Korean J Clin Microbiol.
2008 Oct;11(2):123-128. 10.5145/KJCM.2008.11.2.123.
Epidemiological Investigation of an Outbreak of Escherichia coli Infections in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit of a University Hospital
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Research Center for Resistant Cells, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea. dsmoon@chosun.ac.kr
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- 4Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 1480980
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/KJCM.2008.11.2.123
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
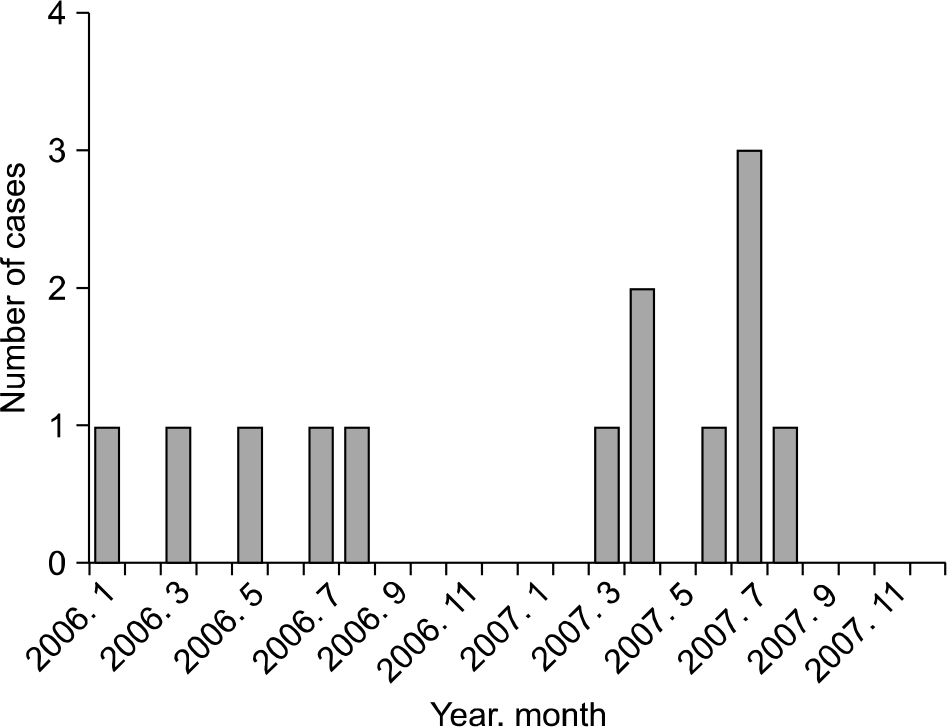
In July 2007, three neonates in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) of Chosun University Hospital expired due to Escherichia coli sepsis. An E. coli outbreak was suspected.
METHODS
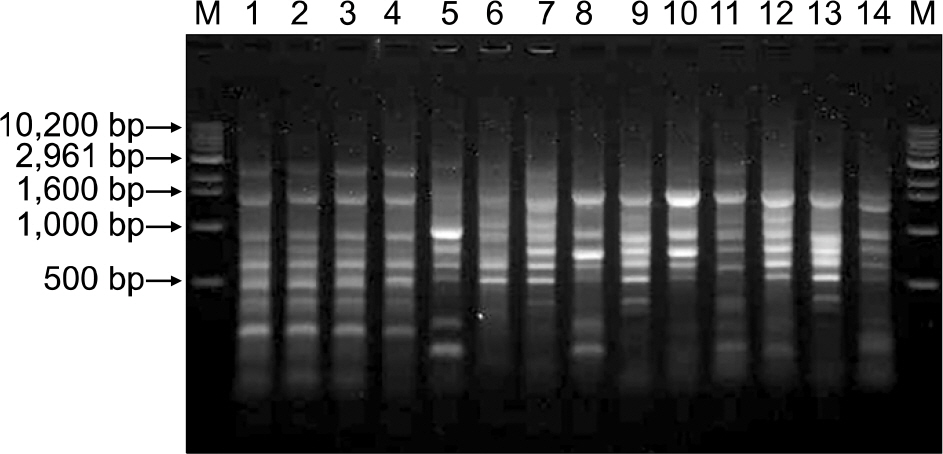
To investigate the outbreak, environmental cultures were taken from NICU. We performed repetitive extragenic palindromic (rep)-PCR to compare genotypes of the three isolates from the cases and one environmental strain of E. coli. A case-control study was done in order to identify risk factors for the infection.
RESULTS
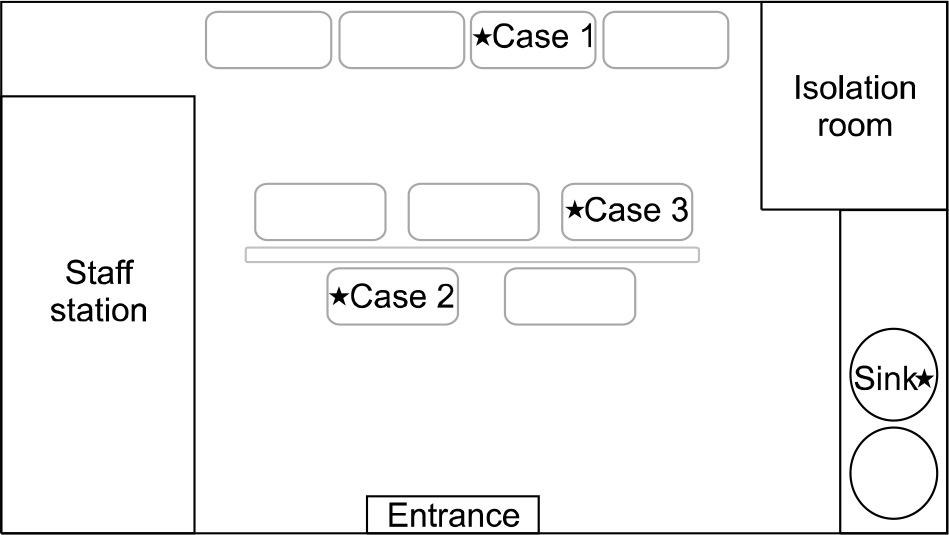
In July 2007, the attack rate of E. coli was 11.1%, which was higher than the basal rate. All the three E. coli isolates from the cases presented the same antimicrobial susceptibility pattern whereas other E. coli isolated from non-outbreak period presented different patterns. Among environmental cultures, only one specimen collected from the surface of a bathtub for neonates was culture positive for E. coli. Three strains of the cases and one environmental strain of E. coli showed the same rep-PCR pattern, while control strains showed different patterns. No statistically significant difference in risk factors was found between the case and control groups in the case-control study.
CONCLUSION
The result of rep-PCR assay showed that the outbreak had originated from a single clone of E. coli. But we could not identify risk factors for the infection. The attack rate of E. coli in NICU returned to the basal level after implement of the infection control measures such as disinfection of NICU environment and equipments, thorough hand washing, and education of health care workers.
MeSH Terms
-
Case-Control Studies
Clone Cells
Delivery of Health Care
Disease Outbreaks
Disinfection
Escherichia
Escherichia coli
Escherichia coli Infections
Genotype
Hand Disinfection
Humans
Infant, Newborn
Infection Control
Intensive Care Units, Neonatal
Intensive Care, Neonatal
Polymerase Chain Reaction
Repetitive Sequences, Nucleic Acid
Risk Factors
Sepsis
Sprains and Strains
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. McGuire W, Clerihew L, Fowlie PW. Infection in the preterm infant. BMJ. 2004; 329:1277–80.
Article2. Vergnano S, Sharland M, Kazembe P, Mwansambo C, Heath PT. Neonatal sepsis: an international perspective. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2005; 90:F220–4.
Article3. Gastmeier P, Loui A, Stamm-Balderjahn S, Hansen S, Zuschneid I, Sohr D, et al. Outbreaks in neonatal intensive care units? They are not like others. Am J Infec Control. 2007; 35:172–6.4. Damjanovic V and van Saene HKF. Outbreaks of infection in neonatal intensive care units (NICU). J Hosp Infect. 1997; 35:237–42.5. Taneja N, Das A, Raman Rao DSV, Jain N, Singh M, Sharma M. Nosocomial outbreak of diarrhoea by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli among preterm neonates in a tertiary care hospital in India: pitfalls in healthcare. J Hosp Infect. 2003; 53:193–7.
Article6. Wong HC and Lin CH. Evaluation of typing of Vibriopa-rahaemolyticus by three PCR methods using specific primers. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 39:4233–40.7. Zaza S and Jarvis WR. Investigation of outbreaks. Mayhall CG, editor. Hospital Epidemiology and Infection Control. 1st ed.Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins;2006. p. 105–13.8. Olive and Bean P. Principles and applications of methods for DNA-based typing of microbial organisms. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:1661–9.
Article9. Hwang JH, Choi CW, Chang YS, Choe YH, Park WS, Shin SM, et al. The efficacy of clinical strategies to reduce nosocomial sepsis in extremely low birth weight infants. J Korean Med Sci. 2005; 20:177–81.
Article10. Warren DK, Zack JE, Mayfield JL, Chen A, Prentice D, Fraser VJ, et al. The effect of an education program on the incidence of central venous catheter-associated bloodstream infection in a medical ICU. Chest. 2004; 126:1612–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An outbreak of inapparent non-O157 enterohemorrhagic escherichia coli infection
- Characterization of a Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium Outbreak Caused by 2 Genetically Different Clones at a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Outbreak Investigation of Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis in a Neonatal Intensive care Unit
- Analyses of Clinical Characteristics and Hematologic Studies of Confirmed Infants by Extended Spectrum beta-lactamase Producing Escherichia coli or Klebsiella pneumonia in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- Clinical and Molecular-epidemiologic Analysis of A Nosocomial Outbreak of Acinetobacter baumannii in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit