Endocrinol Metab.
2012 Jun;27(2):121-125. 10.3803/EnM.2012.27.2.121.
Differential Diagnostic Value of Total T3/Free T4 Ratio in Graves' Disease and Painless Thyroiditis Presenting Thyrotoxicosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. taesikjung@gmail.com
- 2Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1497650
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.2.121
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
It is important to differentiate Graves' disease from that of painless thyroiditis in patients with thyrotoxicosis. In this study, we evaluated the usefulness of total T3 to free T4 ratio in making a differential diagnosis between Graves' disease and painless thyroiditis.
METHODS
We reviewed medical records of thyrotoxic patients, who had been diagnosed with Graves' disease or painless thyroiditis, from October 2009 to July 2011. We assessed clinical characteristics, serum levels of total T3, free T4, thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin-binding inhibitory immunoglobulin, and findings of 99mTechnetium thyroid scan. We analyzed the total T3/free T4 ratios between Graves' disease and painless thyroiditis patients.
RESULTS
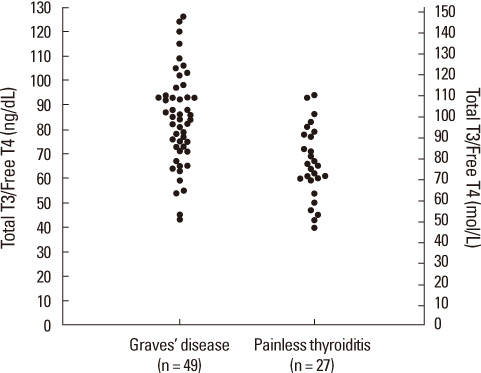
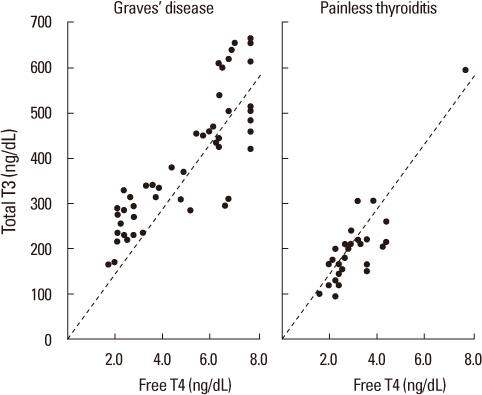
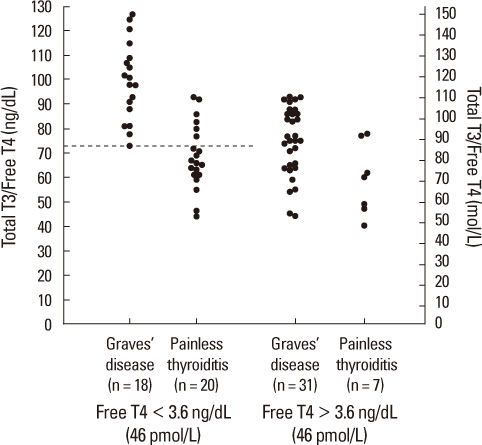
A total of 76 untreated thyrotoxic patients "49 Graves' disease and 27 painless thyroiditis" were examined. The total T3, free T4 levels and the total T3/free T4 ratios were significantly higher in patients with Graves' disease than in those with painless thyroiditis (P < 0.001). In the total T3/free T4 ratio > 73, the possibility of Graves' disease was significantly higher than in painless thyroiditis (sensitivity, 75.5%; specificity, 70.3%). The sensitivity and specificity of the total T3/free T4 ratio in patients with free T4 < 3.6 ng/dL have been increased (sensitivity, 100%; specificity, 71.4%).
CONCLUSION
The total T3/free T4 ratios was useful for making a differential diagnosis between Graves' disease and painless thyroiditis.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Interpretation of puzzling thyroid function tests
Jee Hee Yoon, Ho-Cheol Kang
J Korean Med Assoc. 2018;61(4):241-247. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2018.61.4.241.
Reference
-
1. Nikolai TF, Brosseau J, Kettrick MA, Roberts R, Beltaos E. Lymphocytic thyroiditis with spontaneously resolving hyperthyroidism (silent thyroiditis). Arch Intern Med. 1980. 140:478–482.2. Schorr AB, Miller JL, Shtasel P, Rose LI. Low incidence of painless thyroiditis in the Philadelphia area. Clin Nucl Med. 1986. 11:379–380.3. Vitug AC, Goldman JM. Silent (painless) thyroiditis. Evidence of a geographic variation in frequency. Arch Intern Med. 1985. 145:473–475.4. Cooper DS. Braverman LR, Utiger RD, editors. Treatment of thyrotoxicosis. Werner and Ingbar's the Thyroid: A Fundamental and Clinical Text. 2004. 9th ed. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott Co.;665–694.5. Costagliola S, Morgenthaler NG, Hoermann R, Badenhoop K, Struck J, Freitag D, Poertl S, Weglöhner W, Hollidt JM, Quadbeck B, Dumont JE, Schumm-Draeger PM, Bergmann A, Mann K, Vassart G, Usadel KH. Second generation assay for thyrotropin receptor antibodies has superior diagnostic sensitivity for Graves' disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1999. 84:90–97.6. Sayama N, Yoshida K, Mori K, Fukazawa H, Hori H, Nakazato N, Tani J, Nakagawa Y, Ito S. Measurement of red blood cell zinc concentration with Zn-test kit: discrimination between hyperthyroid Graves' disease and transient thyrotoxicosis. Endocr J. 1998. 45:767–772.7. Schott M, Feldkamp J, Bathan C, Fritzen R, Scherbaum WA, Seissler J. Detecting TSH-receptor antibodies with the recombinant TBII assay: technical and clinical evaluation. Horm Metab Res. 2000. 32:429–435.8. Vos XG, Smit N, Endert E, Tijssen JG, Wiersinga WM. Frequency and characteristics of TBII-seronegative patients in a population with untreated Graves' hyperthyroidism: a prospective study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2008. 69:311–317.9. Morita T, Tamai H, Oshima A, Mukuta T, Fukata S, Kuma K, Kumagai LF, Nagataki S. The occurrence of thyrotropin binding-inhibiting immunoglobulins and thyroid-stimulating antibodies in patients with silent thyroiditis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990. 71:1051–1055.10. Amino N, Yabu Y, Miki T, Morimoto S, Kumahara Y, Mori H, Iwatani Y, Nishi K, Nakatani K, Miyai K. Serum ratio of triiodothyronine to thyroxine, and thyroxine-binding globulin and calcitonin concentrations in Graves' disease and destruction-induced thyrotoxicosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1981. 53:113–116.11. Shigemasa C, Abe K, Taniguchi S, Mitani Y, Ueda Y, Adachi T, Urabe K, Tanaka T, Yoshida A, Mashiba H. Lower serum free thyroxine (T4) levels in painless thyroiditis compared with Graves' disease despite similar serum total T4 levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987. 65:359–363.12. Izumi Y, Hidaka Y, Tada H, Takano T, Kashiwai T, Tatsumi KI, Ichihara K, Amino N. Simple and practical parameters for differentiation between destruction-induced thyrotoxicosis and Graves' thyrotoxicosis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2002. 57:51–58.13. Yanagisawa T, Sato K, Kato Y, Shimizu S, Takano K. Rapid differential diagnosis of Graves' disease and painless thyroiditis using total T3/T4 ratio, TSH, and total alkaline phosphatase activity. Endocr J. 2005. 52:29–36.14. Yoshimura Noh J, Momotani N, Fukada S, Ito K, Miyauchi A, Amino N. Ratio of serum free triiodothyronine to free thyroxine in Graves' hyperthyroidism and thyrotoxicosis caused by painless thyroiditis. Endocr J. 2005. 52:537–542.15. Ota H, Amino N, Morita S, Kobayashi K, Kubota S, Fukata S, Kamiyama N, Miyauchi A. Quantitative measurement of thyroid blood flow for differentiation of painless thyroiditis from Graves' disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2007. 67:41–45.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Painless Thyroiditis Followed by Graves' Disease
- Two Cases of Postpartum Thyroiditis Followed by Graves' Disease
- A Case of Severe Recurrent Painless Thyroiditis Requiring Thyroidectomy
- Differential Diagnostic Value of TSH Receptor Antibody Measurements in Thyrotoxic Postpartum Patients with History of Graves' Disease
- The High Proportion of Painless Thyroiditis as a Cause of Thyrotoxicosis in Korea