J Rheum Dis.
2012 Oct;19(5):274-279. 10.4078/jrd.2012.19.5.274.
Guillain-Barre Syndrome, Antiphospholipid Syndrome and Lupus Nephritis as Initial Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. chsuh@ajou.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 1438536
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2012.19.5.274
Abstract
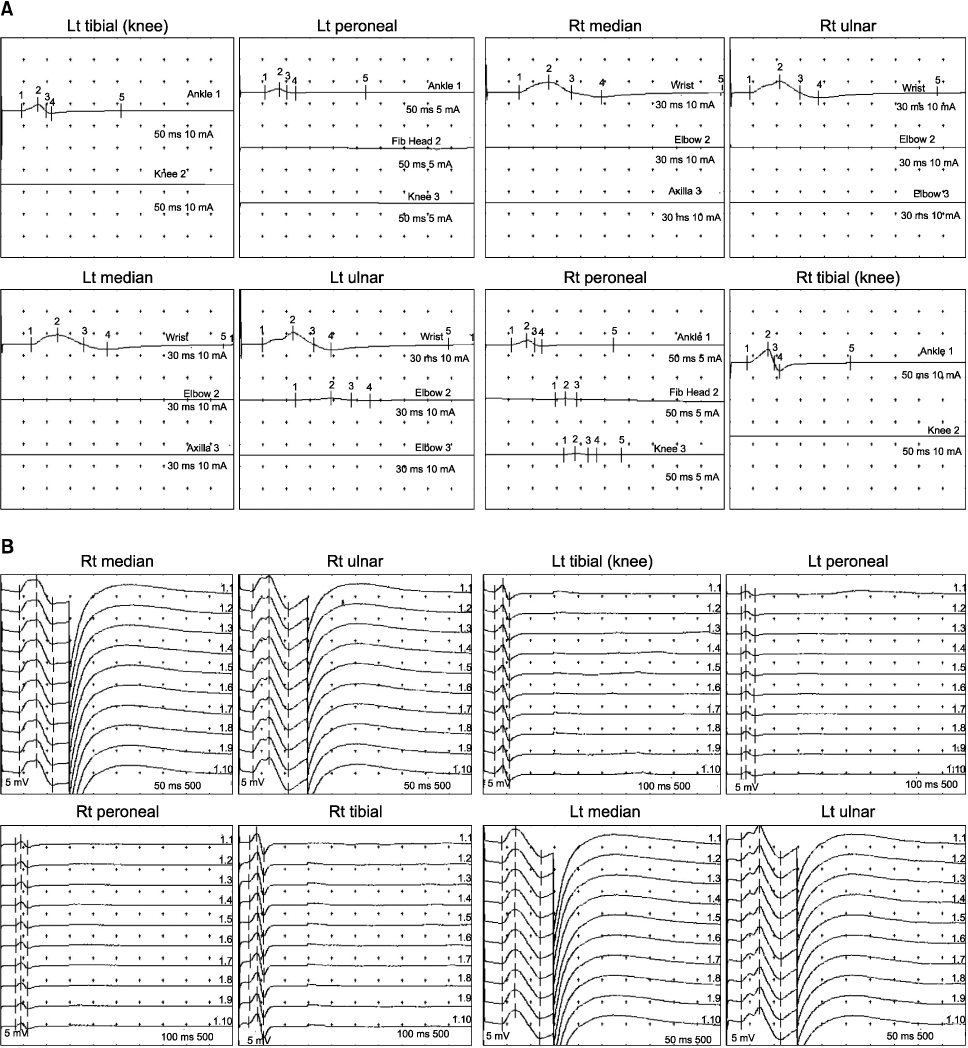
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease with various manifestations, while its autoantibodies and immune reactions involve multiple organs. Neuropsychiatric involvement in SLE is known to be common, however, peripheral neuropathy is relatively rare. Guillain-Barre syndrome is clinically defined as an acute demyelinating peripheral neuropathy causing weakness and numbness in the legs and arms. We describe a case of Guillain-Barre syndrome with antiphospholipid syndrome and lupus nephritis. The patient was admitted with fever and diarrhea. He developed progressive weakness of the upper and lower extremities and dysarthria with characteristic nerve conduction patterns compatible with Guillain-Barre syndrome. He also had proteinuria and gangrene of the hand and toe with antiphospholipid antibody. He received intravenous immunoglobulin and plasmapheresis for progressive neuropathy, intravenous high dose steroid to control activity of SLE, and anticoagulation for antiphospholipid syndrome. Neuropsychiatric manifestation of SLE is related to lupus activity closely, so it is important to control lupus activity.
MeSH Terms
-
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Arm
Autoantibodies
Autoimmune Diseases
Diarrhea
Dysarthria
Fever
Gangrene
Guillain-Barre Syndrome
Hand
Humans
Hypesthesia
Immunoglobulins
Leg
Lower Extremity
Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic
Lupus Nephritis
Neural Conduction
Peripheral Nervous System Diseases
Plasmapheresis
Proteinuria
Toes
Antibodies, Antiphospholipid
Autoantibodies
Immunoglobulins
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Case of Guillain-Barre Syndrome in a Patient of Behçet's Disease
Jihyung Yoo, Nak-Min Kim, Wookyung Sung, Jin-Cheol Myeong, Su-A Yun, Dong-Kyu Lee, Mi-Kyoung Lim, Dong-Hyuk Sheen
J Rheum Dis. 2015;22(4):246-249. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2015.22.4.246.
Reference
-
1. Unterman A, Nolte JE, Boaz M, Abady M, Shoenfeld Y, Zandman-Goddard G. Neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2011. 41:1–11.2. Hughes RA, Cornblath DR. Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet. 2005. 366:1653–1666.3. Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997. 40:1725.4. The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:599–608.5. Sibbitt WL Jr, Sibbitt RR, Brooks WM. Neuroimaging in neuropsychiatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1999. 42:2026–2038.6. Rodrigues CE, Carvalho JF, Shoenfeld Y. Neurological manifestations of antiphospholipid syndrome. Eur J Clin Invest. 2010. 40:350–359.7. Nakos G, Tziakou E, Maneta-Peyret L, Nassis C, Lekka ME. Anti-phospholipid antibodies in serum from patients with Guillain-Barré syndrome. Intensive Care Med. 2005. 31:1401–1408.8. Katzav A, Ben-Ziv T, Chapman J, Blank M, Reichlin M, Shoenfeld Y. Anti-P ribosomal antibodies induce defect in smell capability in a model of CNS -SLE (depression). J Autoimmun. 2008. 31:393–398.9. Eber T, Chapman J, Shoenfeld Y. Anti-ribosomal P-protein and its role in psychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus: myth or reality? Lupus. 2005. 14:571–575.10. Fragoso-Loyo H, Richaud-Patin Y, Orozco-Narváez A, Dávila-Maldonado L, Atisha-Fregoso Y, Llorente L, et al. Interleukin-6 and chemokines in the neuropsychiatric manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2007. 56:1242–1250.11. Pithadia AB, Kakadia N. Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS). Pharmacol Rep. 2010. 62:220–232.12. Bertsias GK, Ioannidis JP, Aringer M, Bollen E, Bombardieri S, Bruce IN, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of systemic lupus erythematosus with neuropsychiatric manifestations: report of a task force of the EULAR standing committee for clinical affairs. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010. 69:2074–2082.13. Kim HS, Lee SC, Hong HI, Han KH, Lee SK, Kim SS. A case of neuropsychiatric lupus presenting as guillainbarre syndrome and cerebral infarction. J Korean Rheum Assoc. 2004. 11:411–416.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Multiple Venous Thrombosis as the First Manifestation of Lupus Nephritis
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus with Chorea as an Initial Manifestation
- A Case of Leg Ulcer with SLE and Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- A Case of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Secondary AntiphospholipidSyndrome Presenting as Livedo Reticularis
- A case of Limited Scleroderma Associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome