Korean J Radiol.
2012 Oct;13(5):541-549. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.5.541.
Imaging Findings of Brain Death on 3-Tesla MRI
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul 110-744, Korea.
- 2Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi 730-728, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Korean Armed Force Daejeon Hospital, Daejeon 305-155, Korea.
- 4Department of Radiology, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea. hyukwonchang@korea.com
- 5Department of Neurosurgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam 463-707, Korea.
- 7Department of Surgery, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Daegu 700-712, Korea.
- 8Department of Biomedical Engineering, Keimyung University College of Medicine, Daegu 704-701, Korea.
- KMID: 1392931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.5.541
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To demonstrate the usefulness of 3-tesla (3T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) including T2-weighted imaging (T2WI), diffusion weighted imaging (DWI), time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), T2*-weighted gradient recalled echo (GRE), and susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) in diagnosing brain death.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Magnetic resonance imaging findings for 10 patients with clinically verified brain death (group I) and seven patients with comatose or stuporous mentality who did not meet the clinical criteria of brain death (group II) were retrospectively reviewed.
RESULTS
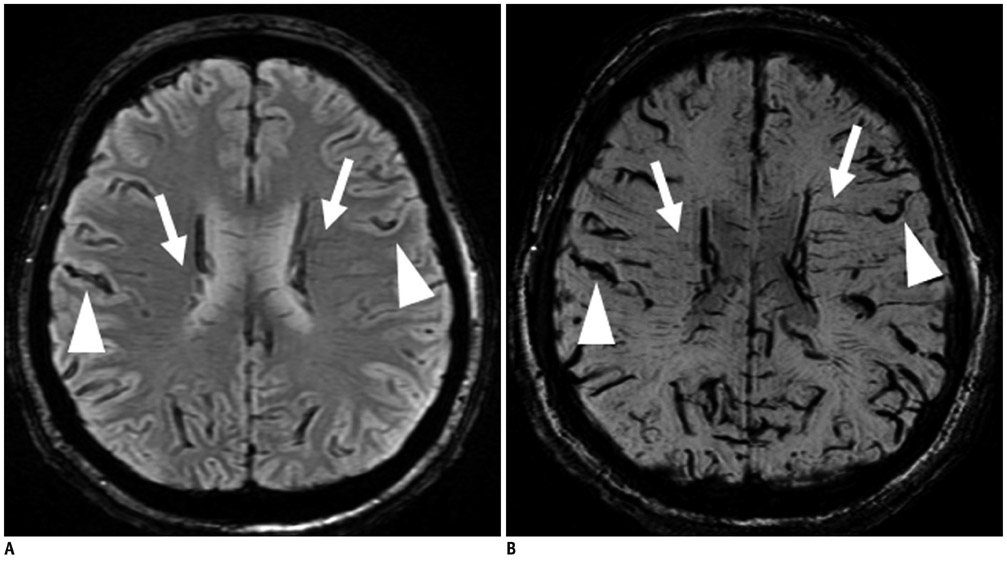
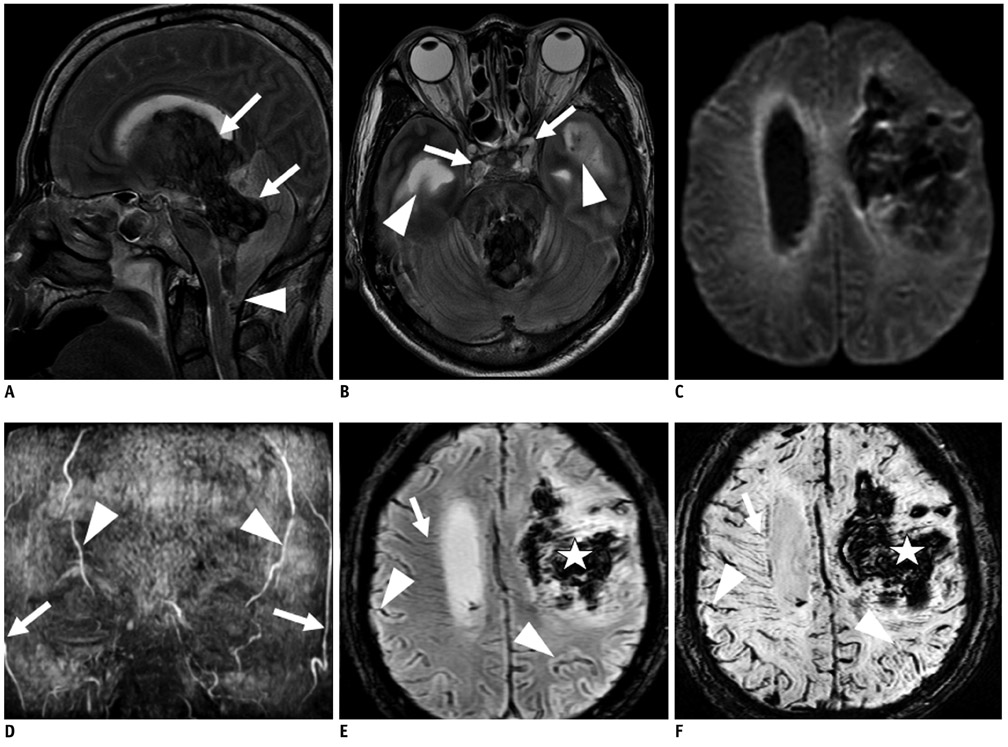
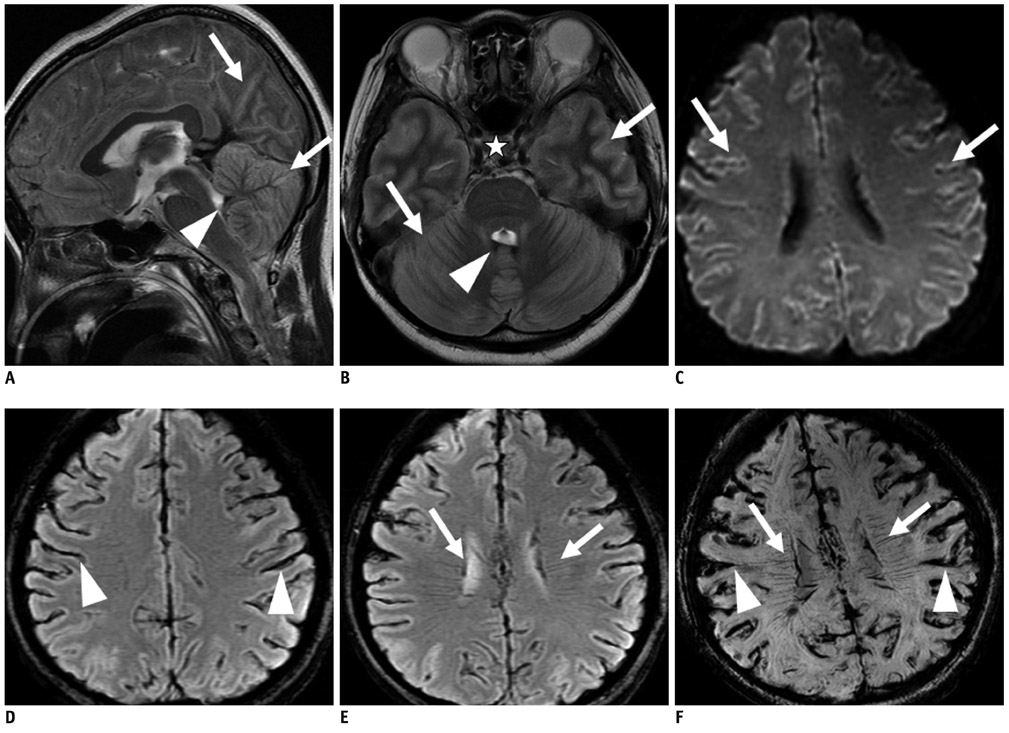
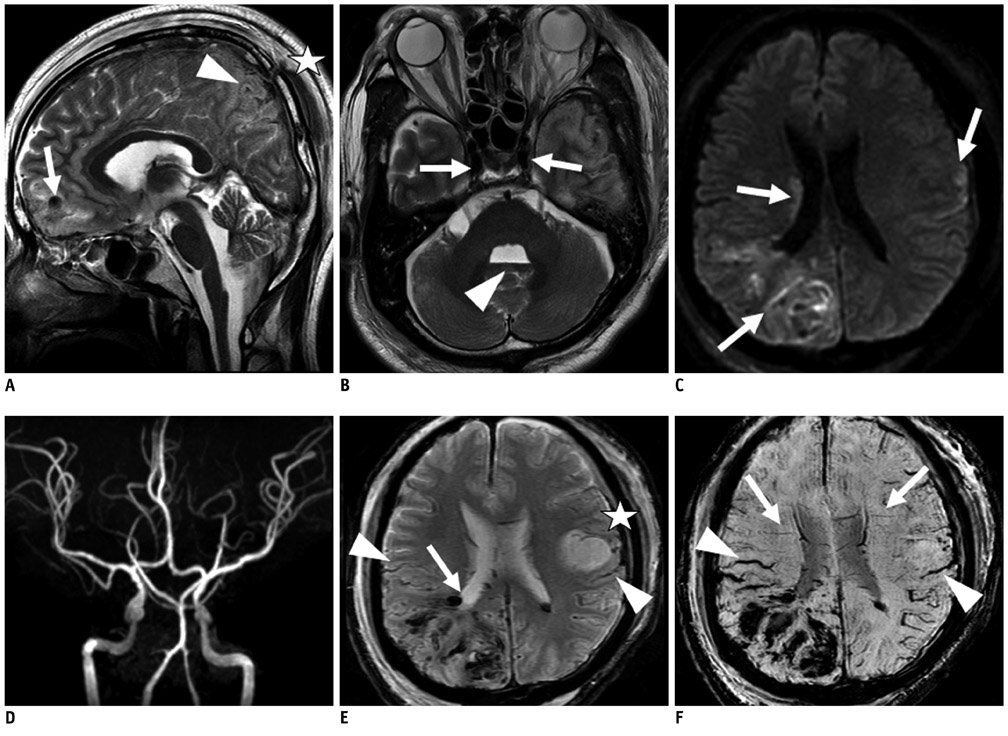
Tonsilar herniation and loss of intraarterial flow signal voids (LIFSV) on T2WI were highly sensitive and specific findings for the diagnosis of brain death (p < 0.001 and < 0.001, respectively). DWI, TOF-MRA, and GRE findings were statistically different between the two groups (p = 0.015, 0.029, and 0.003, respectively). However, cortical high signal intensities in T2WI and SWI findings were not statistically different between the two group (p = 0.412 and 1.0, respectively).
CONCLUSION
T2-weighted imaging, DWI, and MRA using 3T MRI may be useful for diagnosing brain death. However, SWI findings are not specific due to high false positive findings.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wijdicks EF. Brain death worldwide: accepted fact but no global consensus in diagnostic criteria. Neurology. 2002. 58:20–25.2. Baron L, Shemie SD, Teitelbaum J, Doig CJ. Brief review: history, concept and controversies in the neurological determination of death. Can J Anaesth. 2006. 53:602–608.3. Wijdicks EF. Determining brain death in adults. Neurology. 1995. 45:1003–1011.4. Young GB, Shemie SD, Doig CJ, Teitelbaum J. Brief review: the role of ancillary tests in the neurological determination of death. Can J Anaesth. 2006. 53:620–627.5. Kim JY, Lee SB. Diagnostic criteria of brain death. J Korean Med Assoc. 1999. 42:349–357.6. Grigg MM, Kelly MA, Celesia GG, Ghobrial MW, Ross ER. Electroencephalographic activity after brain death. Arch Neurol. 1987. 44:948–954.7. Wijdicks EF, Varelas PN, Gronseth GS, Greer DM. American Academy of Neurology. Evidence-based guideline update: determining brain death in adults: report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology. 2010. 74:1911–1918.8. Alvarez-Linera J. 3T MRI: advances in brain imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2008. 67:415–426.9. Tong KA, Ashwal S, Obenaus A, Nickerson JP, Kido D, Haacke EM. Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging: a review of clinical applications in children. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 29:9–17.10. Hamilton BE. Osborn AG, Salzman KL, Katzman G, Provenzale J, Castillo M, Hedlund G, editors. Brain death. Dignostic imaging. 2004. 1st ed. Salt Lake City, Utah: Amirsys;54–55.11. Hermier M, Nighoghossian N, Derex L, Adeleine P, Wiart M, Berthezène Y, et al. Hypointense transcerebral veins at T2*-weighted MRI: a marker of hemorrhagic transformation risk in patients treated with intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2003. 23:1362–1370.12. Morita N, Harada M, Uno M, Matsubara S, Matsuda T, Nagahiro S, et al. Ischemic findings of T2*-weighted 3-tesla MRI in acute stroke patients. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008. 26:367–375.13. Sohn CH, Baik SK, Lee HJ, Lee SM, Kim IM, Yim MB, et al. MR imaging of hyperacute subarachnoid and intraventricular hemorrhage at 3T: a preliminary report of gradient echo T2*-weighted sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005. 26:662–665.14. Hermier M, Nighoghossian N. Contribution of susceptibility-weighted imaging to acute stroke assessment. Stroke. 2004. 35:1989–1994.15. Boukobza M, Crassard I, Bousser MG, Chabriat H. MR imaging features of isolated cortical vein thrombosis: diagnosis and follow-up. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. 30:344–348.16. A definition of irreversible coma. Report of the Ad Hoc Committee of the Harvard Medical School to Examine the Definition of Brain Death. JAMA. 1968. 205:337–340.17. DuBois JM, Anderson EE. Attitudes toward death criteria and organ donation among healthcare personnel and the general public. Prog Transplant. 2006. 16:65–73.18. Orrison WW Jr, Champlin AM, Kesterson OL, Hartshorne MF, King JN. MR 'hot nose sign' and 'intravascular enhancement sign' in brain death. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1994. 15:913–916.19. Ishii K, Onuma T, Kinoshita T, Shiina G, Kameyama M, Shimosegawa Y. Brain death: MR and MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996. 17:731–735.20. Lövblad KO, Bassetti C. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in brain death. Stroke. 2000. 31:539–542.21. Phan TG, Wijdicks EF. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in brain death. Stroke. 2000. 31:1458–1459. author reply 1459-1460.22. Karantanas AH, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Paterakis K, Sfiras D, Komnos A. Contribution of MRI and MR angiography in early diagnosis of brain death. Eur Radiol. 2002. 12:2710–2716.23. Bell MJ, Robertson CS, Kochanek PM, Goodman JC, Gopinath SP, Carcillo JA, et al. Interstitial brain adenosine and xanthine increase during jugular venous oxygen desaturations in humans after traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med. 2001. 29:399–404.24. Kesavadas C, Thomas B, Misra S, Saini J. Attenuation of cerebral veins in susceptibility-weighted MR imaging performed with the patient under general anesthesia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008. 29:e71.25. Sedlacik J, Löbel U, Kocak M, Loeffler RB, Reichenbach JR, Broniscer A, et al. Attenuation of cerebral venous contrast in susceptibility-weighted imaging of spontaneously breathing pediatric patients sedated with propofol. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. 31:901–906.26. Hori M, Mori H, Aoki S, Abe O, Masumoto T, Kunimatsu S, et al. Three-dimensional susceptibility-weighted imaging at 3 T using various image analysis methods in the estimation of grading intracranial gliomas. Magn Reson Imaging. 2010. 28:594–598.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- High field strength magnetic resonance imaging of cardiovascular diseases
- Comparison of 3 and 7 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Obstructive Hydrocephalus Caused by Tectal Glioma
- Advanced MRI for Pediatric Brain Tumors with Emphasis on Clinical Benefits
- 3.0 T MRI Findings in Cerebral Decompression Sickness: A Case Report
- Introduction to high field strength magnetic resonance imaging