Korean J Radiol.
2012 Dec;13(6):674-683. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.674.
Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Hypointensity of the Pulvinar Nucleus of Patients with Alzheimer Disease: Its Possible Association with Iron Accumulation as Evidenced by the T2* Map
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul 143-792, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurology, Hanyang University Medical Center, Hanyang University School of Medicine, Seoul 133-791, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul 143-792, Korea. alzdoc@kuh.ac.kr
- 4Center for Geriatric Neuroscience Research, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul 143-792, Korea.
- KMID: 1397497
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.6.674
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
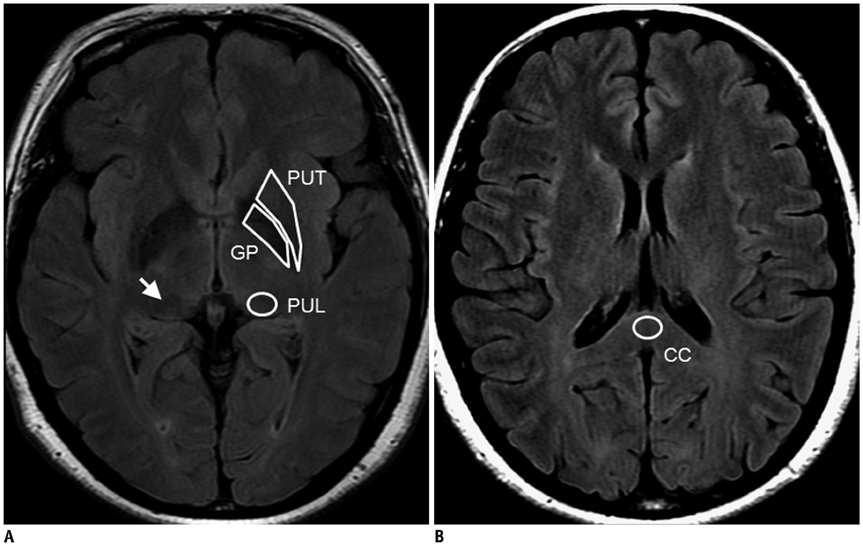
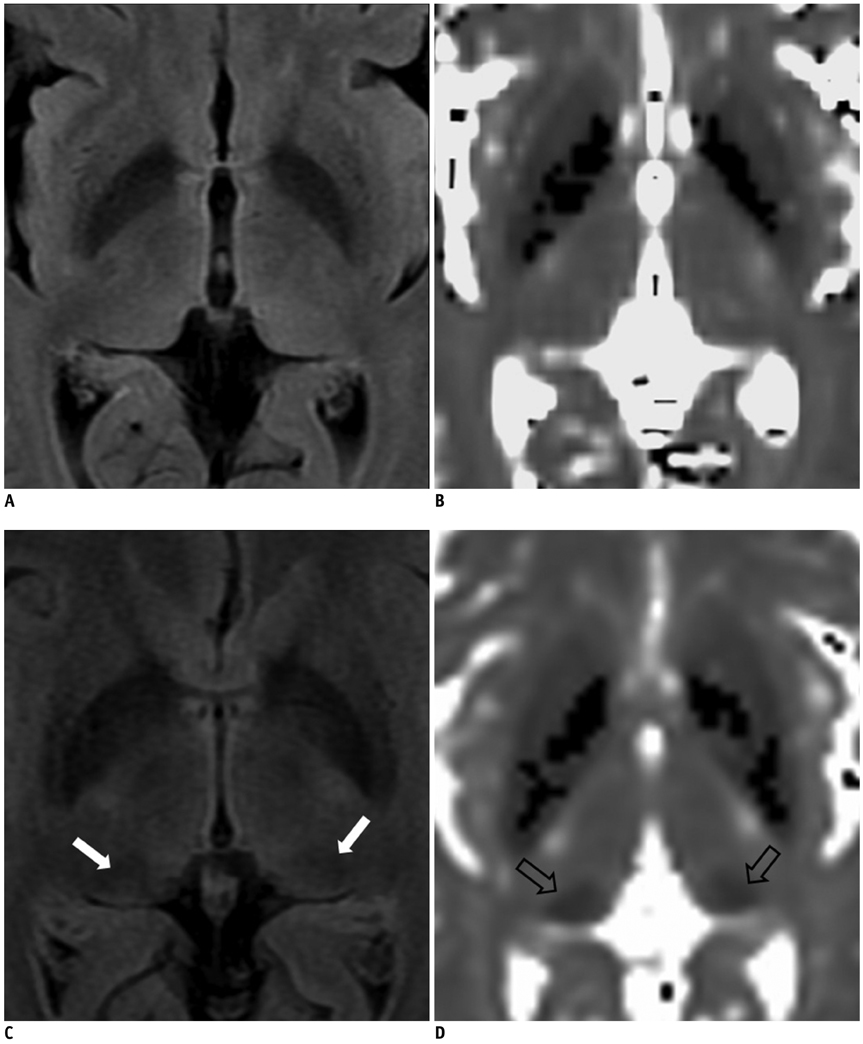
We hypothesized that prominent pulvinar hypointensity in brain MRI represents the disease process due to iron accumulation in Alzheimer disease (AD). We aimed to determine whether or not the pulvinar signal intensity (SI) on the fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) sequences at 3.0T MRI differs between AD patients and normal subjects, and also whether the pulvinar SI is correlated with the T2* map, an imaging marker for tissue iron, and a cognitive scale.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Twenty one consecutive patients with AD and 21 age-matched control subjects were prospectively included in this study. The pulvinar SI was assessed on the FLAIR image. We measured the relative SI ratio of the pulvinar to the corpus callosum. The T2* values were calculated from the T2* relaxometry map. The differences between the two groups were analyzed, by using a Student t test. The correlation between the measurements was assessed by the Pearson's correlation test.
RESULTS
As compared to the normal white matter, the FLAIR signal intensity of the pulvinar nucleus was significantly more hypointense in the AD patients than in the control subjects (p < 0.01). The pulvinar T2* was shorter in the AD patients than in the control subjects (51.5 +/- 4.95 ms vs. 56.5 +/- 5.49 ms, respectively, p = 0.003). The pulvinar SI ratio was strongly correlated with the pulvinar T2* (r = 0.745, p < 0.001). When controlling for age, only the pulvinar-to-CC SI ratio was positively correlated with that of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) score (r = 0.303, p < 0.050). Conversely, the pulvinar T2* was not correlated with the MMSE score (r = 0.277, p = 0.080).
CONCLUSION
The FLAIR hypointensity of the pulvinar nucleus represents an abnormal iron accumulation in AD and may be used as an adjunctive finding for evaluating AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science. 2002. 297:353–356.2. Zecca L, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Connor JR, Crichton RR. Iron, brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004. 5:863–873.3. Dhenain M, El Tannir El Tayara N, Wu TD, Guégan M, Volk A, Quintana C, et al. Characterization of in vivo MRI detectable thalamic amyloid plaques from APP/PS1 mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2009. 30:41–53.4. Braak H, Braak E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991. 82:239–259.5. Kuljis RO. Lesions in the pulvinar in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1994. 53:202–211.6. Leuba G, Saini K. Pathology of subcortical visual centres in relation to cortical degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 1995. 21:410–422.7. Rizzo M, Anderson SW, Dawson J, Myers R, Ball K. Visual attention impairments in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 2000. 54:1954–1959.8. Kaas JH, Lyon DC. Pulvinar contributions to the dorsal and ventral streams of visual processing in primates. Brain Res Rev. 2007. 55:285–296.9. Snow JC, Allen HA, Rafal RD, Humphreys GW. Impaired attentional selection following lesions to human pulvinar: evidence for homology between human and monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. 106:4054–4059.10. Zarei M, Patenaude B, Damoiseaux J, Morgese C, Smith S, Matthews PM, et al. Combining shape and connectivity analysis: an MRI study of thalamic degeneration in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimage. 2010. 49:1–8.11. Willinek WA, Kuhl CK. 3.0 T neuroimaging: technical considerations and clinical applications. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2006. 16:217–228. ix12. Sohn CH, Sevick RJ, Frayne R, Chang HW, Kim SP, Kim DK. Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) imaging of the normal brain: comparisons between under the conditions of 3.0 Tesla and 1.5 Tesla. Korean J Radiol. 2010. 11:19–24.13. Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Thomas B, Shroff MM, Haacke EM. Principles, techniques, and applications of T2*-based MR imaging and its special applications. Radiographics. 2009. 29:1433–1449.14. Allkemper T, Schwindt W, Maintz D, Heindel W, Tombach B. Sensitivity of T2-weighted FSE sequences towards physiological iron depositions in normal brains at 1.5 and 3.0 T. Eur Radiol. 2004. 14:1000–1004.15. Aquino D, Bizzi A, Grisoli M, Garavaglia B, Bruzzone MG, Nardocci N, et al. Age-related iron deposition in the basal ganglia: quantitative analysis in healthy subjects. Radiology. 2009. 252:165–172.16. Siemonsen S, Finsterbusch J, Matschke J, Lorenzen A, Ding XQ, Fiehler J. Age-dependent normal values of T2* and T2' in brain parenchyma. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 29:950–995.17. McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984. 34:939–944.18. Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975. 12:189–198.19. Morris JC. The Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR): current version and scoring rules. Neurology. 1993. 43:2412–2414.20. Péran P, Cherubini A, Luccichenti G, Hagberg G, Démonet JF, Rascol O, et al. Volume and iron content in basal ganglia and thalamus. Hum Brain Mapp. 2009. 30:2667–2675.21. Allkemper T, Tombach B, Schwindt W, Kugel H, Schilling M, Debus O, et al. Acute and subacute intracerebral hemorrhages: comparison of MR imaging at 1.5 and 3.0 T--initial experience. Radiology. 2004. 232:874–881.22. Karaarslan E, Arslan A. Perirolandic cortex of the normal brain: low signal intensity on turbo FLAIR MR images. Radiology. 2003. 227:538–541.23. Bakshi R, Benedict RH, Bermel RA, Caruthers SD, Puli SR, Tjoa CW, et al. T2 hypointensity in the deep gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis: a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol. 2002. 59:62–68.24. Milton WJ, Atlas SW, Lexa FJ, Mozley PD, Gur RE. Deep gray matter hypointensity patterns with aging in healthy adults: MR imaging at 1.5 T. Radiology. 1991. 181:715–719.25. Drayer BP, Olanow W, Burger P, Johnson GA, Herfkens R, Riederer S. Parkinson plus syndrome: diagnosis using high field MR imaging of brain iron. Radiology. 1986. 159:493–498.26. Bowen BC, Pattany PM, Bradley WG, Murdoch JB, Rotta F, Younis AA, et al. MR imaging and localized proton spectroscopy of the precentral gyrus in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000. 21:647–658.27. Cheung G, Gawel MJ, Cooper PW, Farb RI, Ang LC, Gawal MJ. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: correlation of clinical and MR imaging findings. Radiology. 1995. 194:263–270.28. Harder SL, Hopp KM, Ward H, Neglio H, Gitlin J, Kido D. Mineralization of the deep gray matter with age: a retrospective review with susceptibility-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 29:176–183.29. Baleydier C, Mauguiere F. Anatomical evidence for medial pulvinar connections with the posterior cingulate cortex, the retrosplenial area, and the posterior parahippocampal gyrus in monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1985. 232:219–228.30. Carrera E, Bogousslavsky J. The thalamus and behavior: effects of anatomically distinct strokes. Neurology. 2006. 66:1817–1823.31. Yeterian EH, Pandya DN. Corticothalamic connections of the posterior parietal cortex in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1985. 237:408–426.32. Schmahmann JD, Pandya DN. Anatomical investigation of projections from thalamus to posterior parietal cortex in the rhesus monkey: a WGA-HRP and fluorescent tracer study. J Comp Neurol. 1990. 295:299–326.33. Leh SE, Chakravarty MM, Ptito A. The connectivity of the human pulvinar: a diffusion tensor imaging tractography study. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2008. 2008:789539.34. Casanova C, Freeman RD, Nordmann JP. Monocular and binocular response properties of cells in the striate-recipient zone of the cat's lateral posterior-pulvinar complex. J Neurophysiol. 1989. 62:544–557.35. Casanova C, Merabet L, Desautels A, Minville K. Higher-order motion processing in the pulvinar. Prog Brain Res. 2001. 134:71–82.36. Villeneuve MY, Kupers R, Gjedde A, Ptito M, Casanova C. Pattern-motion selectivity in the human pulvinar. Neuroimage. 2005. 28:474–480.37. Johnson MD, Ojemann GA. The role of the human thalamus in language and memory: evidence from electrophysiological studies. Brain Cogn. 2000. 42:218–230.38. Braak H, Braak E. Alzheimer's disease affects limbic nuclei of the thalamus. Acta Neuropathol. 1991. 81:261–268.39. Ogren MP, Mateer CA, Wyler AR. Alterations in visually related eye movements following left pulvinar damage in man. Neuropsychologia. 1984. 22:187–196.40. Petersen SE, Robinson DL, Keys W. Pulvinar nuclei of the behaving rhesus monkey: visual responses and their modulation. J Neurophysiol. 1985. 54:867–886.41. Robinson DL, Petersen SE. The pulvinar and visual salience. Trends Neurosci. 1992. 15:127–132.42. Bartzokis G. Age-related myelin breakdown: a developmental model of cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2004. 25:5–18. author reply 49-62.43. Hallgren B, Sourander P. The effect of age on the non-haemin iron in the human brain. J Neurochem. 1958. 3:41–51.44. Dobson J. Nanoscale biogenic iron oxides and neurodegenerative disease. FEBS Lett. 2001. 496:1–5.45. Haacke EM, Cheng NY, House MJ, Liu Q, Neelavalli J, Ogg RJ, et al. Imaging iron stores in the brain using magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 2005. 23:1–25.46. Ge Y, Jensen JH, Lu H, Helpern JA, Miles L, Inglese M, et al. Quantitative assessment of iron accumulation in the deep gray matter of multiple sclerosis by magnetic field correlation imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. 28:1639–1644.47. McNeill A, Birchall D, Hayflick SJ, Gregory A, Schenk JF, Zimmerman EA, et al. T2* and FSE MRI distinguishes four subtypes of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Neurology. 2008. 70:1614–1619.48. Zhu WZ, Zhong WD, Wang W, Zhan CJ, Wang CY, Qi JP, et al. Quantitative MR phase-corrected imaging to investigate increased brain iron deposition of patients with Alzheimer disease. Radiology. 2009. 253:497–504.49. Drayer B, Burger P, Hurwitz B, Dawson D, Cain J. Reduced signal intensity on MR images of thalamus and putamen in multiple sclerosis: increased iron content? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987. 149:357–363.50. Cross PA, Atlas SW, Grossman RI. MR evaluation of brain iron in children with cerebral infarction. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1990. 11:341–348.51. Grisoli M, Piperno A, Chiapparini L, Mariani R, Savoiardo M. MR imaging of cerebral cortical involvement in aceruloplasminemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:657–661.52. Brar S, Henderson D, Schenck J, Zimmerman EA. Iron accumulation in the substantia nigra of patients with Alzheimer disease and parkinsonism. Arch Neurol. 2009. 66:371–374.53. Braakman N, Matysik J, van Duinen SG, Verbeek F, Schliebs R, de Groot HJ, et al. Longitudinal assessment of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid plaque development in transgenic mice monitored by in vivo magnetic resonance microimaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006. 24:530–536.54. Jack CR Jr, Garwood M, Wengenack TM, Borowski B, Curran GL, Lin J, et al. In vivo visualization of Alzheimer's amyloid plaques by magnetic resonance imaging in transgenic mice without a contrast agent. Magn Reson Med. 2004. 52:1263–1271.55. Lee SP, Falangola MF, Nixon RA, Duff K, Helpern JA. Visualization of beta-amyloid plaques in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease using MR microscopy without contrast reagents. Magn Reson Med. 2004. 52:538–544.56. Vanhoutte G, Dewachter I, Borghgraef P, Van Leuven F, Van der Linden A. Noninvasive in vivo MRI detection of neuritic plaques associated with iron in APP[V717I] transgenic mice, a model for Alzheimer's disease. Magn Reson Med. 2005. 53:607–613.57. Meadowcroft MD, Connor JR, Smith MB, Yang QX. MRI and histological analysis of beta-amyloid plaques in both human Alzheimer's disease and APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009. 29:997–1007.58. Yang X, Sammet S, Schmalbrock P, Knopp MV. Postprocessing correction for distortions in T2* decay caused by quadratic cross-slice B0 inhomogeneity. Magn Reson Med. 2010. 63:1258–1268.59. Schenck JF, Zimmerman EA. High-field magnetic resonance imaging of brain iron: birth of a biomarker? NMR Biomed. 2004. 17:433–445.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery (FLAIR) Imaging of the Normal Brain: Comparisons between Under the Conditions of 3.0 Tesla and 1.5 Tesla
- T1-, T2-weighted, and FLAIR Imaging: Clinical Application
- Importance of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Various Intracranial Pathologic Conditions
- Hyperintense Vessels on FLAIR MRI in Patients With Acute Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction Revealed Pial Collateral on Cerebral Angiography
- Isolated Leptomeningeal Enhancement in Anti-N-Methyl D-Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis: The Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging