Lab Anim Res.
2012 Jun;28(2):83-90. 10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.83.
Effects of male silkworm pupa powder on the erectile dysfunction by chronic ethanol consumption in rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Huvet Co. Ltd, Iksan, Korea.
- 2Clinical Trial Center for Functional Foods, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Clinical Trial Center, Chonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea.
- 4Department of Agricultural Biology, National Academy of Agricultural Science, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Pharmacology, School of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 6Center for Animal Resources Development, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea. kimoj@wku.ac.kr
- 7Department of Urology, School of Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea. rain@jbnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1436699
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5625/lar.2012.28.2.83
Abstract
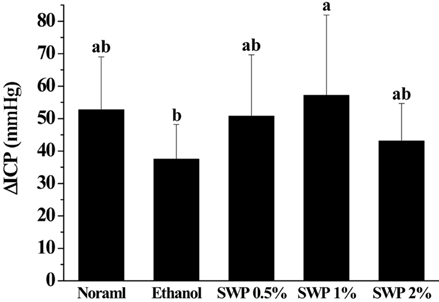
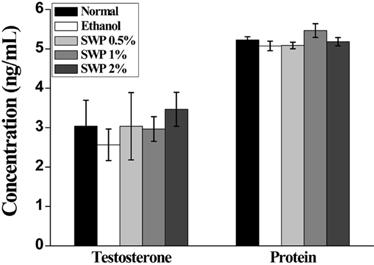
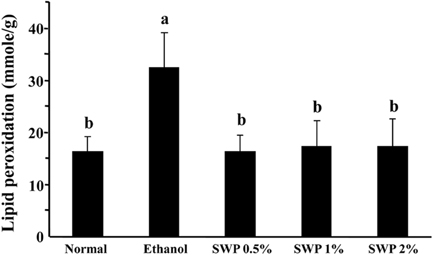
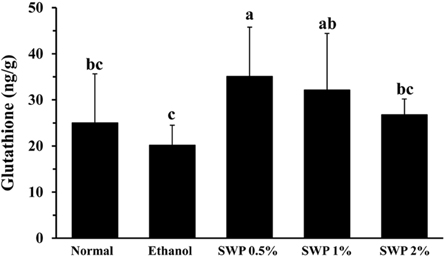
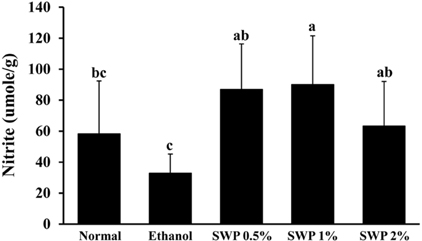
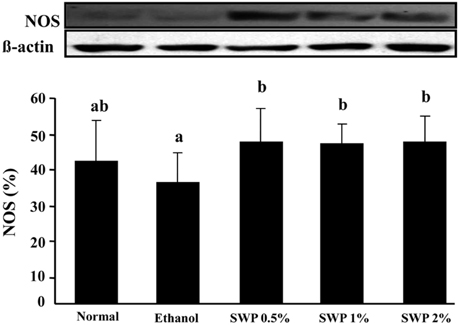
- Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a highly prevalent disorder that affects millions of men worldwide. ED is now considered an early manifestation of atherosclerosis, and consequently, a precursor of systemic vascular disease. This study was designed to investigate the effects of male silkworm pupa powder (SWP) on the levels of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) expression, nitrite, and glutathione (GSH); lipid peroxidation; libido; and erectile response of the corpus cavernosum of the rat penis. We induced ED in the study animals by oral administration of 20% ethanol over 8 weeks. The SWP-treated male rats were divided into 3 groups that were orally administered 200, 400, and 800 mg/kg. The libido of the SWP-administered male rats was higher than that of the ethanol control group. In addition, the erectile response of the corpus cavernosum was restored in males on SWP administration, to a level similar to that of the normal group without ED. The testosterone concentration did not increase significantly. The lipid peroxidation in the corpus cavernosum of the male rats administered SWP decreased significantly. In contrast, compared to the ethanol group, SWP-administered male rats showed increased GSH levels in the corpus cavernosum. The level of nitrite and NOS expression in the corpus cavernosum of SWP-administered male rats increased significantly. These results indicated that SWP effectively restored ethanol-induced ED in male rats.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Status and Clinical Studies of Oriental Herbs in Sexual Medicine in Korea
Yu Seob Shin, Chen Zhao, Li Tao Zhang, Jong Kwan Park
World J Mens Health. 2015;33(2):62-72. doi: 10.5534/wjmh.2015.33.2.62.
Reference
-
1. Maas R, Schwedhelm E, Albsmeier J, Boger RH. The pathophysiology of erectile dysfunction related to endothelial dysfunction and mediators of vascular function. Vasc Med. 2002. 7(3):213–225.2. Benet AE, Melman A. The epidemiology of erectile dysfunction. Urol Clin North Am. 1995. 22(4):699–709.3. Cheng JY, Ng EM, Chen RY, Ko JS. Alcohol consumption and erectile dysfunction: meta-analysis of population-based studies. Int J Impot Res. 2007. 19(4):343–352.4. Christ GJ. The penis as a vascular organ. The importance of corporal smooth muscle tone in the control of erection. Urol Clin North Am. 1995. 22(4):727–745.5. Hedlund H, Andersson KE. Contraction and relaxation induced by some prostanoids in isolated human penile erectile tissue and cavernous artery. J Urol. 1985. 134(6):1245–1250.6. Saenz de Tejada I, Blanco R, Goldstein I, Azadzoi K, de las Morenas A, Krane RJ, Cohen RA. Cholinergic neurotransmission in human corpus cavernosum. I. Responses of isolated tissue. Am J Physiol. 1988. 254(3):H459–H467.7. Saenz de Tejada I, Goldstein I, Azadzoi K, Krane RJ, Cohen RA. Impaired neurogenic and endothelium-mediated relaxation of penile smooth muscle from diabetic men with impotence. N Engl J Med. 1989. 320(16):1025–1030.8. Furchgott RF. Introduction to EDRF research. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993. 22(Suppl 7):S1–S2.9. Ignarro LJ, Buga GM, Wood KS, Byrns RE, Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1987. 84(24):9265–9269.10. Forstermann U, Munzel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vascular disease: from marvel to menace. Circulation. 2006. 113(13):1708–1714.11. Garg UC, Hassid A. Nitric oxide-generating vasodilators and 8-bromo-cyclic guanosine monophosphate inhibit mitogenesis and proliferation of cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1989. 83(5):1774–1777.12. Ross R. Atherosclerosis--an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999. 340(2):115–126.13. Palmer RM, Ashton DS, Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988. 333(6174):664–666.14. Rajfer J, Aronson WJ, Bush PA, Dorey FJ, Ignarro LJ. Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavernosum in response to nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission. N Engl J Med. 1992. 326(2):90–94.15. Bredt DS, Ferris CD, Snyder SH. Nitric oxide synthase regulatory sites. Phosphorylation by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C, and calcium/calmodulin protein kinase; identification of flavin and calmodulin binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1992. 267(16):10976–10981.16. Singh KC, Suryanarayna N. Eri pupae: A popular cuisine too. Indian Silk. 2003. 41:57–58.17. Zhou J, Han DX. Proximate, amino acid and mineral composition of pupae of the silkworm Antheraea pernyi in China. J Food Compos Anal. 2006. 19:850–853.18. Usub T, Lertsatitthanakorn C, Poomsa-ad N, Wiset L, Yang LF, Siriamornpun S. Experimental performance of a solar tunnel dryer for drying silkworm pupae. Biosyst Eng. 2008. 101:209–216.19. Wei ZJ, Liao AM, Zhang HX, Liu J, Jiang ST. Optimization of supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of silkworm pupal oil applying the response surface methodology. Bioresour Technol. 2009. 100:4214–4219.20. Ryu KS, Ahn MY, Lee HS, Kim IK, Kim JW, Kim SH, Choi JH. The tonic effect of the extract from male silkworm (Bombyx mori L.) pupae on rats. Int J Indust Entomol. 2002. 5(1):123–126.21. Tirapelli CR, Fukada SY, Yogi A, Chignalia AZ, Tostes RC, Bonaventura D, Lanchote VL, Cunha FQ, de Oliveira AM. Gender-specific vascular effects elicited by chronic ethanol consumption in rats: a role for inducible nitric oxide synthase. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. 153(3):468–479.22. Shinoda M, Latour MG, Lavoie JM. Effects of physical training on body composition and organ weights in ovariectomized and hyperestrogenic rats. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2002. 26(3):335–343.23. Fung MM, Bettencourt R, Barrett-Connor E. Heart disease risk factors predict erectile dysfunction 25 years later: the Rancho Bernardo Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004. 43(8):1405–1411.24. Luc TF. Erectile dysfunction. N Engl J Med. 2000. 342(24):1802–1813.25. Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975. 44:147–159.26. Kono Y, Fridovich I. Superoxide radical inhibits catalase. J Biol Chem. 1982. 257(10):5751–5754.27. Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM. Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem J. 1984. 219(1):1–14.28. Bendich A, D'Apolito P, Gabriel E, Machlin LJ. Interaction of dietary vitamin C and vitamin E on guinea pig immune responses to mitogens. J Nutr. 1984. 114(9):1588–1593.29. Ross D. Glutathione, free radicals and chemotherapeutic agents. Mechanisms of free-radical induced toxicity and glutathione-dependent protection. Pharmacol Ther. 1988. 37(2):231–249.30. Hornsby PJ, Crivello JF. The role of lipid peroxidation and biological antioxidants in the function of the adrenal cortex. Part 2. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983. 30(2):123–147.31. Furchegott RF. Role of endothelium in response of vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983. 53(5):557–573.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Antioxidant Effects and Improvement of Lipid Metabolism of Mulberry fruit, Mulberry Leaves and Silkworm Powder with Different Mixing Ratios in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Allergenic Characterization of 27-kDa Glycoprotein, a Novel Heat Stable Allergen, from the Pupa of Silkworm, Bombyx mori
- Letter to the Editor: Effects of Omega-3 Fatty Acids on Erectile Dysfunction in a Rat Model of Atherosclerosis-induced Chronic Pelvic Ischemia
- Effects of Chronic Treatment with a Type 5 Phosphodiesterase Inhibitor on Erectile Function in Diabetic Rats
- Evaluation of General Toxicity and Genotoxicity of the Silkworm Extract Powder