Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
2013 Feb;17(1):57-64. 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.1.57.
Acute Hypoxia Activates an ENaC-like Channel in Rat Pheochromocytoma (PC12) Cells
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Institute of Health Sciences and Medical Research Center for Neural Dysfunction, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju 660-751, Korea. hong149@gnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1432764
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.1.57
Abstract
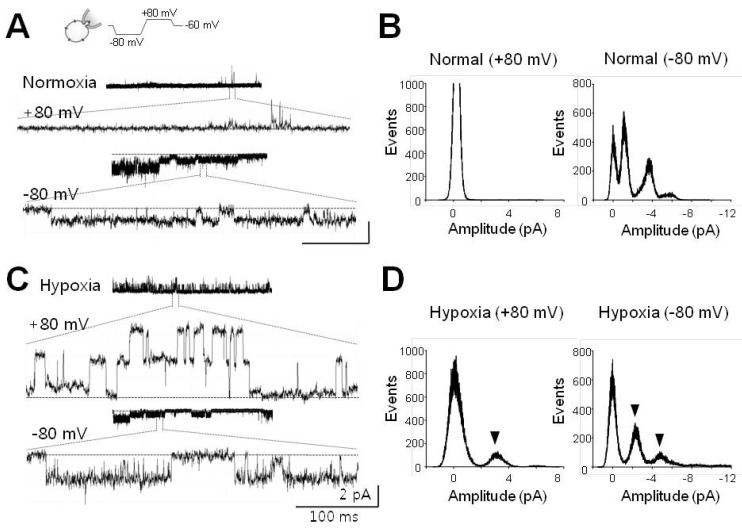
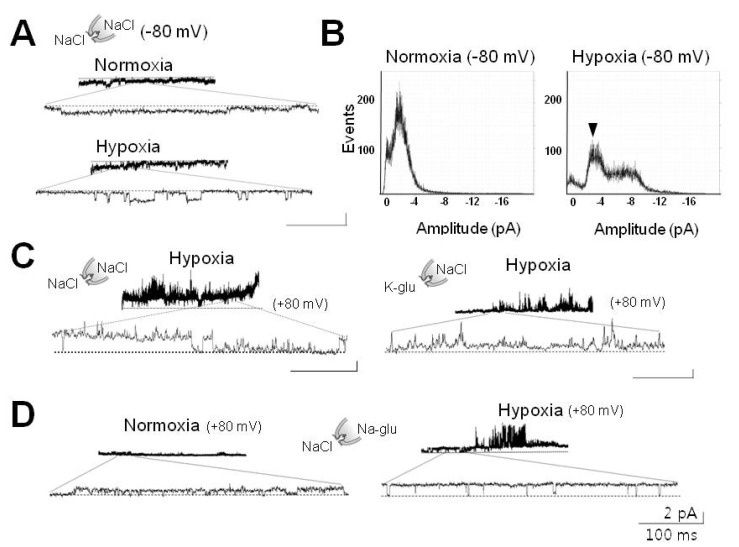
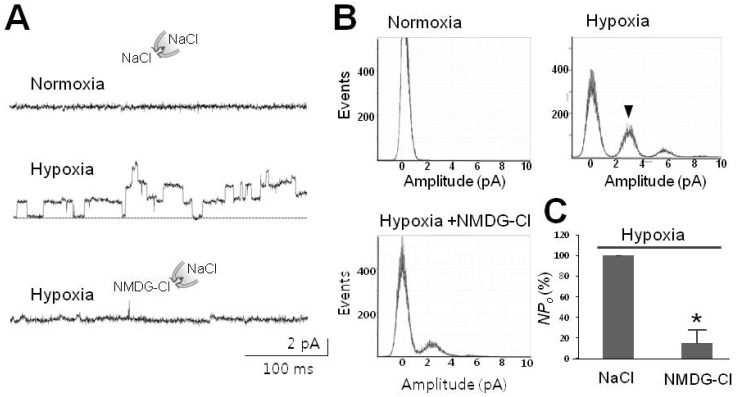
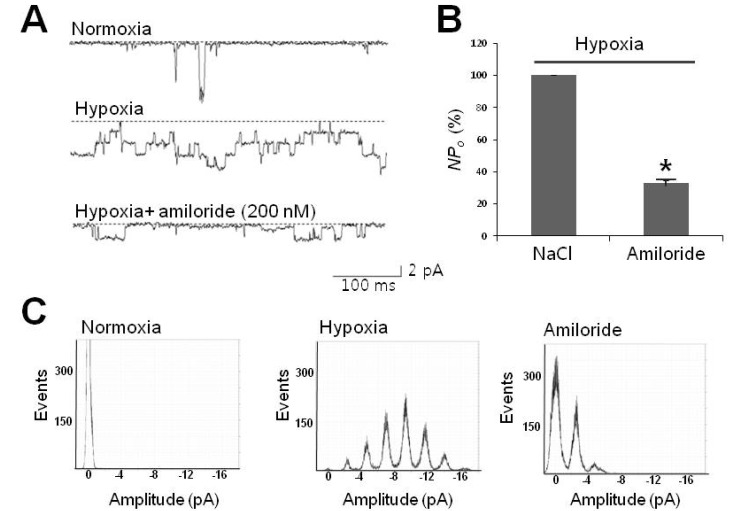
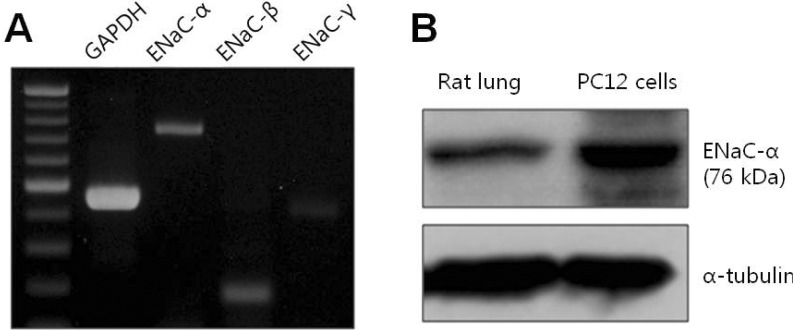
- Cells can resist and even recover from stress induced by acute hypoxia, whereas chronic hypoxia often leads to irreversible damage and eventually death. Although little is known about the response(s) to acute hypoxia in neuronal cells, alterations in ion channel activity could be preferential. This study aimed to elucidate which channel type is involved in the response to acute hypoxia in rat pheochromocytomal (PC12) cells as a neuronal cell model. Using perfusing solution saturated with 95% N2 and 5% CO2, induction of cell hypoxia was confirmed based on increased intracellular Ca2+ with diminished oxygen content in the perfusate. During acute hypoxia, one channel type with a conductance of about 30 pS (2.5 pA at -80 mV) was activated within the first 2~3 min following onset of hypoxia and was long-lived for more than 300 ms with high open probability (Po, up to 0.8). This channel was permeable to Na+ ions, but not to K+, Ca+, and Cl- ions, and was sensitively blocked by amiloride (200 nM). These characteristics and behaviors were quite similar to those of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC). RT-PCR and Western blot analyses confirmed that ENaC channel was endogenously expressed in PC12 cells. Taken together, a 30-pS ENaC-like channel was activated in response to acute hypoxia in PC12 cells. This is the first evidence of an acute hypoxia-activated Na+ channel that can contribute to depolarization of the cell.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cross JL, Meloni BP, Bakker AJ, Lee S, Knuckey NW. Modes of neuronal calcium entry and homeostasis following cerebral ischemia. Stroke Res Treat. 2010; 2010:316862. PMID: 21052549.
Article2. Fung ML. Role of voltage-gated Na+ channels in hypoxia-induced neuronal injuries. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2000; 27:569–574. PMID: 10901384.3. Ratan RR, Siddiq A, Smirnova N, Karpisheva K, Haskew-Layton R, McConoughey S, Langley B, Estevez A, Huerta PT, Volpe B, Roy S, Sen CK, Gazaryan I, Cho S, Fink M, LaManna J. Harnessing hypoxic adaptation to prevent, treat, and repair stroke. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007; 85:1331–1338. PMID: 18043901.
Article4. Conrad PW, Conforti L, Kobayashi S, Beitner-Johnson D, Rust RT, Yuan Y, Kim HW, Kim RH, Seta K, Millhorn DE. The molecular basis of O2-sensing and hypoxia tolerance in pheochromocytoma cells. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol. 2001; 128:187–204. PMID: 11207433.5. Conforti L, Millhorn DE. Selective inhibition of a slow-inactivating voltage-dependent K+ channel in rat PC12 cells by hypoxia. J Physiol. 1997; 502:293–305. PMID: 9263911.6. Zhu WH, Conforti L, Czyzyk-Krzeska MF, Millhorn DE. Membrane depolarization in PC-12 cells during hypoxia is regulated by an O2-sensitive K+ current. Am J Physiol. 1996; 271:C658–C665. PMID: 8770007.7. Conforti L, Bodi I, Nisbet JW, Millhorn DE. O2-sensitive K+ channels: role of the Kv1.2 -subunit in mediating the hypoxic response. J Physiol. 2000; 524:783–793. PMID: 10790158.8. Kim D. K+ channels in O2 sensing and postnatal development of carotid body glomus cell response to hypoxia. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2013; 185:44–56. PMID: 22801091.9. López-López J, González C, Ureña J, López-Barneo J. Low pO2 selectively inhibits K channel activity in chemoreceptor cells of the mammalian carotid body. J Gen Physiol. 1989; 93:1001–1015. PMID: 2738574.
Article10. López-López JR, González C, Pérez-García MT. Properties of ionic currents from isolated adult rat carotid body chemoreceptor cells: effect of hypoxia. J Physiol. 1997; 499:429–441. PMID: 9080372.
Article11. Ji HL, Benos DJ. Degenerin sites mediate proton activation of deltabetagamma-epithelial sodium channel. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:26939–26947. PMID: 15084585.12. Wesch D, Miranda P, Afonso-Oramas D, Althaus M, Castro-Hernández J, Dominguez J, Morty RE, Clauss W, González-Hernández T, Alvarez de la Rosa D, Giraldez T. The neuronalneuronal-specific SGK1.1 kinase regulates δ-epithelial Na+ channel independently of PY motifs and couples it to phospholipase C signaling. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2010; 299:C779–C790. PMID: 20631247.13. Seta KA, Spicer Z, Yuan Y, Lu G, Millhorn DE. Responding to hypoxia: lessons from a model cell line. Sci STKE. 2002; 2002:re11. PMID: 12189251.
Article14. Abe E, Fujiki M, Nagai Y, Shiqi K, Kubo T, Ishii K, Abe T, Kobayashi H. The phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase/Akt pathway mediates geranylgeranylacetone-induced neuroprotection against cerebral infarction in rats. Brain Res. 2010; 1330:151–157. PMID: 20206146.
Article15. Tong Q, Gamper N, Medina JL, Shapiro MS, Stockand JD. Direct activation of the epithelial Na+ channel by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate and phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate produced by phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:22654–22663. PMID: 15028718.16. Chen Y, Shi G, Xia W, Kong C, Zhao S, Gaw AF, Chen EY, Yang GP, Giaccia AJ, Le QT, Koong AC. Identification of hypoxia-regulated proteins in head and neck cancer by proteomic and tissue array profiling. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:7302–7310. PMID: 15492250.
Article17. Lebowitz J, Edinger RS, An B, Perry CJ, Onate S, Kleyman TR, Johnson JP. Ikappab kinase-beta (ikkbeta) modulation of epithelial sodium channel activity. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:41985–41990. PMID: 15292220.18. Choi SW, Ahn JS, Kim HK, Kim N, Choi TH, Park SW, Ko EA, Park WS, Song DK, Han J. Increased expression of atp-sensitive K+ channels improves the right ventricular tolerance to hypoxia in rabbit hearts. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011; 15:189–194. PMID: 21994476.
Article19. Wood JN, Boorman JP, Okuse K, Baker MD. Voltage-gated sodium channels and pain pathways. J Neurobiol. 2004; 61:55–71. PMID: 15362153.
Article20. Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG. International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol Rev. 2005; 57:397–409. PMID: 16382098.
Article21. Kellenberger S, Schild L. Epithelial sodium channel/degenerin family of ion channels: a variety of functions for a shared structure. Physiol Rev. 2002; 82:735–767. PMID: 12087134.
Article22. Hammarström AK, Gage PW. Hypoxia and persistent sodium current. Eur Biophys J. 2002; 31:323–330. PMID: 12202908.
Article23. Waldmann R, Champigny G, Bassilana F, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M. A proton-gated cation channel involved in acid-sensing. Nature. 1997; 386:173–177. PMID: 9062189.
Article24. Alexander SPH, Mathie A, Peters JA. Guide to receptors and Channels (GRAC), 5th edition. Br J Pharmacol. 2011; 164(Suppl 1):S1–S324. PMID: 22040146.
Article25. Ohbuchi T, Sato K, Suzuki H, Okada Y, Dayanithi G, Murphy D, Ueta Y. Acid-sensing ion channels in rat hypothalamic vasopressin neurons of the supraoptic nucleus. J Physiol. 2010; 588:2147–2162. PMID: 20442265.
Article26. Chu XP, Miesch J, Johnson M, Root L, Zhu XM, Chen D, Simon RP, Xiong ZG. Proton-gated channels in PC12 cells. J Neurophysiol. 2002; 87:2555–2561. PMID: 11976391.
Article27. Garty H, Palmer LG. Epithelial sodium channels: function, structure, and regulation. . Physiol Rev. 1997; 77:359–396. PMID: 9114818.
Article28. Kellenberger S, Hoffmann-Pochon N, Gautschi I, Schneeberger E, Schild L. On the molecular basis of ion permeation in the epithelial Na+ channel. J Gen Physiol. 1999; 114:13–30. PMID: 10398689.29. Anantharam A, Palmer LG. Determination of epithelial Na+ channel subunit stoichiometry from single-channel conductances. J Gen Physiol. 2007; 130:55–70. PMID: 17562820.30. Ismailov II, Berdiev BK, Bradford AL, Awayda MS, Fuller CM, Benos DJ. Associated proteins and renal epithelial Na+ channel function. J Membr Biol. 1996; 149:123–132. PMID: 8834119.31. Kelly O, Lin C, Ramkumar M, Saxena NC, Kleyman TR, Eaton DC. Characterization of an amiloride binding region in the alpha-subunit of ENaC. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2003; 285:F1279–F1290. PMID: 12928313.32. Ma HP, Al-Khalili O, Ramosevac S, Saxena S, Liang YY, Warnock DG, Eaton DC. Steroids and exogenous γ-ENaC subunit modulate cation channels formed by α-ENaC in human B lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 2004; 279:33206–33212. PMID: 15187080.
Article33. Ma HP, Chou CF, Wei SP, Eaton DC. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel by phosphatidylinositides: experiments, implications, and speculations. Pflugers Arch. 2007; 455:169–180. PMID: 17605040.
Article34. Yamashima T, Saido TC, Takita M, Miyazawa A, Yamano J, Miyakawa A, Nishijyo H, Yamashita J, Kawashima S, Ono T, Yoshioka T. Transient brain ischaemia provokes Ca2+, PIP2 and calpain responses prior to delayed neuronal death in monkeys. Eur J Neurosci. 1996; 8:1932–1944. PMID: 8921284.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effects of Calcium Antagonists on the PC12 Cell Damage Induced by Hypoxia
- An Effect of Testesterone on the Proliferation of Artificially Induced Senescent PC12 Pheochromocytoma Cells
- p190RhoGAP and Rap-dependent RhoGAP (ARAP3) inactivate RhoA in response to nerve growth factor leading to neurite outgrowth from PC12 cells
- Neurotrophic and Neuritogenic Effects of Water Extracts of Rhizoma of Coptis chinensis Franch in PC12 Cells
- Subcellular Distribution of Microtubule in Artificially Induced Senescent PC12 Cells