J Clin Neurol.
2011 Mar;7(1):19-24. 10.3988/jcn.2011.7.1.19.
Dementia with Lewy Bodies versus Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease Dementia: A Comparison of Cognitive Profiles
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. neuropark@dau.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Hanseo Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 1452568
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3988/jcn.2011.7.1.19
Abstract
- BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
It is particularly difficult to differentiate dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) from the related dementias of Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease dementia (PDD). Few studies have been designed to comparatively analyze detailed neuropsychological assessments of DLB patients and patients with AD and PDD.
METHODS
Three groups of patients participated in this study: 10 with DLB, 76 with AD, and 17 with PDD, who had been diagnosed as probable DLB, AD, and PDD, respectively, according to the clinical criteria of the consortium on DLB, National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Diseases and Stroke/Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorder Association, and the clinical diagnostic criteria for PDD. All patients were evaluated by careful neurological examination with detailed neuropsychological testing.
RESULTS
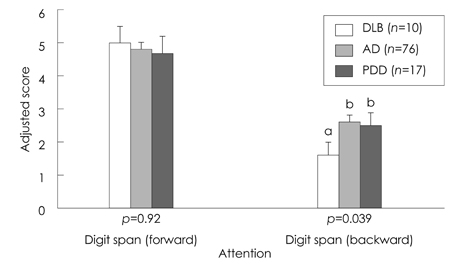
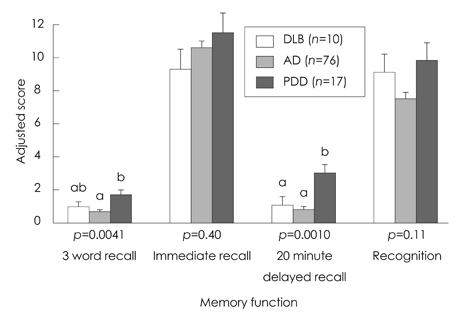
Significant differences among the three groups were found for attention, memory, and executive function, which included tasks of backward digit span, three-word recall, verbal delayed recall, and the Stroop test. Post hoc analysis revealed that the deficiencies of attention on the digit span task were greater in the DLB group than in the AD and PDD groups. The scores for episodic verbal memory tasks were significantly lower in the DLB and AD groups than in the PDD group. The performance in frontal executive function, as indicated by the Stroop test, was significantly worse in the DLB and PDD groups than in the AD group.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of the present study show that the pattern of cognitive dysfunction, in terms of attention, episodic memory, and executive functions, differ between patients with DLB and patients with AD and PDD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease with Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Combined with Cognitive Training: A Prospective, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Juyoun Lee, Byong Hee Choi, Eungseok Oh, Eun Hee Sohn, Ae Young Lee
J Clin Neurol. 2016;12(1):57-64. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2016.12.1.57.
Reference
-
1. Lopez OL, Wisnieski SR, Becker JT, Boller F, DeKosky ST. Extrapyramidal signs in patients with probable Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 1997. 54:969–975.
Article2. Marder K, Tang MX, Cote L, Stern Y, Mayeux R. The frequency and associated risk factors for dementia in patients with Parkinson's disease. Arch Neurol. 1995. 52:695–701.
Article3. McKeith IG, Galasko D, Kosaka K, Perry EK, Dickson DW, Hansen LA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the clinical and pathologic diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB): report of the consortium on DLB international workshop. Neurology. 1996. 47:1113–1124.
Article4. McKeith IG, Dickson DW, Lowe J, Emre M, O'Brien JT, Feldman H, et al. Diagnosis and management of dementia with Lewy bodies: third report of the DLB Consortium. Neurology. 2005. 65:1863–1872.
Article5. Perry RH, Irving D, Blessed G, Perry EK, Fairbairn AF. Clinically and neuropathologically distinct form of dementia in the elderly. Lancet. 1989. 1:166.
Article6. Stern Y, Tang MX, Jacobs DM, Sano M, Marder K, Bell K, et al. Prospective comparative study of the evolution of probable Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 1998. 4:279–284.
Article7. McKeith IG, Ballard CG, Perry RH, Ince PG, O'Brien JT, Neill D, et al. Prospective validation of consensus criteria for the diagnosis of dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology. 2000. 54:1050–1058.
Article8. Ballard CG, Aarsland D, McKeith I, O'Brien J, Gray A, Cormack F, et al. Fluctuations in attention: PD dementia vs DLB with parkinsonism. Neurology. 2002. 59:1714–1720.
Article9. Aarsland D, Litvan I, Salmon D, Galasko D, Wentzel-Larsen T, Larsen JP. Performance on the dementia rating scale in Parkinson's disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies: comparison with progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2003. 74:1215–1220.
Article10. Noe E, Marder K, Bell KL, Jacobs DM, Manly JJ, Stern Y. Comparison of dementia with Lewy bodies to Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease with dementia. Mov Disord. 2004. 19:60–67.
Article11. Metzler-Baddeley C. A review of cognitive impairments in dementia with Lewy bodies relative to Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease with dementia. Cortex. 2007. 43:583–600.
Article12. Tröster AI. Neuropsychological characteristics of dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease with dementia: differentiation, early detection, and implications for "mild cognitive impairment" and biomarkers. Neuropsychol Rev. 2008. 18:103–119.
Article13. Mondon K, Gochard A, Marqué A, Armand A, Beauchamp D, Prunier C, et al. Visual recognition memory differentiates dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007. 78:738–741.
Article14. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984. 34:939–944.
Article15. Emre M, Aarsland D, Brown R, Burn DJ, Duyckaerts C, Mizuno Y, et al. Clinical diagnostic criteria for dementia associated with Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord. 2007. 22:1689–1707.
Article16. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975. 12:189–198.17. Kang Y, Na DL, Hahn S. A validity study on the korean mini-mental state examination (K-MMSE) in dementia patients. J Korean Neurol Assoc. 1997. 15:300–308.18. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993. 43:2412–2414.19. Kang Y, Na DL. Seoul Neuropsychological Screening Battery. 2003. Incheon: Human Brain Research & Consulting Co.20. Kim H, Na DL. Normative data on the Korean version of the Boston Naming Test. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 1999. 21:127–133.21. Gómez-Isla T, Growdon WB, McNamara M, Newell K, Gómez-Tortosa E, Hedley-Whyte ET, et al. Clinicopathologic correlates in temporal cortex in dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurology. 1999. 53:2003–2009.
Article22. Aarsland D, Ballard CG, Halliday G. Are Parkinson's disease with dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies the same entity? J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2004. 17:137–145.
Article23. McKeith IG, Mosimann UP. Dementia with Lewy bodies and Parkinson's disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2004. 10:Suppl 1. S15–S18.
Article24. Simard M, van Reekum R, Myran D, Panisset M, Cohen T, Freedman M, et al. Differential memory impairment in dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer's disease. Brain Cogn. 2002. 49:244–249.25. Hamilton JM, Salmon DP, Galasko D, Delis DC, Hansen LA, Masliah E, et al. A comparison of episodic memory deficits in neuropathologically-confirmed Dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer's disease. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2004. 10:689–697.
Article26. Calderon J, Perry RJ, Erzinclioglu SW, Berrios GE, Dening TR, Hodges JR. Perception, attention, and working memory are disproportionately impaired in dementia with Lewy bodies compared with Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001. 70:157–164.
Article27. Lambon Ralph MA, Powell J, Howard D, Whitworth AB, Garrard P, Hodges JR. Semantic memory is impaired in both dementia with Lewy bodies and dementia of Alzheimer's type: a comparative neuropsychological study and literature review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2001. 70:149–156.
Article28. Downes JJ, Priestley NM, Doran M, Ferran J, Ghadiali E, Cooper P. Intellectual, mnemonic, and frontal functions in dementia with Lewy bodies: A comparison with early and advanced Parkinson's disease. Behav Neurol. 1998. 11:173–183.
Article29. Edison P, Rowe CC, Rinne JO, Ng S, Ahmed I, Kemppainen N, et al. Amyloid load in Parkinson's disease dementia and Lewy body dementia measured with [11C]PIB positron emission tomography. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008. 79:1331–1338.
Article30. Brooks DJ. Imaging amyloid in Parkinson's disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies with positron emission tomography. Mov Disord. 2009. 24:Suppl 2. S742–S747.
Article31. Varanese S, Perfetti B, Monaco D, Thomas A, Bonanni L, Tiraboschi P, et al. Fluctuating cognition and different cognitive and behavioural profiles in Parkinson's disease with dementia: comparison of dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol. 2010. 257:1004–1011.
Article