Lab Anim Res.
2012 Jun;28(2):147-150. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.147.
Expression of deafness protein Tmie in postnatal developmental stages of C57BL/6J mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Genetics, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea. jgsuh@hallym.ac.kr
- 2Institute of Natural Medicine, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 1436718
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.147
Abstract
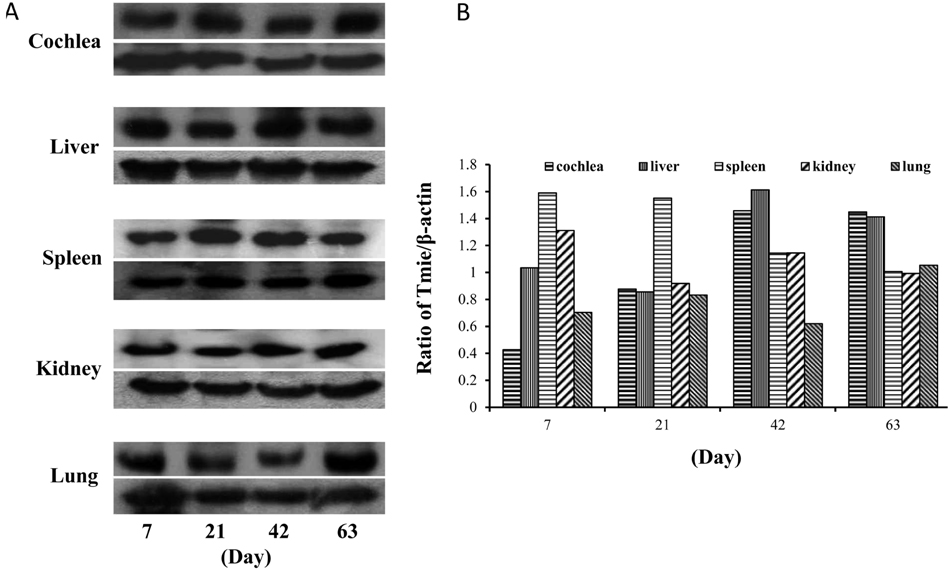
- Loss-of function mutations in the transmembrane inner ear expressed (Tmie/TMIE) gene have been shown to cause deafness in mice and humans (DFNB6). Previous studies report that the circling mouse can be an animal model for DFNB6. However, the expression pattern of Tmie protein in postnatal developmental stages has not been clearly revealed. In this study we tried to investigate the expression of Tmie protein in the liver, spleen, kidney, and lung, as well as in the cochlea. We examined various tissue samples from five different age groups of C57BL/6J animals. Using western blotting analysis, the expression of Tmie protein in these organs has been identified. The results show that Tmie protein expression in the cochlea has been increased in postnatal developmental stages, indicating that Tmie plays an important role in not only the development and also in the function of the cochlea. The expression pattern of Tmie in adult mouse organs such as the liver, spleen, kidney, and spleen significantly vary in adult rats. The order of Tmie expression level in mice (63 days after birth) was spleen, liver, lung, cochlea, and kidney, whereas in the adult rat it was liver, cochlea, lung, spleen, and kidney.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morton NE. Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991. 630:16–31.2. Mehl AL, Thomson V. Newborn hearing screening: the great omission. Pediatrics. 1998. 101(1):E4.3. Petit C, Levilliers J, Hardelin JP. Molecular genetics of hearing loss. Annu Rev Genet. 2001. 35:589–646.4. Resendes BL, Williamson RE, Morton CC. At the speed of sound: gene discovery in the auditory system. Am J Hum Genet. 2001. 69(5):923–935.5. Keats BJ, Berlin CI. Genomics and hearing impairment. Genome Res. 1999. 9(1):7–16.6. Mitchem KL, Hibbard E, Beyer LA, Bosom K, Dootz GA, Dolan DF, Johnson KR, Raphael Y, Kohrman DC. Mutation of the novel gene Tmie results in sensory cell defects in the inner ear of spinner, a mouse model of human hearing loss DFNB6. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. 11(16):1887–1898.7. Chung WH, Kim KR, Cho YS, Cho DY, Woo JH, Ryoo ZY, Cho KI, Hong SH. Cochlear pathology of the circling mouse: a new mouse model of DFNB6. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007. 127(3):244–251.8. Probst FJ, Camper SA. The role of mouse mutants in the identification of human hereditary hearing loss genes. Hear Res. 1999. 130(1-2):1–6.9. Steel KP, Kros CJ. A genetic approach to understanding auditory function. Nat Genet. 2001. 27(2):143–149.10. Lee JW, Ryoo ZY, Lee EJ, Hong SH, Chung WH, Lee HT, Chung KS, Kim TY, Oh YS, Suh JG. Circling mouse, a spontaneous mutant in the inner ear. Exp Anim. 2002. 51(2):167–171.11. Cho KI, Suh JG, Lee JW, Hong SH, Kang TC, Oh YS, Ryoo ZY. The circling mouse (C57BL/6J-cir) has a 40-kilobase genomic deletion that includes the transmembrane inner ear (tmie) gene. Comp Med. 2006. 56(6):476–481.12. Nam YY, Karuppasamy S, Park BK, Kwon HJ, Suh JG. Production and characterization of polyclonal antibody to transmembrane inner ear protein. Lab Anim Res. 2009. 25(2):145–150.13. Karuppasamy S, Nam YY, Jung H, Park B, Kwon HJ, Suh JG. Subcellular localization of the transmembrane inner ear (Tmie) protein in a stable Tmie-expressing cell line. Lab Anim Res. 2011. 27(4):339–342.14. Naz S, Giguere CM, Kohrman DC, Mitchem KL, Riazuddin S, Morell RJ, Ramesh A, Srisailpathy S, Deshmukh D, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB, Smith RJ, Wilcox ER. Mutations in a novel gene, TMIE, are associated with hearing loss linked to the DFNB6 locus. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. 71(3):632–636.15. Su MC, Yang JJ, Chou MY, Hsin CH, Su CC, Li SY. Expression and localization of Tmie in adult rat cochlea. Histochem Cell Biol. 2008. 130(1):119–126.16. Chung WH, Kim KR, Cho YS, Cho DY, Woo JH, Ryoo ZY, Cho KI, Hong SH. Cochlear pathology of the circling mouse: a new mouse model of DFNB6. Acta Otolaryngol. 2007. 127(3):244–251.17. Op de Beeck K, Van Camp G, Thys S, Cools N, Callebaut I, Vrijens K, Van Nassauw L, Van Tendeloo VF, Timmermans JP, Van Laer L. The DFNA5 gene, responsible for hearing loss and involved in cancer, encodes a novel apoptosis-inducing protein. Eur J Hum Genet. 2011. 19(9):965–973.18. Rifai K, Kirchner GI, Bahr MJ, Cantz T, Rosenau J, Nashan B, Klempnauer JL, Manns MP, Strassburg CP. A new side effect of immunosuppression: high incidence of hearing impairment after liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2006. 12(3):411–415.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Over-expression of myosin7A in cochlear hair cells of circling mice
- Subcellular localization of the transmembrane inner ear (Tmie) protein in a stable Tmie-expressing cell line
- Investigation of Developmental Changes of Convergence Ratios of MNTB-LSO Synapses in Circling Mice
- Strain - Specific Differences in Radiation - Induced Apoptosis in Murine Tissues
- Biological Analysis of a New Spontaneous Mutant Mouse Showing Deafness and Circling Behavior