Korean J Urol.
2008 May;49(5):387-391. 10.4111/kju.2008.49.5.387.
Robot-assisted Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute and Brain Korea 21 Project for Medical Science, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. khrha@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1204517
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4111/kju.2008.49.5.387
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: Laparoscopic partial nephrectomy is a treatment option for small renal masses. However, such time-consuming techniques such as tumor excision, hemostasis and intracoporeal suturing are still challenging procedures even for experienced laparoscopists. Incorporation of a robotic system would facilitate tumor excision, hemostasis and intracoporeal suturing. Herein, we review our technique and the short term outcomes for robot-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy(RLPN).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
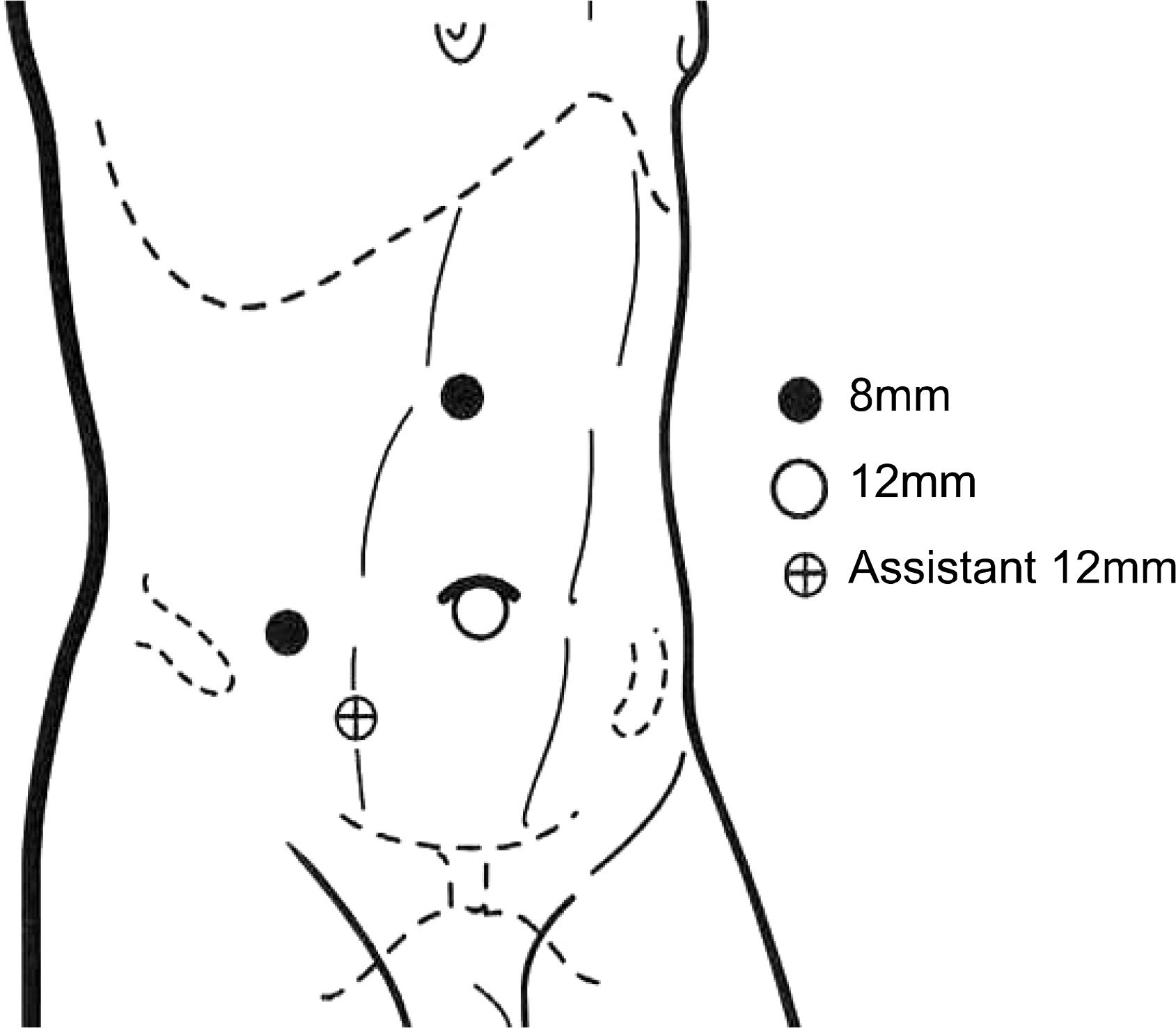
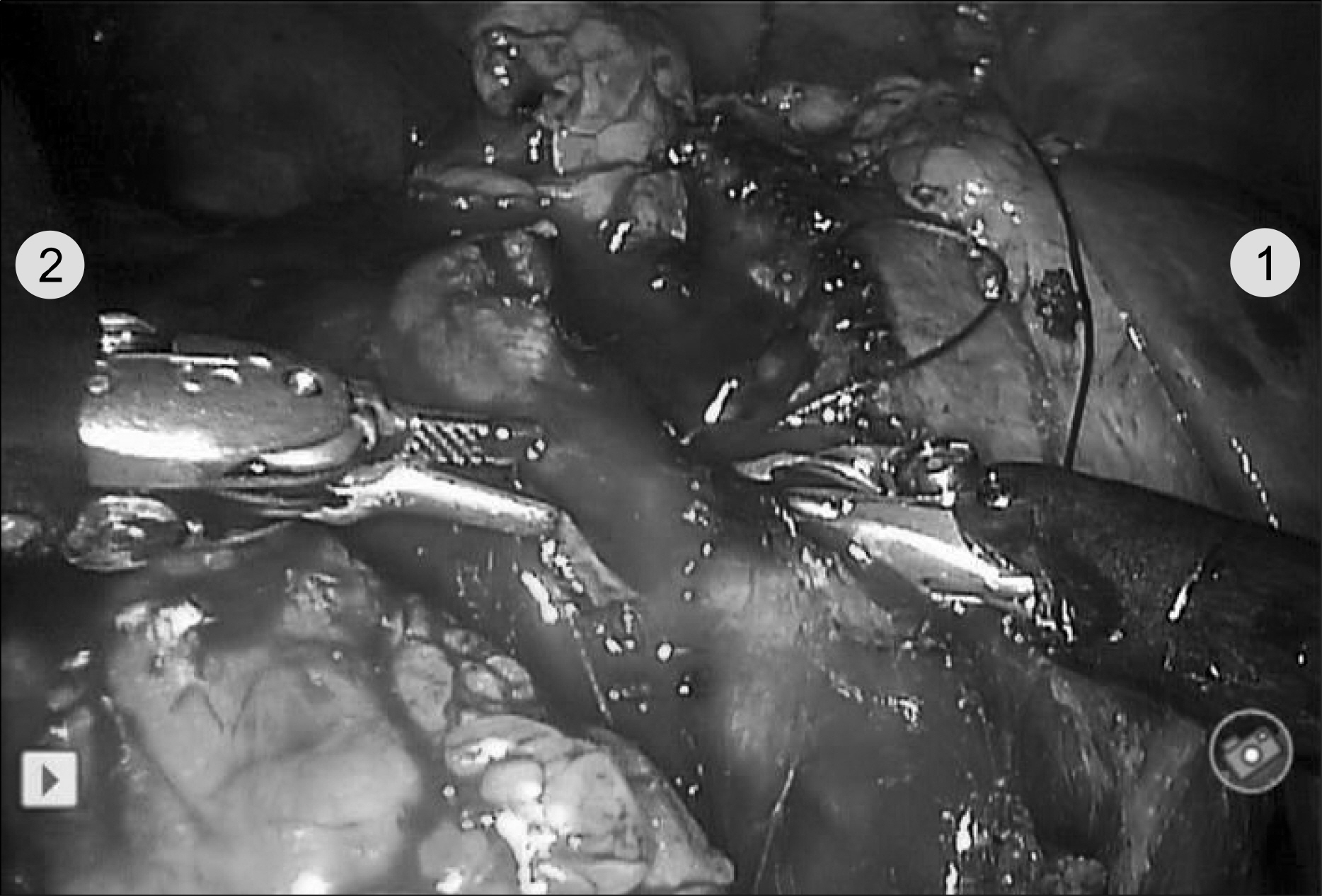
Eleven patients underwent RLPN for small renal masses. RLPN were performed with the da Vinci(R) robot system(Intuitive Surgical, Sunnyvale, USA) with three robot arms. In 7 cases, the renal hilum was clamped. Tumor excision and intracorporeal suturing were performed entirely with the robotic system. The specimen was extracted through the extended umbilical port incision.
RESULTS
The mean tumor diameter was 2.5+/-1.5cm. The mean operative time was 179.5+/-49.4 minutes and the mean estimated blood loss was 354.5+/-440.7ml. The mean warm ischemia time was 30.4+/-5.9 minutes for 7 patients. There were no major complications. The surgical pathology showed clear cell type renal cell carcinoma in 7, papillary type renal cell carcinoma in 1, angiomyolipoma in 2 and lipoma in 1. There were no positive surgical margins. The mean hospital stay was 4.2+/-1.3 days. No recurrence had been observed after 3 to 18 months of follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
We were able to verify the feasibility and safety of using a RLPN in the management of small renal masses. Longer follow-up data and larger prospective studies are necessary to confirm these results.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1.Abbou CC., Hoznek A., Salomon L., Olsson LE., Lobontiu A., Saint F, et al. Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy with a remote controlled robot. J Urol. 2001. 165:1964–6.
Article2.Sung GT., Gill IS., Hsu TH. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic pyeloplasty: a pilot study. Urology. 1999. 53:1099–103.
Article3.Guillonneau B., Jayet C., Tewari A., Vallancien G. Robot assisted laparoscopic nephrectomy. J Urol. 2001. 166:200–1.
Article4.Kim HJ. Robot-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. Korean J Endourol. 2007. 6:27–30.5.Gettman MT., Blute ML., Chow GK., Neururer R., Bartsch G., Peschel R. Robotic-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: technique and initial clinical experience with DaVinci robotic system. Urology. 2004. 64:914–8.6.Gettman MT., Blute ML., Peschel R., Bartsch G. Current status of robotics in urologic laparoscopy. Eur Urol. 2003. 43:106–12.
Article7.Phillips CK., Taneja SS., Stifelman MD. Robot-assisted laparo-scopic partial nephrectomy: the NYU technique. J Endourol. 2005. 19:441–5.
Article8.Stifelman MD., Caruso RP., Nieder AM., Taneja SS. Robot-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. JSLS. 2005. 9:83–6.9.Caruso RP., Phillips CK., Kau E., Taneja SS., Stifelman MD. Robot assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: initial experience. J Urol. 2006. 176:36–9.
Article10.Kaul S., Laungani R., Sarle R., Stricker H., Peabody J., Littleton R, et al. da Vinci-assisted robotic partial nephrectomy: technique and results at a mean of 15 months of follow-up. Eur Urol. 2007. 51:186–91.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Seeding Metastasis of Chromophobe Renal Cell Carcinoma after Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy
- Cost Aspects of Radical Nephrectomy for the Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Korea: Open, Laparoscopic, Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic, and Video-Assisted Minilaparotomy Surgeries
- Initial Clinical Experience with Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy for Complex Renal Tumors
- Simultaneous Robot-Assisted Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Partial Nephrectomy and Standard Radical Prostatectomy
- Laparoscopic Partial Nephrectomy using a Microwave Tissue Coagulator for Small Renal Tumor