Lab Anim Res.
2011 Dec;27(4):339-342. 10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.339.
Subcellular localization of the transmembrane inner ear (Tmie) protein in a stable Tmie-expressing cell line
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Genetics, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. jgsuh@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Natural Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Microbiology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1444967
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.339
Abstract
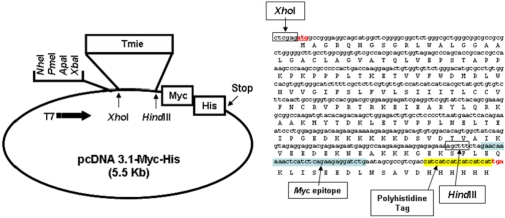
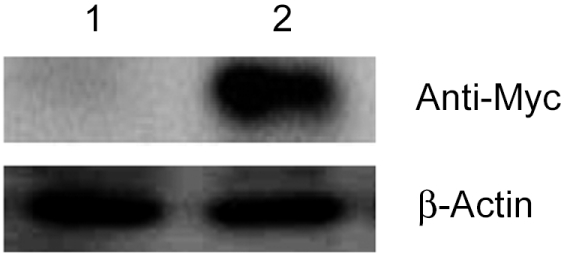
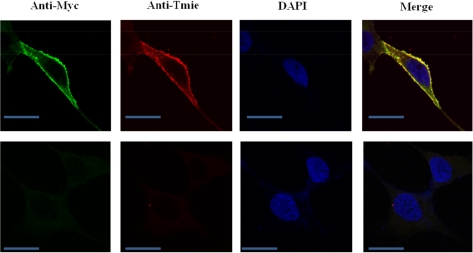
- Mutations in the transmembrane inner ear (Tmie) gene, which encodes the Tmie protein, have been attributed to deafness autosomal recessive 6 (DFNB6), an autosomal nonsyndromic recessive hearing loss disorder. Although the Tmie gene was identified a few years ago, little is known about subcellular localization of the Tmie protein. In order to address this, we developed a stable cell line expressing Tmie protein. The expression of Myc-tagged Tmie protein was confirmed by Western blot analysis using an anti-Myc antibody and localization of the Tmie protein was confirmed by immunostaining, using the anti-Myc antibody as well as the anti-tmie antibody. Our study demonstrates that the Tmie protein is localized mostly in the cellular membrane and to a lesser extent in cytoplasm. These results suggest that our Tmie expressing stable cell line provides a suitable in vitro model to explore Tmie synthesis and functions.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dror AA, Avraham KB. Hearing impairment: a panoply of genes and functions. Neuron. 2010; 68(2):293–308. PMID: 20955936.
Article2. Raviv D, Dror AA, Avraham KB. Hearing loss: a common disorder caused by many rare alleles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010; 1214:168–179. PMID: 21175685.
Article3. Lalwani AK, Castelein CM. Cracking the Auditory Genetic Code: nonsyndromic hereditary hearing impairment. Am J Otol. 1999; 20:115–132. PMID: 9918184.4. Naz S, Giguere CM, Kohrman DC, Mitchem KL, Riazuddin S, Morell RJ, Ramesh A, Srisailpathy S, Deshmukh D, Riazuddi S, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB, Smith RJ, Wilcox ER. Mutations in a novel gene, TMIE, are associated with hearing loss linked to the DFNB6 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 2002; 71(3):632–636. PMID: 12145746.
Article5. Mitchem KL, Hibbard E, Beyer LA, Bosom K, Dootz GA, Dolan DF, Johnson KR, Raphael Y, Kohrman DC. Mutation of the novel gene Tmie results in sensory cell defects in the inner ear of spinner, a mouse model of human hearing loss DFNB6. Hum Mol Genet. 2002; 11(16):1887–1898. PMID: 12140191.
Article6. Cho KI, Suh JG, Lee JW, Hong SH, Kang TC, Oh YS, Ryoo ZY. The circling mouse (C57BL/6J-cir) has a 40-kilobase genomic deletion that includes the transmembrane inner ear (tmie) gene. Comp Med. 2006; 56:476–481. PMID: 17219777.7. Santos RL, El-Shanti H, Sikandar S, Lee K, Bhatti A, Yan K, Chahrour MH, McArthur N, Pham TL, Mahasneh AA, Ahmad W, Leal SM. Novel sequence variants in the TMIE gene in families with autosomal recessive nonsyndromic hearing impairment. J Mol Med. 2006; 84(3):226–231. PMID: 16389551.
Article8. Sirmaci A, Oztükmen-Akay H, Erbek S, Incesulu A, Duman D, Taşir-Yilmaz S, Ozdağ H, Tekin M. A founder TMIE mutation is a frequent cause of hearing loss in Southeastern Anatolia. Clin Genet. 2009; 75(6):562–567. PMID: 19438934.9. Yang JJ, Su MC, Chien KH, Hsin CH, Li SY. Identification of novel variants in the TMIE gene of patients with nonsyndromic hearing loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2010; 74(5):489–493. PMID: 20206386.
Article10. Lee JW, Ryoo ZY, Lee EJ, Hong SH, Chung WH, Lee HT, Chung KS, Kim TY, Oh YS, Suh JG. Circling mouse, a spontaneous mutant in the inner ear. Exp Anim. 2002; 51:167–171. PMID: 12012726.
Article11. Cho KI, Lee JW, Kim KS, Lee EJ, Suh JG, Lee HJ, Kim HT, Hong SH, Chung WH, Chang KT, Hyun BH, Oh YS, Ryoo ZY. Fine mapping of the circling (cir) gene on the distal portion of mouse chromosome 9. Comp Med. 2003; 53:642–648. PMID: 14727813.12. Nam YY, Karuppasamy S, Byoungkwon Park, Kwon HJ, Suh JG. Production and Characterization of polyclonal antibody to transmembrane inner ear protein. Lab Anim Res. 2009; 25(2):145–150.13. Kothiyal P, Cox S, Ebert J, Husami A, Kenna MA, Greinwald JH, Aronow BJ, Rehm HL. High-throughput detection of mutations responsible for childhood hearing loss using resequencing microarrays. BMC Biotechnol. 2010; 10:10. PMID: 20146813.
Article14. Chung WH, Kim KR, Cho YS, Cho DY, Woo JH, Ryoo ZY, Cho KI, Hong SH. Cochlear pathology of the circling mouse: a new mouse model of DFNB6. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007; 127(3):244–251. PMID: 17364360.
Article15. Shin MJ, Lee JH, Yu DH, Kim HJ, Bae KB, Yuh HS, Kim MO, Hyun BH, Lee S, Park R, Ryoo ZY. Spatiotemporal expression of tmie in the inner ear of rats during postnatal development. Comp Med. 2010; 60(4):288–294. PMID: 20819378.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Expression of deafness protein Tmie in postnatal developmental stages of C57BL/6J mice
- Over-expression of myosin7A in cochlear hair cells of circling mice
- Biological Analysis of a New Spontaneous Mutant Mouse Showing Deafness and Circling Behavior
- Expression and Intracellular Localization of Hepatitis C Viral Core Protein in Human Hepatoma Cell Line Transfected with Viral cDNA
- Conservation of Mucous Epithelial Characteristics in the Human Middle Ear Epithelial Cell Line