique overaction (IOOA), and extorsion.
METHODS
Thirty-one patients with congenital unilateral superior oblique palsy were evaluated. Visual acuity tests, refraction tests, ocular movement tests, prism cover tests, and fundus photography were performed. The correlations of vertical deviation, IOOA, and extorsion were analyzed. The operation method involved weakening the inferior oblique muscle, and then a comparison was made between measurements 1 month preoperative and 1 month postoperative for vertical deviation, inferior oblique overaction, and extorsion.
RESULTS
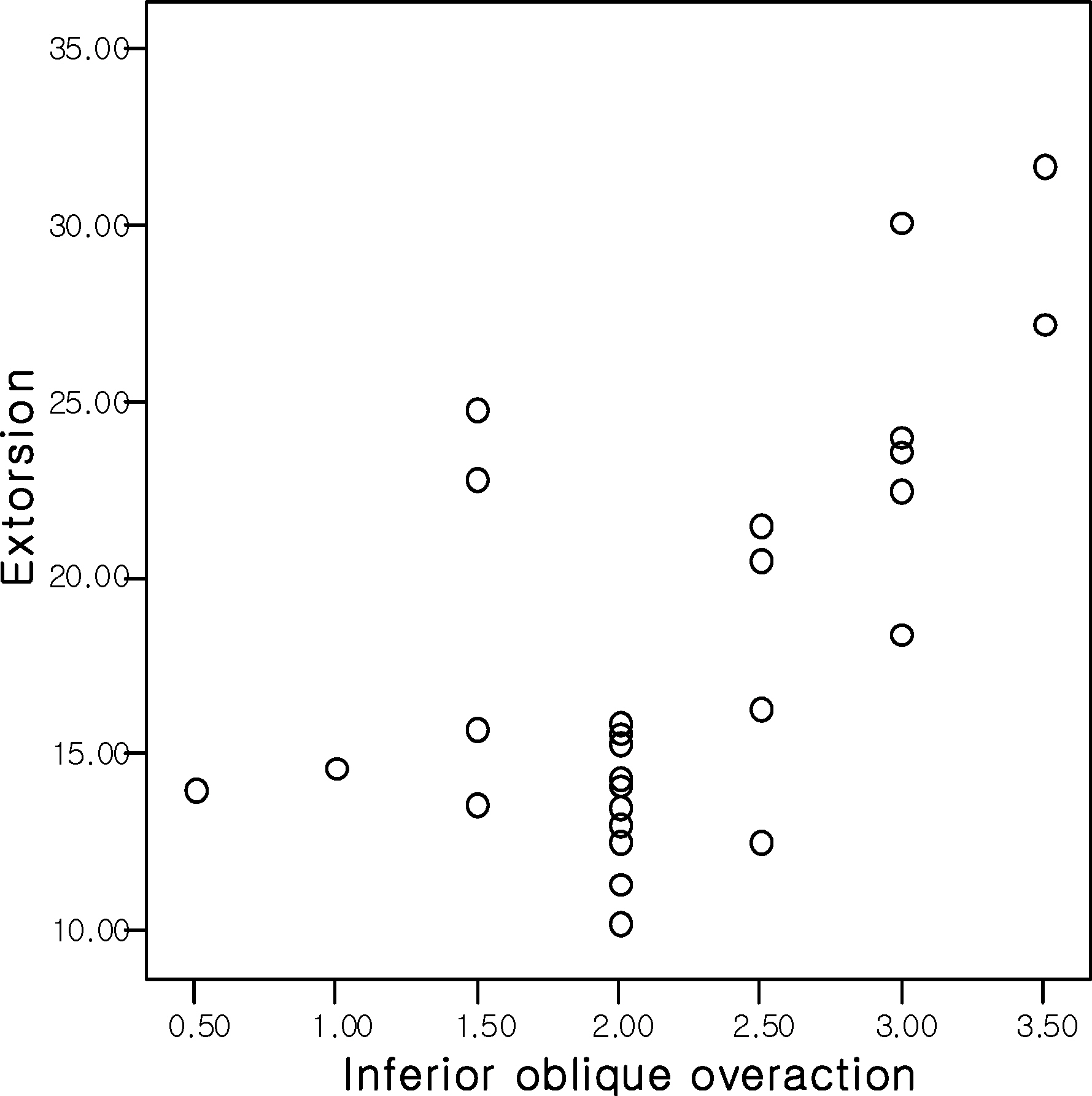
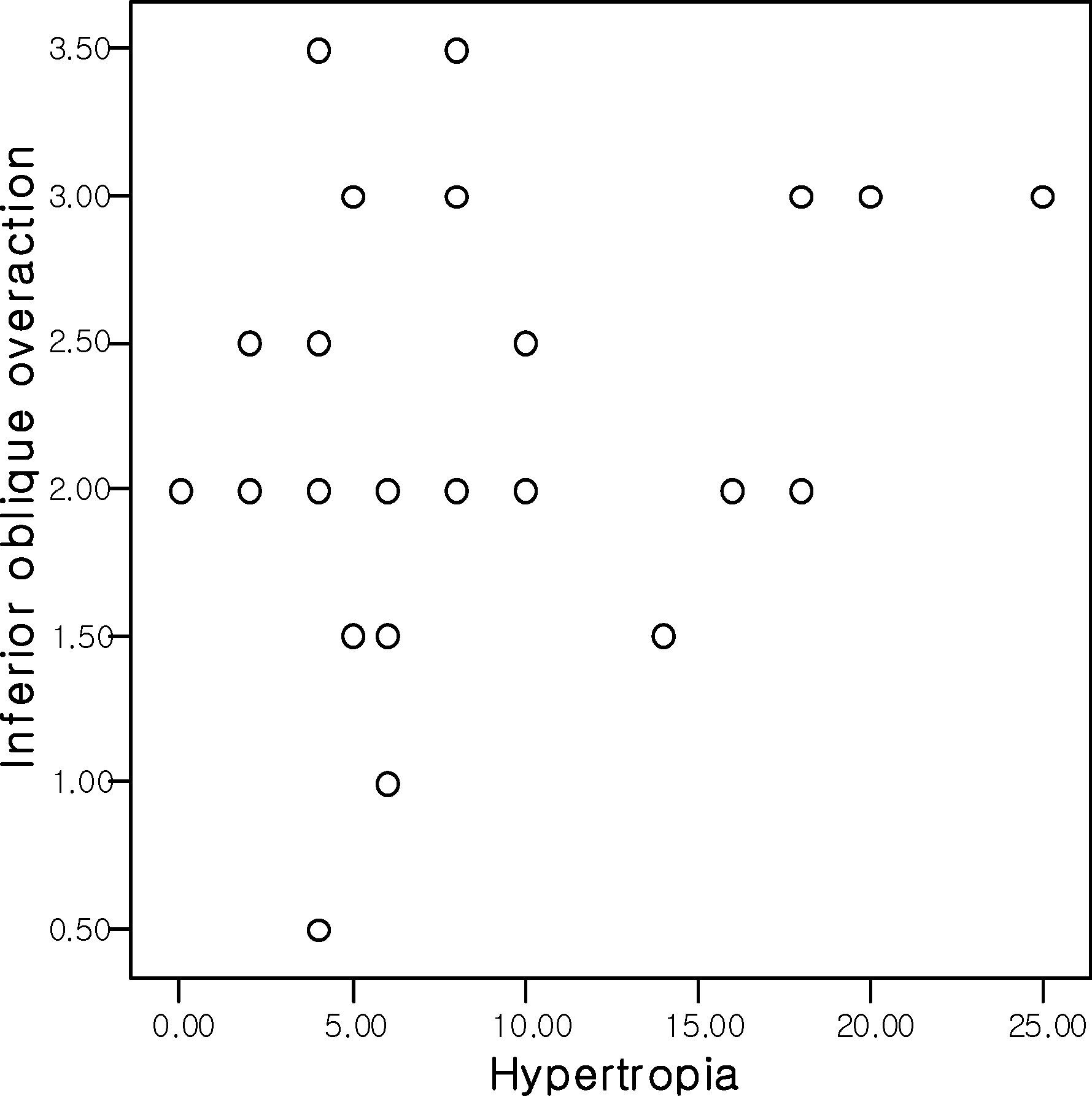
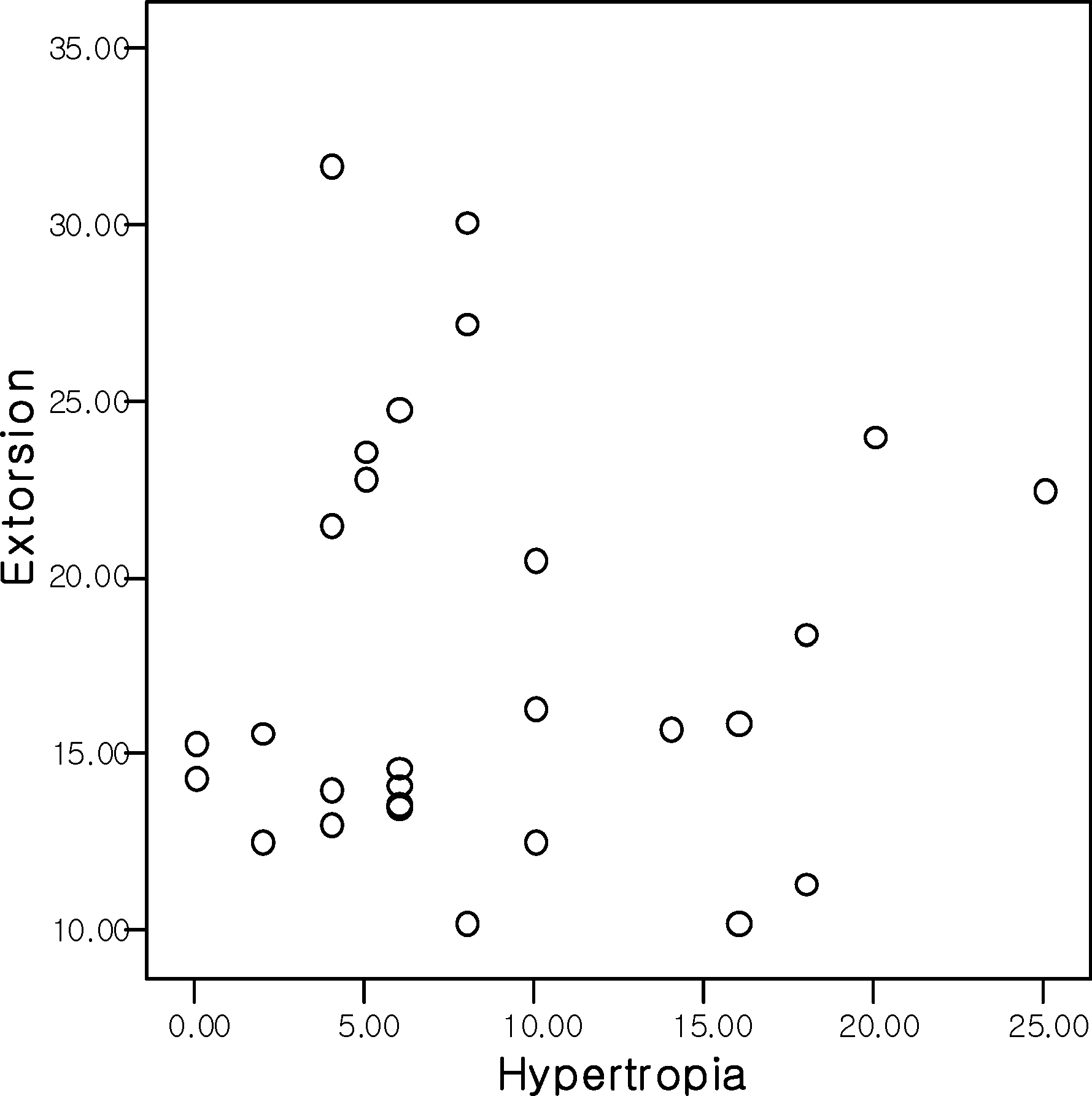
On average, preoperative hypertropia was 8.84+/-6.88 prism diopters (PD), IOOA was 2.20+/-0.69, and extorsion was 18.06+/-5.83 degrees. The Pearson's correlation of IOOA and extorsion, hypertropia and IOOA, and extorsion and hypertropia were r=0.620, r=0.327, and r=0.126, respectively. Postoperative hypertropia, IOOA, and extorsion were reduced to 1.42+/-3.11PD, 0.42+/-1.11, and 8.63+/-5.09, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
Both extorsion and hypertropia showed significant positive correlations with IOOA, whereas hypertropia and extorsion revealed somewhat weaker positive correlations in congenital monocular superior oblique palsy. In addition, the amount of hypertropia was reduced, and extorsion and IOOA improved after recession of the inferior oblique muscle.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Han HS, Cho YA. Facial asymmetry and head tilting in superior oblique palsy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1998; 39:1563–70.2. Von Noorden GK, Murray E, Wong SY. Superior oblique paralysis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1986; 104:1771–6.
Article3. Wilson ME, Hoxie J. Facial asymmetry in superior oblique muscle palsy. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1993; 30:315–8.
Article4. Kwon HG, Lee SY, Lee YC. Superior oblique palsy combined with horizontal strabismus. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:1846–51.5. Kim EH, Lee SJ, Choi HY. Ocular torsion according to fixation in fundus photograph. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:449–54.6. Bixenman WW, Von Noorden GK. Apparent foveal displacement in the normal subject and in cyclotropia. Ophthalmology. 1982; 89:58–62.7. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP. Clinical strabismus management. Philadelphia: Saunders;1999. p. 219–29.8. Paysee EA, Coats DK, Plager DA. Facial asymmetry and tendon laxity in superior oblique palsy. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1995; 32:158–61.
Article9. David L, Guyton DL. Clinical assessment of ocular torsion. Am Orthopt J. 1983; 33:7–15.10. Fray KJ, Philips PH. Strabismus with a twist: Pre- and postoperative torsion. Am Orthopt J. 2003; 53:12–9.
Article11. Wright KW. Alphabet Patterns and Oblique Muscle Dysfunctions. In : Wright KW, Spiegel PH, editors. Pediatric Ophthalmology and Strabismus. 2nd ed.New York: Springer;2003. Chap. 15.12. Kushner BJ, Kraft SE, Vrabec M. Ocular torsional movements in humans with normal and abnormal ocular motility, Part I: Objective measurements. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1984; 21:172.13. Chang BL. Superior oblique palsy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1991; 32:300–6.14. Souza-Dias C. The diagnosis and treatment of Bilateral masked superior oblique palsy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1988; 106:371–2.
Article15. Kraft SP, Scott WE. Masked bilateral superior oblique palsy: clinical features and diagnosis. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1986; 23:264–72.
Article16. Bielschowsky A. Lectures on motor anomalies: I. The Physiology of ocular movements. Am J Ophthalmol. 1938; 21:843–55.17. Kushner BJ. Ocular Torsion: Rotations Around the “WHY” Axis. J AAPOS. 2004; 8:1–12.
Article18. Saunders RA, Roberts EL. Abnormal head posture in patients with fouth cranial nerve palsy. Am Orthopt J. 1995; 45:24–32.19. Kim JW, Kim MM. The effect of inferior oblique weakening procedures in the congenital superior oblique palsies. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2004; 45:1893–8.20. Shin KS, Yoo JM. The effect of modified anterior transposition of the inferior oblique muscle for hypertropia in superior oblique muscle palsy with inferior oblique muscle overaction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2003; 44:384–9.21. Sim JH, Lee SY. The effect of inferior oblique weakening procedures on the correction of ocular torsion. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005; 46:1020–6.22. Paik HJ, Choi JS. Comparison of recession, anterior transposition, and myectomy for inferior oblique overaction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006; 47:600–6.23. Heo H, Park SW, Park YG. The effect of inferior oblique muscle surgery in congenital superior oblique palsy. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2007; 48:541–6.24. Souza-Dias C. The surgical treatment of unilateral superior oblique palsy. Am Orthopt J. 1992; 42:16–25.
Article25. Knapp P. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of hypertropia. First Annual Richard Scobee Memorial Lecture. Am Orthopt J. 1971; 21:29–37.26. Knapp P. Classification and treatment of superior oblique palsy. Am Orthopt J. 1974; 24:18–22.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Anterior Transposition of the Inferior Oblique Muscle for Treatment of Hypertropia in Superior Oblique Muscle Palsy
- The Effect of Inferior Oblique Muscle Transposition in Primary and Secondary Inferior Oblique Muscle Overaction
- The Effect of Modified Anterior Transposition of the Inferior Oblique Muscle for Hypertropia in Superior Oblique Muscle Palsy with Inferior Oblique Muscle Overaction
- A Case of Contralateral Pseudo Inferior Oblique Overaction after Unilateral Inferior Oblique Anterior Transposition
- Secondary Superior Oblique Overaction after Inferior Oblique Muscle Myectomy in a Patient Misdiagnosed with Inferior Oblique Muscle Overaction