Endocrinol Metab.
2012 Jun;27(2):147-150. 10.3803/EnM.2012.27.2.147.
A Case of Painless Thyroiditis Followed by Graves' Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea. yeojoo@schmc.ac.kr
- KMID: 1497655
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.2.147
Abstract
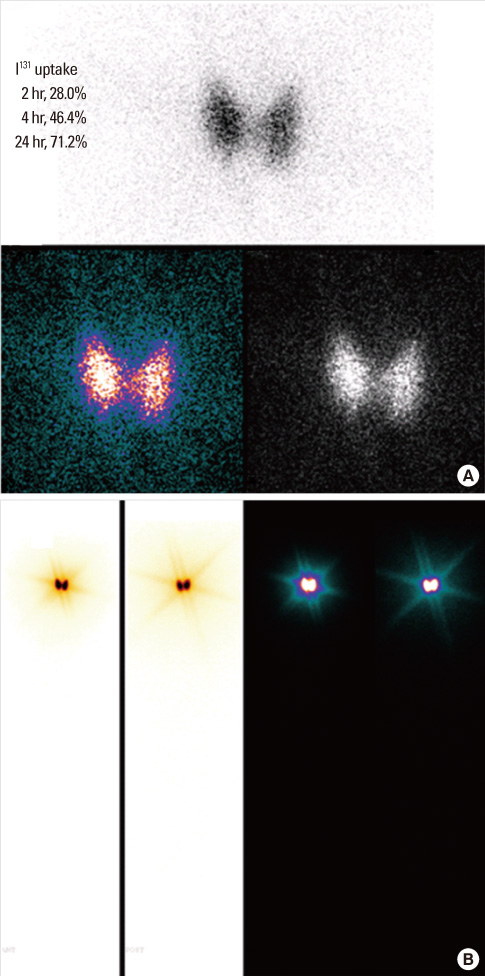
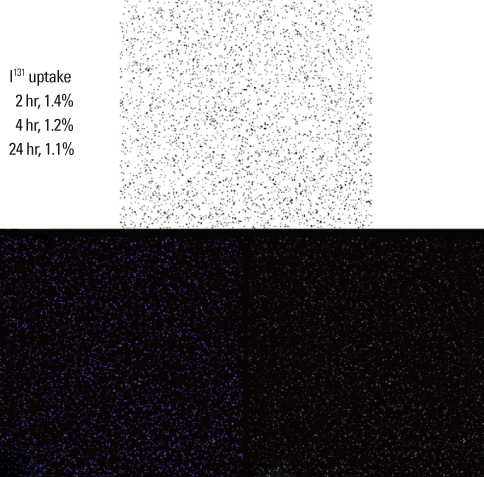
- A 30-year-old man was admitted to our hospital because of fatigue, palpitation and severe weakness of both legs. The admission laboratory findings revealed thyrotoxicosis, and 131I thyroid scintigraphic imaging revealed a low radioactive iodine uptake. He was treated for painless thyroiditis for about 4 months. However, thyrotoxic state had continued and radioactive iodine uptake was markedly increased in the follow up scan. Painless thyroiditis often relapses, but rarely develops into Graves' disease. This is a rare case in which painless thyroiditis was followed by Graves' disease.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pearce EN, Farwell AP, Braverman LE. Thyroiditis. N Engl J Med. 2003. 348:2646–2655.2. Trzepacz PT, Klein I, Roberts M, Greenhouse J, Levey GS. Graves' disease: an analysis of thyroid hormone levels and hyperthyroid signs and symptoms. Am J Med. 1989. 87:558–561.3. Eckel RH, Green WL. Postpartum thyrotoxicosis in a patient with Graves' disease. Association with low radioactive iodine uptake. JAMA. 1980. 243:1454–1456.4. Umena S, Takano T, Iijima T, Hidaka Y, Yagoro A, Takai S, Amino N. A case of repeated painless thyroiditis followed by Graves' disease. Endocr J. 1995. 42:821–826.5. Amino N, Mori H, Iwatani Y, Tanizawa O, Kawashima M, Tsuge I, Ibaragi K, Kumahara Y, Miyai K. High prevalence of transient post-partum thyrotoxicosis and hypothyroidism. N Engl J Med. 1982. 306:849–852.6. Momotani N, Noh J, Ishikawa N, Ito K. Relationship between silent thyroiditis and recurrent Graves' disease in the postpartum period. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994. 79:285–289.7. Iitaka M, Morgenthaler NG, Momotani N, Nagata A, Ishikawa N, Ito K, Katayama S. Stimulation of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) receptor antibody production following painless thyroiditis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2004. 60:49–53.8. Amino N, Tada H, Hidaka Y. Postpartum autoimmune thyroid syndrome: a model of aggravation of autoimmune disease. Thyroid. 1999. 9:705–713.9. Inoue N, Watanabe M, Nanba T, Wada M, Akamizu T, Iwatani Y. Involvement of functional polymorphisms in the TNFA gene in the pathogenesis of autoimmune thyroid diseases and production of anti-thyrotropin receptor antibody. Clin Exp Immunol. 2009. 156:199–204.10. Baumgarth N, Tung JW, Herzenberg LA. Inherent specificities in natural antibodies: a key to immune defense against pathogen invasion. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 2005. 26:347–362.11. Desailloud R, Hober D. Viruses and thyroiditis: an update. Virol J. 2009. 6:5.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Differential Diagnostic Value of Total T3/Free T4 Ratio in Graves' Disease and Painless Thyroiditis Presenting Thyrotoxicosis
- A Case of Graves' Disease Following Subacute Thyroiditis
- Graves' disease associated with Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- Riedel Thyroiditis in a Patient with Graves Disease
- Progression of Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis to Graves’ Disease: a Report of Two Pediatric Cases