Electrolyte Blood Press.
2009 Jun;7(1):14-19. 10.5049/EBP.2009.7.1.14.
Expression of Rh Glycoproteins in the Mammalian Kidney
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anatomy, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khhan@ewha.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Division of Nephrology, University of Florida College of Medicine, FL, USA. david.weiner@medicine.ufl.edu
- 4Renal Section, North Florida/South Georgia Veterans Health System, Gainesville, FL, USA.
- KMID: 1464784
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5049/EBP.2009.7.1.14
Abstract
- Ammonia metabolism is a fundamental process in the maintenance of life in all living organisms. Recent studies have identified ammonia transporter family proteins in yeast (Mep), plants (Amt), and mammals (Rh glycoproteins). In mammalian kidneys, where ammonia metabolism and transport are critically important for the regulation of systemic acid - base homeostasis, basolateral Rh B glycoprotein and apical/basolateral Rh C glycoprotein are expressed along the distal nephron segments. Data from experimental animal models and knockout mice suggest that the Rh glycoproteins appear to mediate important roles in urinary ammonia excretion.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
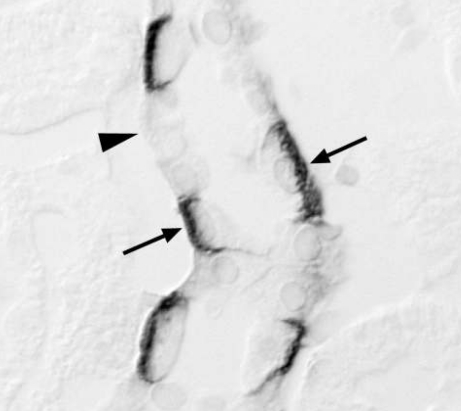
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alper SL, Natale J, Gluck S, Lodish HF, Brown D. Subtypes of intercalated cells in rat kidney collecting duct defined by antibodies against erythroid band 3 and renal vacuolar H+-ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989; 86:5429–5433. PMID: 2526338.2. Kim J, Kim YH, Cha JH, Tisher CC, Madsen KM. Intercalated cell subtypes in connecting tubule and cortical collecting duct of rat and mouse. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999; 10:1–12. PMID: 9890303.
Article3. Knepper MA, Packer R, Good DW. Ammonium transport in the kidney. Physiol Rev. 1989; 69:179–249. PMID: 2643123.
Article4. Weiner ID, Verlander JW. Renal and hepatic expression of the ammonium transporter proteins, Rh B Glycoprotein and Rh C Glycoprotein. Acta Physiol Scand. 2003; 179:331–338. PMID: 14656370.
Article5. Weiner ID. The Rh gene family and renal ammonium transport. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2004; 13:533–540. PMID: 15300160.
Article6. Lang W, Block TM, Zander R. Solubility of NH3 and apparent pK of NH4+ in human plasma, isotonic salt solutions and water at 37 degrees C. Clin Chim Acta. 1998; 273:43–58. PMID: 9620469.7. Echevarría M, Muñoz-Cabello AM, Sánchez-Silva R, Toledo-Aral JJ, López-Barneo J. Development of cytosolic hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor stabilization are facilitated by aquaporin-1 expression. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:30207–30215. PMID: 17673462.
Article8. Han KH, Mekala K, Babida V, Kim HY, Handlogten ME, Verlander JW, et al. Expression of the gas transporting proteins, Rh B glycoprotein and Rh C glycoprotein, in the murine lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. in press.9. Marini AM, Vissers S, Urrestarazu A, Andre B. Cloning and expression of the MEP1 gene encoding an ammonium transporter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1994; 13:3456–3463. PMID: 8062822.
Article10. Ninnemann O, Jauniaux JC, Frommer WB. Identification of a high affinity NH4+ transporter from plants. EMBO J. 1994; 13:3464–3471. PMID: 8062823.
Article11. Marini AM, Matassi G, Raynal V, Andre B, Cartron JP, Cherif-Zahar B. The human Rhesus-associated RhAG protein and a kidney homologue promote ammonium transport in yeast. Nat Genet. 2000; 26:341–344. PMID: 11062476.
Article12. Marini AM, Urrestarazu A, Beauwens R, Andre B. The Rh (rhesus) blood group polypeptides are related to NH4+ transporters. Trends Biochem Sci. 1997; 22:460–461. PMID: 9433124.
Article13. Liu Z, Chen Y, Mo R, Hui C, Cheng JF, Mohandas N, et al. Characterization of human RhCG and mouse Rhcg as novel nonerythroid Rh glycoprotein homologues predominantly expressed in kidney and testis. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275:25641–25651. PMID: 10852913.
Article14. Liu Z, Peng J, Mo R, Hui C, Huang CH. Rh type B glycoprotein is a new member of the Rh superfamily and a putative ammonia transporter in mammals. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:1424–1433. PMID: 11024028.
Article15. Khademi S, O'Connell J 3rd, Remis J, Robles-Colmenares Y, Miercke LJ, Stroud RM. Mechanism of ammonia transport by Amt/MEP/Rh: structure of AmtB at 1.35 A. Science. 2004; 305:1587–1594. PMID: 15361618.
Article16. Zheng L, Kostrewa D, Bernèche S, Winkler FK, Li XD. The mechanism of ammonia transport based on the crystal structure of AmtB of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101:17090–17095. PMID: 15563598.17. Han KH, Kim HY, Croker BP, Reungjui S, Lee SY, Kim J, et al. Effects of Ischemia-reperfusion Injury on Renal Ammonia Metabolism and the Collecting Duct. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007; 293:F1342–F1354. PMID: 17686949.
Article18. Kim HY, Baylis C, Verlander JW, Han KH, Reungjui S, Handlogten ME, et al. Effect of Reduced Renal Mass on Renal Ammonia Transporter Family, Rh C Glycoprotein and Rh B Glycoprotein, Expression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007; 293:F1238–F1247. PMID: 17652373.
Article19. Quentin F, Eladari D, Cheval L, Lopez C, Goossens D, Colin Y, et al. RhBG and RhCG, the putative ammonia transporters, are expressed in the same cells in the distal nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2003; 14:545–554. PMID: 12595489.
Article20. Seshadri RM, Klein JD, Kozlowski S, Sands JM, Kim YH, Han KH, et al. Renal Expression of the Ammonia Transporters, Rhbg and Rhcg, In Response to Chronic Metabolic Acidosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006; 290:F397–F408. PMID: 16144966.
Article21. Seshadri RM, Klein JD, Smith T, Sands JM, Handlogten ME, Verlander JW, et al. Changes in subcellular distribution of the ammonia transporter, Rhcg, in response to chronic metabolic acidosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2006; 290:F1443–F1452. PMID: 16434569.
Article22. Verlander JW, Miller RT, Frank AE, Royaux IE, Kim YH, Weiner ID. Localization of the ammonium transporter proteins RhBG and RhCG in mouse kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003; 284:F323–F337. PMID: 12388412.23. Brown AC, Hallouane D, Mawby WJ, Karet FE, Saleem MA, Howie AJ, et al. RhCG is the major putative ammonia transporter expressed in the human kidney, and RhBG is not expressed at detectable levels. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 296:F1279–F1290. PMID: 19357182.
Article24. Eladari D, Cheval L, Quentin F, Bertrand O, Mouro I, Cherif-Zahar B, et al. Expression of RhCG, a new putative NH3/NH4+ transporter, along the rat nephron. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002; 13:1999–2008. PMID: 12138130.25. Han KH, Croker BP, Clapp WL, Werner D, Sahni M, Kim J, et al. Expression of the ammonia transporter, Rh C glycoprotein, in normal and neoplastic human kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006; 17:2670–2679. PMID: 16928804.
Article26. Kim HY, Verlander JW, Bishop JM, Cain BD, Han KH, Igarashi P, et al. Basolateral Expression of the ammonia transporter family member, Rh C Glycoprotein, in the Mouse Kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009; 296:F543–F555. PMID: 19129254.
Article27. Lim SW, Ahn KO, Kim WY, Han DH, Li C, Ghee JY, et al. Expression of ammonia transporters, Rhbg and Rhcg, in chronic cyclosporine nephropathy in rats. Nephron Exp Nephrol. 2008; 110:e49–e58. PMID: 18776723.
Article28. Chambrey R, Goossens D, Bourgeois S, Picard N, Bloch-Faure M, Leviel F, et al. Genetic ablation of Rhbg in the mouse does not impair renal ammonium excretion. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005; 289:F1281–F1290. PMID: 16077082.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Ammonia Transporters in the Kidney with Ureteral Obstruction
- Expression and Characterization of the Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Mutant Envelope Glycoproteins in Mammalian Cells
- Renal Expression of Ammonia Transporters in Rats with Amiloride-Induced Renal Tubular Acidosis
- Eukaryotic Expression of Human Cytomegalovirus ( HCMV ) Glycoprotein H ( gH )
- Renal Expression of an Ammonia Transporter in Rats with a Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction