Korean J Hematol.
2008 Mar;43(1):58-61. 10.5045/kjh.2008.43.1.58.
A Case of Congenital Hemolytic Anemia of Unknown Cause Combined with Gilbert's Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea. ysm0530@hanmail.net
- KMID: 1485159
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5045/kjh.2008.43.1.58
Abstract
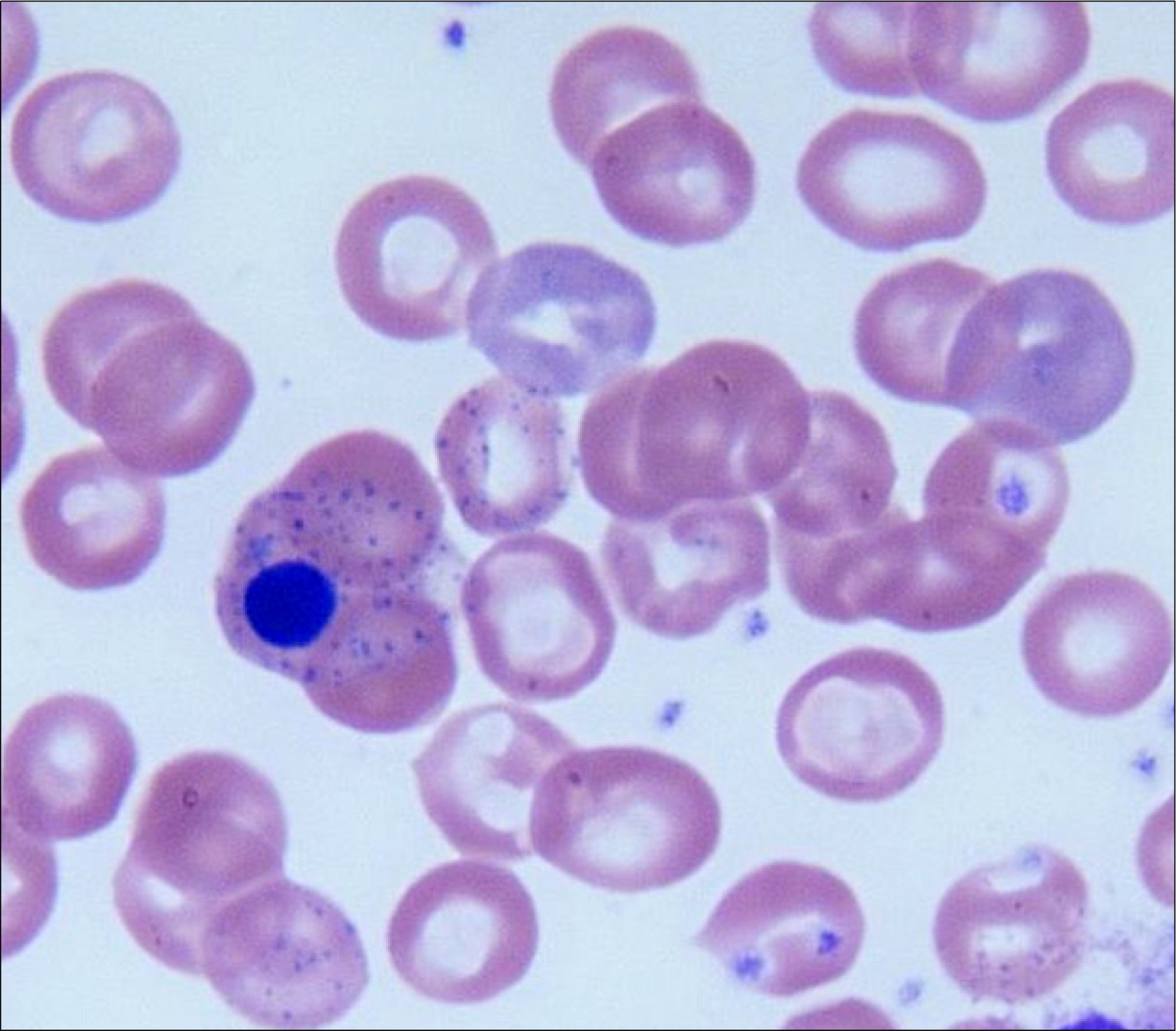
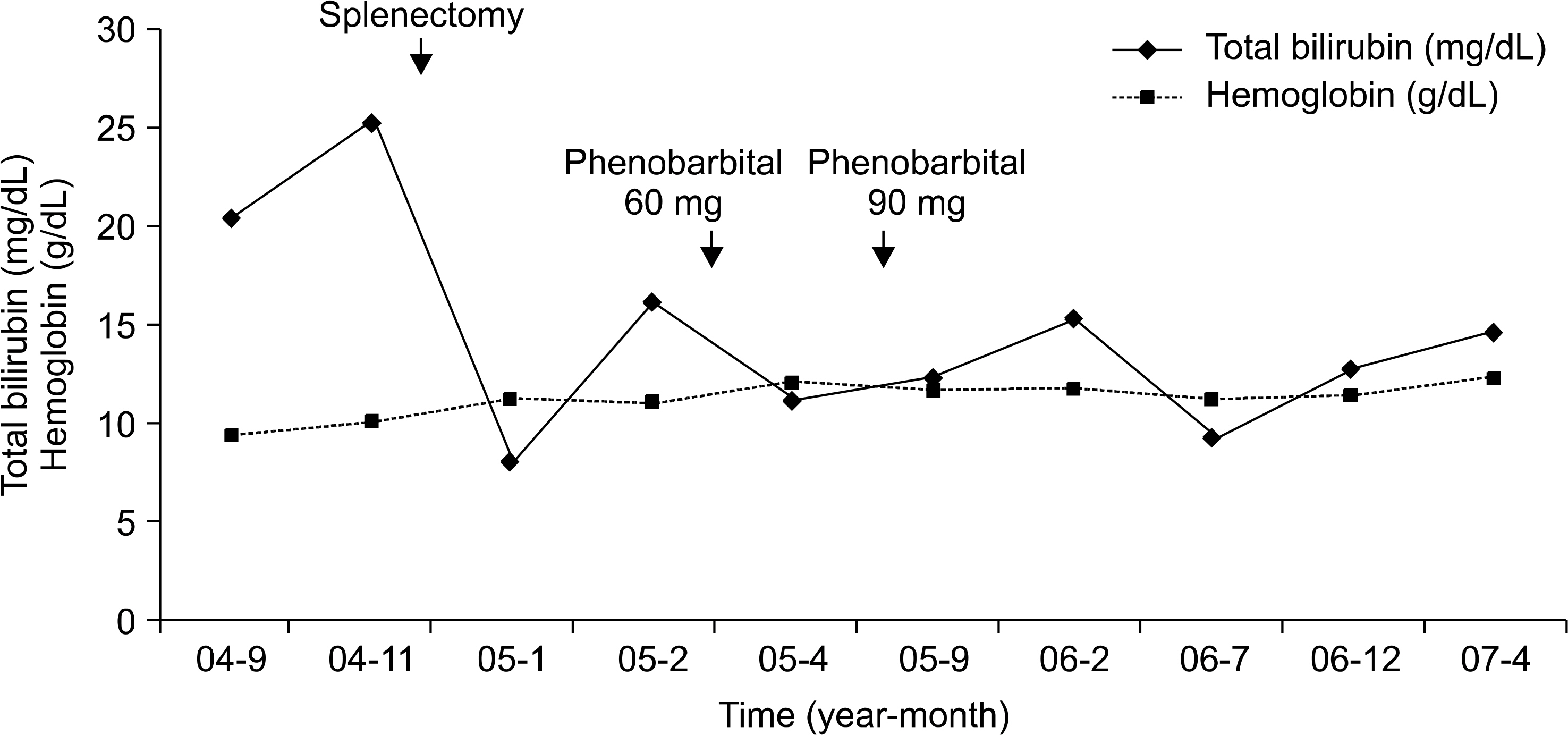
- Congenital hemolytic anemia is mainly developed due to intrinsic defects of erythrocytes, but in some cases the cause of hemolytic anemia is unclear. Gilbert's syndrome shows mild, chronic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia that is due to reduced UDP glucuronosyltransferase (UGT-1A1) activity and this develops because of UGT-1A1 gene mutation. We report here on a case of severe hyperbilirubinemia in a 17-year-old male who was diagnosed with congenital hemolytic anemia of an unknown cause combined with Gilbert's syndrome.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Coexistence of Gilbert Syndrome and Hereditary Spherocytosis in a Child Presenting with Extreme Jaundice
Jae Hee Lee, Kyung Rye Moon
Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2014;17(4):266-269. doi: 10.5223/pghn.2014.17.4.266.
Reference
-
1). Hah JO. Hemolytic anemia in pediatrics. Korean J Pediatr. 2007. 50:511–8.
Article2). Ahn DH., Sohn KC., Kang IJ, et al. Statistical analysis of hemolytic anemia in Korea. Korean J Hematol. 1991. 26:445–61.3). Kwon HS., Kang JC., Won SC., Oh SH., Lyu CJ. A clinical study of childhood hemolytic anemia according to etiological classification. Korean J Pediatr. 2003. 46:883–8.4). Bosma PJ., Chowdhury NR., Goldhoorn BG, et al. Sequence of exons and the flanking regions of human bilirubin-UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene complex and identification of a genetic mutation in a patient with Crigler-Najjar syndrome, type 1. Hepatology. 1992. 15:941–7.5). Onishi S., Kawade N., Itoh S., Isobe K., sugiyama S. Postnatal development of uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase activity towards bilirubin and 2-aminophenol in human liver. Biochem J. 1979. 184:705–7.6). Bosma PJ., Chowdhury JR., Bakker C, et al. The genetics basis of the reduced expression of bilirubin UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 in Gilbert's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1995. 333:1171–5.7). Burchell B., Hume R. Molecular genetic basis of Gilbert's syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996. 14:960–6.
Article8). Kim YH., Yeon JE., Jung GM, et al. A study of polymorphism in UDP-glucurono glucuronosyltransferase 1 (UGT-1A1) promoter gene in korean patients with Gilbert's syndrome. Korean J Hepatol. 2002. 8:132–8.9). Sugita K., Maruo Y., Kurosawa H, et al. Severe hyperbilirubinemia in a 10-year-old girl with a combined disorder of hereditary spherocytosis and Gilbert syndrome. Pediatr Int. 2007. 49:540–2.
Article10). Choi KB., Han KS., Kim MK, et al. A case of Gilberts syndrome with hemolysis. Ewha Med J. 1985. 8:69–75.11). Powell LW., Billing BH., Williams HS. An assessment of red cell survival in idiopathic unconjugated hy-perbilirubinaemia (Gilbert's syndrome) by the use of radioactive isopropylfluorophosphate and chromium. Australas Ann Med. 1967. 16:221–5.12). Powell LW., Hemingway E., Billing BH., Sherlock S. Idiopathic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert's syndrome). A study of 42 families. N Engl J Med. 1967. 227:1108–12.13). Berk PD., Blaschke TF. Detection of Gilbert's syndrome in patients with hemolysis. A method using radioactive chromium. Ann Int Med. 1972. 77:527–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coexistence of Gilbert Syndrome and Hereditary Spherocytosis in a Child Presenting with Extreme Jaundice
- A Case of Gilbert's Syndrome with Severe Neonatal Hyperbilirubinemia
- A Case of Congenital Nonspherocytic Hemolytic Anemia
- A Case of Microangiopathic Hemolytic Anemia after Myxoma Excision and Mitral Valve Repair Presenting as Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- A new paradigm in the diagnosis of hereditary hemolytic anemia