J Korean Soc Radiol.
2010 Apr;62(4):351-355. 10.3348/jksr.2010.62.4.351.
Radiologic Placement of Tunneled Central Venous Catheters in Pediatric Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea. songsy01@gmail.com
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Korea.
- KMID: 1460067
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2010.62.4.351
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We evaluated the technical success and complication rates associated with the radiological placement of tunneled central venous catheters in pediatric patients.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
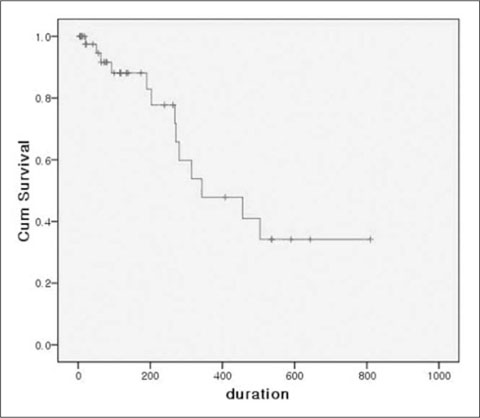
Between May 1, 2005 and March 31, 2008, a total of 46 tunneled central venous catheters were placed in 34 children (M:F = 22:12; mean age, 9.9 years [9 months to 16.8 years]). All procedures were performed under ultrasonographic and fluoroscopic guidance. Follow-up data were obtained through the retrospective review of the medical records. We used the Kaplan-Meier survival method for the evaluation of survival rate of the catheters.
RESULTS
All procedures were technically successful. The observed periprocedural complications included hematoma formation in three patients. The mean catheter life was 189.3 days (total, 8710 days; range, 7-810). Catheters were removed due to death (n=9), the end of treatment (n=8), catheter sepsis (n=4), malfunction (n=8), and accidental removal (n=4). The rate of catheter sepsis and malfunction was 0.459 and 0.919 for every 1000 catheter days, respectively. The expected mean catheter life was 479.6 days as per the Kaplan-Meier analysis.
CONCLUSION
The results suggest that the radiologic placement of a tunneled central venous catheter is an effective technique with a high technical success rate and low complication rate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Karapinar B, Alphan C. Complications of central venous catheterization in critically ill children. Pediatr Int. 2007; 49:593–599.2. Cruzeiro PC, Paulo Augusto MC, Marcelo EM. Central venous catheter placement in children: a prospective study of complications in a brazilian public hospital. Pediatr Surg Int. 2006; 22:536–540.3. Sarper N, Zengin E, Corapcioglu F, Tugay M. Totally implantable central venous access devices in children with hemato-oncologic malignancies: evaluation of complications and comparison of incidence of febrile episodes with similar patients without central venous access devices. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2006; 23:459–470.4. Sheridan RL, Weber JM. Mechanical and infectious complications of central venous cannulation in children: lessons learned from a 10-year experience placing more than 1000 catheters. J Burn Care Res. 2006; 27:713–718.5. Perdikaris P, Petsios K, Vasilatou-Kosmidis H, Matziou V. Complications of hickman-broviac catheters in children with malignancies. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2008; 25:375–384.6. Adler A, Yaniv I, Steinberg R, Solter E, Samra Z, Stein J, et al. Infectious complications of implantable ports and hickman catheters in paediatric haematology-oncology patients. J Hosp Infect. 2006; 62:358–365.7. Lee YH. Clinical Study of Hickman Catheters in Pediatric Oncologic Patients. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1996; 39:682–690.8. Robertson LJ, Mauro MA, Jaques PF. Radiologic placement of Hickman catheters. Radiology. 1989; 170:1007–1009.9. Morris SL, Jaques PF, Mauro MA. Radiology-assisted placement of implantable subcutaneous infusion ports for long-term venous access. Radiology. 1992; 184:149–151.10. Gebauer B, Teichgraber UM, Werk M, Beck A, Wagner HJ. Sonographically guided venous puncture and fluoroscopically guided placement of tunneled, large-bore central venous catheters for bone marrow transplantation-high success rates and low complication rates. Support Care Cancer. 2008; 16:897–904.11. Masci G, Magagnoli M, Pedicini V, Poretti D, Castagna L, Carnaghi C, et al. Long-term, tunneled, noncuffed central venous catheter in cancer patients (vygon): safety, efficacy, and complications. Support Care Cancer. 2006; 14:1141–1146.12. Nosher JL, Shami MM, Siegel RL, DeCandia M, Bodner L. Tunneled central venous access catheter placement in the pediatric population: comparison of radiologic and surgical results. Radiology. 1994; 192:265–268.13. Basford TJ, Poenaru D, Silva M. Comparison of delayed complications of central venous catheters placed surgically or radiologically in pediatric oncology patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2003; 38:788–792.14. Arul GS, Lewis N, Bromley P, Bennett J. Ultrasound-guided percutaneous insertion of hickman lines in children. Prospective study of 500 consecutive procedures. J Pediatr Surg. 2009; 44:1371–1376.15. Silberzweig JE, Sacks D, Khorsandi AS, Bakal CW. Reporting standards for central venous access. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003; 14:S443–S452.16. Mansfield PF, Hohn DC, Fornage BD, Gregurich MA, Ota DM. Complications and failures of subclavian-vein catheterization. N Engl J Med. 1994; 331:1735–1738.17. Lameris JS, Post PJ, Zonderland HM, Gerritsen PG, Kappers-Klunne MC, Schutte HE. Percutaneous placement of Hickman catheters: comparison of sonographically guided and blind techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990; 155:1097–1099.18. Kuter DJ. Thrombotic complications of central venous catheters in cancer patients. Oncologist. 2004; 9:207–216.19. Pinon M, Bezzio S, Tovo PA, Fagioli F, Farinasso L, Calabrese R, et al. A prospective 7-year survey on central venous catheter-related complications at a single pediatric hospital. Eur J Pediatr. 2009; Forthcoming.20. Polderman KH, Girbes AJ. Central venous catheter use. Part 1: mechanical complications. Intensive Care Med. 2002; 28:1–17.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Insertion and Management of Central Venous Catheters
- Radiologic Placement of Tunneled Central Venous Catheter
- Interventional Radiologic Placement of Tunneled Central Venous Catheters: Results and Complications in 557Cases
- Radiologic Placement of Implantable Chest Ports in Pediatric Patients Under Sedation
- Outcome of Tunneled Infusion Catheters Inserted via the Right Internal Jugular Vein