Yonsei Med J.
2014 Mar;55(2):535-538.
Simultaneous Robot-Assisted Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Partial Nephrectomy and Standard Radical Prostatectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Urology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea.
- 2Department of Urology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 3Department of Urology, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Department of Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University Health System, Seoul, Korea. khrha@yuhs.ac
Abstract
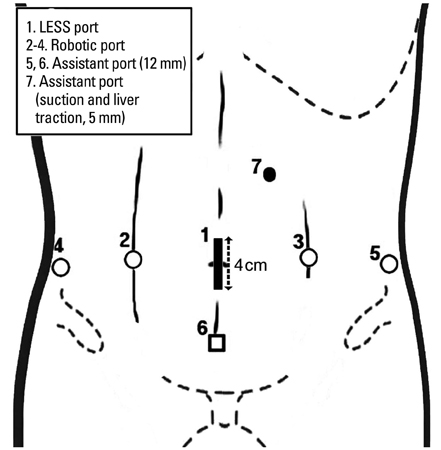
- Recently, patients with urologic malignancies are treated with robot-assisted surgery and the expanded role of robot-assisted surgery includes even those patients with two concomitant primary urologic malignancies. In an effort to further reduce port site-related morbidity, robot-assisted laparoendoscopic single-site surgery (RLESS) has been developed. Therefore, we present herein our early experience and feasibility of simultaneous RLESS partial nephrectomy and standard robotrobot-assisted laparoendoscopic radical prostatectomy (RALP) on 3 patients with synchronous renal masses and prostate cancer.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boncher N, Vricella G, Greene G, Madi R. Concurrent robotic renal and prostatic surgery: initial case series and safety data of a new surgical technique. J Endourol. 2010; 24:1625–1629.
Article2. Jung JH, Arkoncel FR, Lee JW, Oh CK, Yusoff NA, Kim KJ, et al. Initial clinical experience of simultaneous robot-assisted bilateral partial nephrectomy and radical prostatectomy. Yonsei Med J. 2012; 53:236–239.
Article3. Rha KH. Robot-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Korean J Urol. 2009; 50:97–104.
Article4. Singh I. Robot-assisted laparoscopic partial nephrectomy: current review of the technique and literature. J Minim Access Surg. 2009; 5:87–92.
Article5. Lee DH, Jung HB, Chung MS, Lee SH, Chung BH. The change of prostate cancer treatment in Korea: 5 year analysis of a single institution. Yonsei Med J. 2013; 54:87–91.
Article6. Han WK, Kim DS, Jeon HG, Jeong W, Oh CK, Choi KH, et al. Robot-assisted laparoendoscopic single-site surgery: partial nephrectomy for renal malignancy. Urology. 2011; 77:612–616.
Article7. Kaouk JH, Goel RK. Single-port laparoscopic and robotic partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol. 2009; 55:1163–1169.
Article8. Kaouk JH, Goel RK, Haber GP, Crouzet S, Desai MM, Gill IS. Single-port laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2008; 72:1190–1193.
Article9. Ye H, Kong X, He TW, Jolis T, Choi K, Lepor H, et al. Intraoperative frozen section analysis of urethral margin biopsies during radical prostatectomy. Urology. 2011; 78:399–404.
Article10. Meininger D, Westphal K, Bremerich DH, Runkel H, Probst M, Zwissler B, et al. Effects of posture and prolonged pneumoperitoneum on hemodynamic parameters during laparoscopy. World J Surg. 2008; 32:1400–1405.
Article11. Patel MN, Krane LS, Bhandari A, Laungani RG, Shrivastava A, Siddiqui SA, et al. Robotic partial nephrectomy for renal tumors larger than 4 cm. Eur Urol. 2010; 57:310–316.12. Boorjian SA, Blute ML. Surgical management of high risk prostate cancer: the Mayo Clinic experience. Urol Oncol. 2008; 26:530–532.
Article13. Leonardo C, Simone G, Papalia R, Franco G, Guaglianone S, Gallucci M. Salvage radical prostatectomy for recurrent prostate cancer after radiation therapy. Int J Urol. 2009; 16:584–586.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Initial Clinical Experience of Simultaneous Robot-Assisted Bilateral Partial Nephrectomy and Radical Prostatectomy
- Simultaneous Retzius-sparing robot-assisted radical prostatectomy and partial nephrectomy
- Yonsei Experience in Robotic Urologic Surgery-Application in Various Urological Procedures
- Robot-assisted laparoendoscopic single-site upper urinary tract surgery with da Vinci Xi surgical system: Initial experience
- Erratum: Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy