Lab Anim Res.
2012 Jun;28(2):99-107. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.99.
Autophagy contributes to retardation of cardiac growth in diabetic rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Science in Interdisciplinary PhD Program, Graduate School of Inje University, Gimhae, Korea. yonghong@inje.ac.kr
- 2National Primate Research Center (NPRC), Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Ochang, Korea.
- 3Cardiovascular & Metabolic Disease Center, College of Biomedical Science & Engineering, Inje University, Gimhae, Korea.
- KMID: 1436703
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.99
Abstract
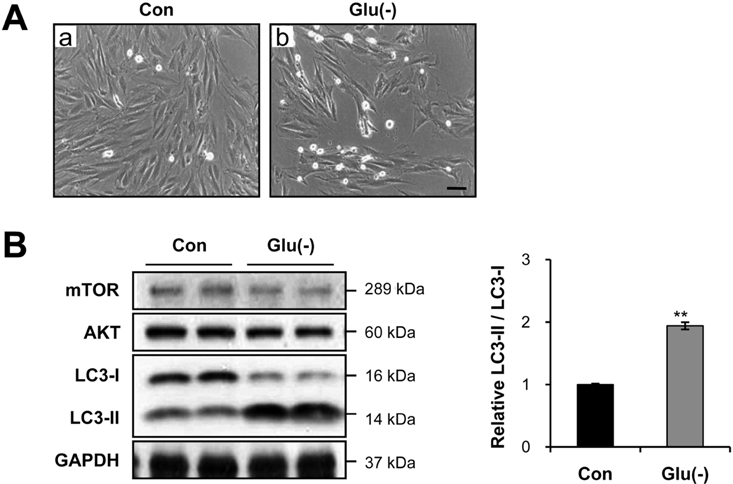
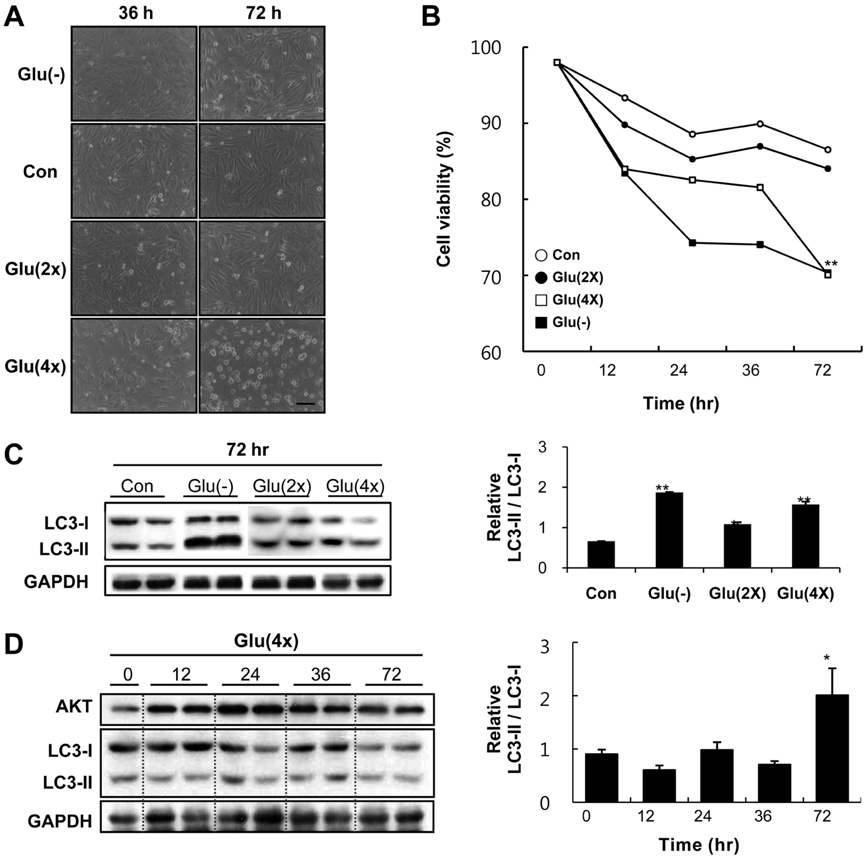
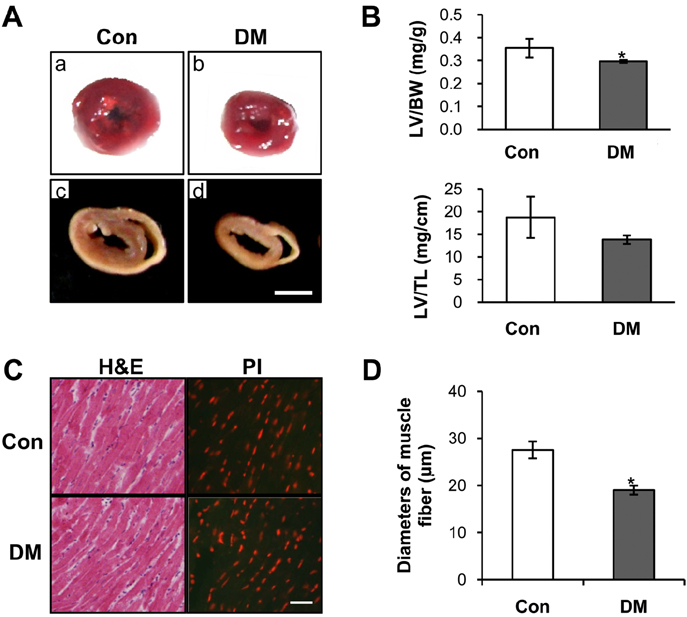
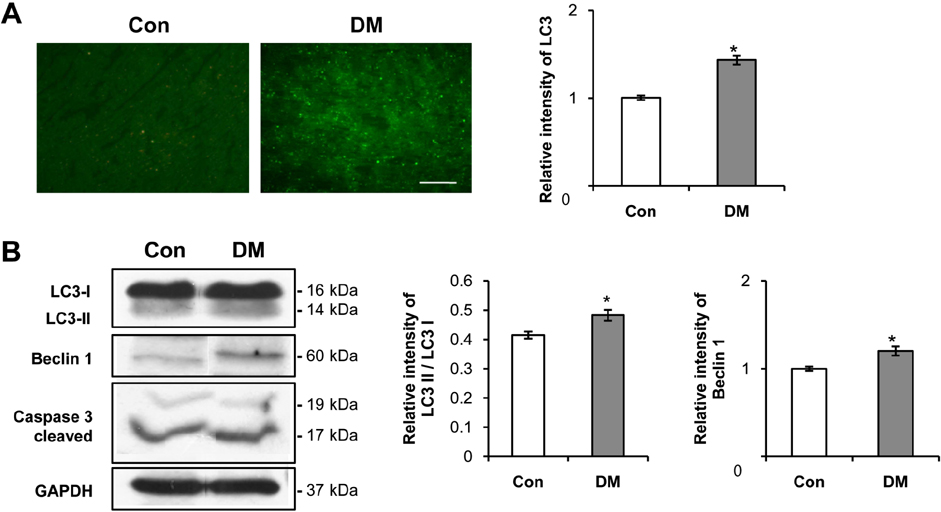
- Diabetes mellitus is a major predictor of heart failure, although the mechanisms by which the disease causes cardiomyopathy are not well understood. The purpose of this study was to determine whether prolonged exposure of cardiomyocytes to high glucose concentrations induces autophagy and contributes to cardiomyopathy. Interestingly, there were no differences in the autophagic activation produced by different glucose concentrations. However, cell viability was decreased by high glucose. In the diabetic rats, we found a higher level of microtubule-associated protein light chain 3 (LC3) expression and a reduction in the size of the left ventricle (LV) (P<0.05) caused by growth retardation, suggesting activated autophagy. Our in vitro findings indicate that hyperglycemic oxidative stress induces autophagy, and our in vivo studies reveal that autophagy is involved in the progression of pathophysiological remodeling of the heart. Taken together, the studies suggest that autophagy may play a role in the pathogenesis of juvenile diabetic cardiomyopathy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Stereological study of the diabetic heart of male rats
Ali Noorafshan, Hajar Khazraei, Hossein Mirkhani, Saied Karbalay-Doust
Lab Anim Res. 2013;29(1):12-18. doi: 10.5625/lar.2013.29.1.12.
Reference
-
1. Trost S, LeWinter M. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Curr Treat Options Cardiovasc Med. 2001. 3(6):481–492.2. Giles TD. The patient with diabetes mellitus and heart failure: atrisk issues. Am J Med. 2003. 115(Suppl 8A):107S–110S.3. Aneja A, Tang WH, Bansilal S, Garcia MJ, Farkouh ME. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: insights into pathogenesis, diagnostic challenges, and therapeutic options. Am J Med. 2008. 121(9):748–757.4. Sowers JR. Johnstone MT, Veves A, editors. Diabetes and hypertension. Contemporary cardiology: Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. 2001. 1st ed. Totowa, N.J.: Humana Press;123–129.5. Rubler S, Dlugash J, Yuceoglu YZ, Kumral T, Branwood AW, Grishman A. New type of cardiomyopathy associated with diabetic glomerulosclerosis. Am J Cardiol. 1972. 30(6):595–602.6. Devereux RB, Roman MJ, Paranicas M, O'Grady MJ, Lee ET, Welty TK, Fabsitz RR, Robbins D, Rhoades ER, Howard BV. Impact of diabetes on cardiac structure and function: the strong heart study. Circulation. 2000. 101(19):2271–2276.7. Singh JP, Larson MG, O'Donnell CJ, Wilson PF, Tsuji H, Lloyd-Jones DM, Levy D. Association of hyperglycemia with reduced heart rate variability (The Framingham Heart Study). Am J Cardiol. 2000. 86(3):309–312.8. Kawasaki D, Kosugi K, Waki H, Yamamoto K, Tsujino T, Masuyama T. Role of activated renin-angiotensin system in myocardial fibrosis and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in diabetic patients--reversal by chronic angiotensin II type 1A receptor blockade. Circ J. 2007. 71(4):524–529.9. Cai L, Kang YJ. Oxidative stress and diabetic cardiomyopathy: a brief review. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2001. 1(3):181–193.10. Depre C, Young ME, Ying J, Ahuja HS, Han Q, Garza N, Davies PJ, Taegtmeyer H. Streptozotocin-induced changes in cardiac gene expression in the absence of severe contractile dysfunction. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2000. 32(6):985–996.11. Pawelczyk T, Sakowicz M, Szczepanska-Konkel M, Angielski S. Decreased expression of adenosine kinase in streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus rats. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2000. 375(1):1–6.12. Swynghedauw B. Molecular mechanisms of myocardial remodeling. Physiol Rev. 1999. 79(1):215–262.13. Feuerstein GZ, Young PR. Apoptosis in cardiac diseases: stress- and mitogen-activated signaling pathways. Cardiovasc Res. 2000. 45(3):560–569.14. Frustaci A, Kajstura J, Chimenti C, Jakoniuk I, Leri A, Maseri A, Nadal-Ginard B, Anversa P. Myocardial cell death in human diabetes. Circ Res. 2000. 87(12):1123–1132.15. Kajstura J, Fiordaliso F, Andreoli AM, Li B, Chimenti S, Medow MS, Limana F, Nadal-Ginard B, Leri A, Anversa P. IGF-1 overexpression inhibits the development of diabetic cardiomyopathy and angiotensin II-mediated oxidative stress. Diabetes. 2001. 50(6):1414–1424.16. Cai L, Li W, Wang G, Guo L, Jiang Y, Kang YJ. Hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis in mouse myocardium: mitochondrial cytochrome C-mediated caspase-3 activation pathway. Diabetes. 2002. 51(6):1938–1948.17. Unger RH. Lipotoxic diseases. Annu Rev Med. 2002. 53:319–336.18. Wang H, Kouri G, Wollheim CB. ER stress and SREBP-1 activation are implicated in beta-cell glucolipotoxicity. J Cell Sci. 2005. 118(Pt 17):3905–3915.19. Nakatani Y, Kaneto H, Kawamori D, Yoshiuchi K, Hatazaki M, Matsuoka TA, Ozawa K, Ogawa S, Hori M, Yamasaki Y, Matsuhisa M. Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in insulin resistance and diabetes. J Biol Chem. 2005. 280(1):847–851.20. Kiffin R, Christian C, Knecht E, Cuervo AM. Activation of chaperone-mediated autophagy during oxidative stress. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. 15(11):4829–4840.21. Levine B, Klionsky DJ. Development by self-digestion: molecular mechanisms and biological functions of autophagy. Dev Cell. 2004. 6(4):463–477.22. Zhu H, Tannous P, Johnstone JL, Kong Y, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Le V, Levine B, Rothermel BA, Hill JA. Cardiac autophagy is a maladaptive response to hemodynamic stress. J Clin Invest. 2007. 117(7):1782–1793.23. Lum JJ, DeBerardinis RJ, Thompson CB. Autophagy in metazoans: cell survival in the land of plenty. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005. 6(6):439–448.24. Yu L, Alva A, Su H, Dutt P, Freundt E, Welsh S, Baehrecke EH, Lenardo MJ. Regulation of an ATG7-beclin 1 program of autophagic cell death by caspase-8. Science. 2004. 304(5676):1500–1502.25. Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB, Tsujimoto Y. Role of Bcl-2 family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 2004. 6(12):1221–1228.26. Mizushima N, Yamamoto A, Matsui M, Yoshimori T, Ohsumi Y. In vivo analysis of autophagy in response to nutrient starvation using transgenic mice expressing a fluorescent autophagosome marker. Mol Biol Cell. 2004. 15(3):1101–1111.27. Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. 2000. 19(21):5720–5728.28. Yu XY, Song YH, Geng YJ, Lin QX, Shan ZX, Lin SG, Li Y. Glucose induces apoptosis of cardiomyocytes via microRNA-1 and IGF-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008. 376(3):548–552.29. Baumgartner-Parzer SM, Wagner L, Pettermann M, Grillari J, Gessl A, Waldhäusl W. High-glucose--triggered apoptosis in cultured endothelial cells. Diabetes. 1995. 44(11):1323–1327.30. Du XL, Sui GZ, Stockklauser-Färber K, Weiss J, Zink S, Schwippert B, Wu QX, Tschöpe D, Rösen P. Introduction of apoptosis by high proinsulin and glucose in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species. Diabetologia. 1998. 41(3):249–256.31. Ho FM, Liu SH, Liau CS, Huang PJ, Lin-Shiau SY. High glucose-induced apoptosis in human endothelial cells is mediated by sequential activations of c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase and caspase-3. Circulation. 2000. 101(22):2618–2624.32. Bornfeldt KE, Arnqvist HJ, Enberg B, Mathews LS, Norstedt G. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I and growth hormone receptor gene expression by diabetes and nutritional state in rat tissues. J Endocrinol. 1989. 122(3):651–656.33. Chiarelli F, Giannini C, Mohn A. Growth, growth factors and diabetes. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004. 151:Suppl 3. U109–U117.34. Teiger E, Than VD, Richard L, Wisnewsky C, Tea BS, Gaboury L, Tremblay J, Schwartz K, Hamet P. Apoptosis in pressure overload-induced heart hypertrophy in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1996. 97(12):2891–2897.35. Kang YJ. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of cardiotoxicity. Environ Health Perspect. 2001. 109:Suppl 1. 27–34.36. Fiordaliso F, Li B, Latini R, Sonnenblick EH, Anversa P, Leri A, Kajstura J. Myocyte death in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats in angiotensin II-dependent. Lab Invest. 2000. 80(4):513–527.37. Ghosh S, Qi D, An D, Pulinilkunnil T, Abrahani A, Kuo KH, Wambolt RB, Allard M, Innis SM, Rodrigues B. Brief episode of STZ-induced hyperglycemia produces cardiac abnormalities in rats fed a diet rich in n-6 PUFA. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2004. 287(6):H2518–H2527.38. Ghosh S, An D, Pulinilkunnil T, Qi D, Lau HC, Abrahani A, Innis SM, Rodrigues B. Role of dietary fatty acids and acute hyperglycemia in modulating cardiac cell death. Nutrition. 2004. 20(10):916–923.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The role of autophagy in the placenta as a regulator of cell death
- Prophylactic effects of swimming exercise on autophagy-induced muscle atrophy in diabetic rats
- Role of Autophagy in Granulocyte-Colony Stimulating Factor Induced Anti-Apoptotic Effects in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids Attenuate Renal Fibrosis and Enhance Autophagy of Renal Tubular Cells in Diabetic Mice Through the HDAC2/ULK1 Axis
- Responses to Growth Hormone Treatment in Children with Short Stature Secondary to Intrauterine Growth Retardation