Korean J Ophthalmol.
2009 Sep;23(3):198-203. 10.3341/kjo.2009.23.3.198.
Reunion of the Rabbit Superior Oblique Tendon After Weakening Procedures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology Kyungpook National University, School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. jykwon@mail.knu.ac.kr
- KMID: 1115753
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2009.23.3.198
Abstract
- PURPOSE
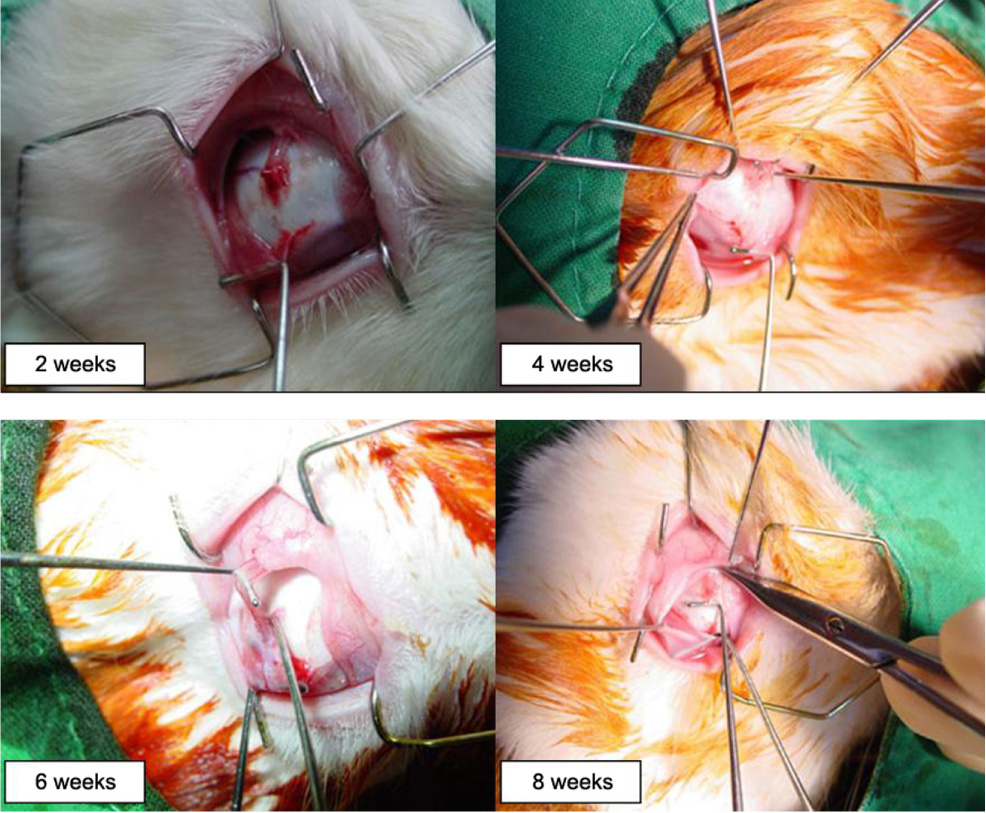
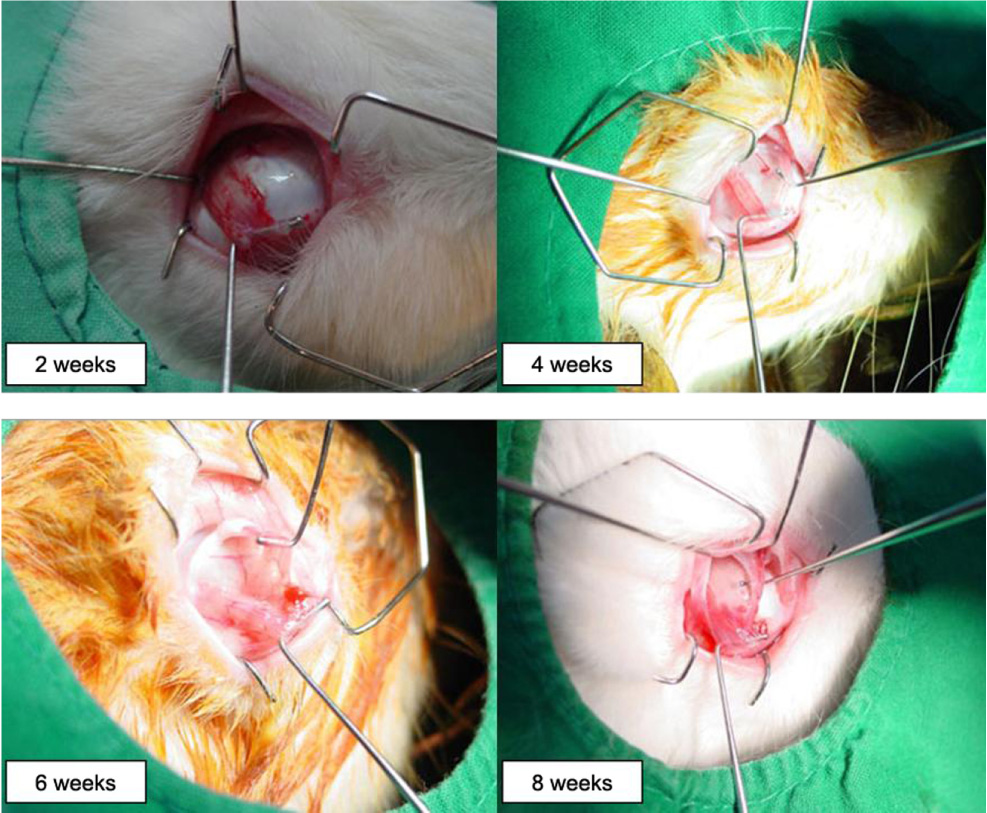
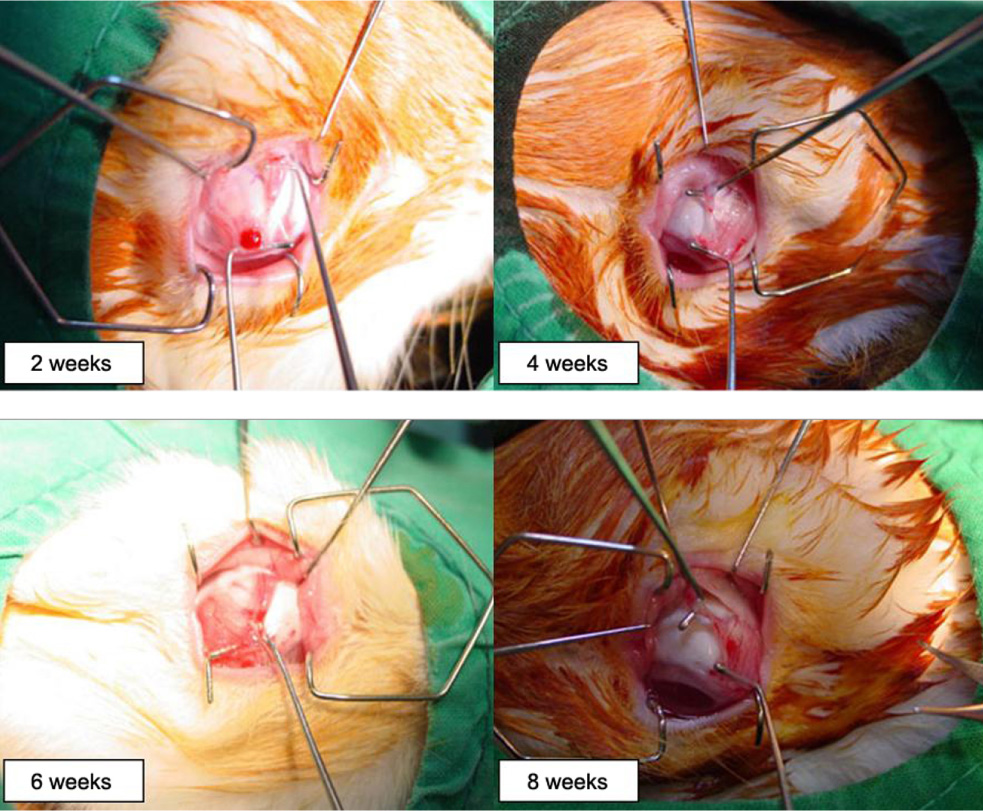
To investigate the degree of reunion in rabbit eyes of the superior oblique tendon after several surgical weakening procedures. METHODS: A total of 32 rabbits (64 eyes) were used in this study. The rabbits were randomly assigned to four groups, eight rabbits (16 eyes) in the tenotomy group, eight rabbits (16 eyes) in the tenectomy group, eight rabbits (16 eyes) in the disinsertion group and eight rabbits (16 eyes) in the recession group. The degree of reunion or reattachment of the superior oblique tendon on the globe were examined on four eyes in each group at postoperative weeks two, four, six and eight. RESULTS: At eight weeks, the newly created insertion site remained at the same site in all eyes in the recession group, and the distal end of the superior oblique tendon was reattached at the medial border of the superior rectus muscle in all four eyes in the tenotomy and disinsertion groups, and in three of four eyes in the tenectomy group. CONCLUSIONS: From this experimental study, it was speculated that superior oblique recession is more effective than other superior oblique weakening procedures. This result could be helpful in the prediction of time of recurrence for superior oblique overaction after superior oblique weakening procedures.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Von Noorden GK, Campos EC. Binocular vision and ocular motility. 2002. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;396–457.2. Parks MM. Ocular motility and strabismus. 1975. Hargestown: Harpers & Row;100–108.3. Wright KW, Spiegel PH. Pediatric Ophthalmology and strabismus. 2002. 2nd ed. New York: Springer;204–223.4. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP. Clinical strabismus management: Principles and surgical technique. 1999. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;459–475.5. Parks MM. Surgery for Brown syndrome. Symposium on Strabismus: Transection of the New Orleans Academy of Ophthalmology. 1978. St Louis: CV Mosby;157–177.6. Prieto-Diaz J. Superior oblique overaction. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1989. 29:43–50.7. Buckley EG, Flynn JT. Superior oblique recession versus tenotomy: a comparison of surgical results. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983. 20:112–117.8. Crawford JS. Surgical treatment of true Brown syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1976. 81:289–295.9. Parks MM. Management of overacting superior oblique Clinical course of accommodative esotropia. Optom Vis Sci. 1998. 75:97–102.10. Scott WE, Jampolsky AJ, Redmond MR. Superior oblique teno tomy: Indications and complications. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1976. 16:151–159.11. McNeer KW. Untoward effects of superior oblique tenotomy. Ann Ophthalmol. 1972. 4:747–755.12. Urist MJ. Complications following bilateral superior oblique weakening surgical procedures for A-pattern horizontal deviation. Am J Ophthalmol. 1970. 70:583–587.13. Rubin SE, Nelson LB, Harley RD. A complication in weakening the superior oblique muscle in A-pattern exotropia. Ophthalmic Surg. 1984. 15:134–135.14. Souza-Diaz C, Uesugui CF. Efficacy of different techniques of superior oblique weakening in the correction of the A anisotropia. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1986. 23:82–86.15. Romano P, Roholt P. Measured graduated recession of the superior oblique muscle. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983. 20:134–140.16. Wright KW. Superior oblique silicone expander for Brown syndrome and superior oblique overaction. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1991. 28:102–107.17. Wright KW, Min BM, Park C. Comparison of superior oblique tendon expander to superior oblique tenotomy for the management of superior oblique overaction and Brown syndrome. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1992. 29:92–97.18. Yim HB, Park C. Effects of the superior oblique tendon silicone expander for superior oblique overaction. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 1992. 33:970–976.19. Berke RN. Tenotomy of the superior oblique for hypertropia. Trans am Ophthalmol Soc. 1946. 44:304–338.20. Parks MM, Helveston EM. Direct visualization of the superior oblique tendon. Arch Ophthalmol. 1970. 84:491–494.21. Ciancia AO, Prieto-Diaz J. Retroceso del Oblicuo superior. Arch Ofthalmol B Aires. 1970. 45:193.22. Prieto-Diaz J. Resultados y complicaciones del retroceso del oblicuo superior. Actas dell IV Congresso del CLADE. 1974. Mexico: 186.23. Parks MM. Commentary on superior oblique tenotomy for A-pattern strabismus in patients with fusion. Binocular Viaion. 1988. 3:39.24. Von Noorden GK, Olivier P. Superior oblique tenectomy in Brown syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1982. 89:303–309.25. Rosenbaum AL, Santiago AP. Clinical strabismus management: Principles and surgical technique. 1999. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders;219–229.26. Reynolds JD, Wackerhagen M. Bilateral superior oblique tenotomy for A-pattern strabismus in patients with fusion. Binocular Vision. 1988. 3:33–38.27. Romano P, Roholt P. Measured graduated recession of the superior oblique muscle. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 1983. 20:134–140.28. Caldeira JAF. Graduated recession of the superior oblique muscle. Br J Ophthalmol. 1975. 59:553–559.29. Wertz RD, Romano PE, Wright P. Inferior oblique myectomy, disinsertion and recession in Rhesus monkeys. Arch Ophthalmol. 1977. 95:857–860.30. Guyton DL. Exaggerated traction test for the oblique muscles. Ophthalmology. 1981. 88:1035–1040.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Superior Oblique Tenotomy with Silicone Expander for Superior Oblique Overaetion and Brown Syndrome
- The Effect of Inferior Oblique Weakening Procedures in the Congenital Superior Oblique Palsies
- Tenectomy and Posterior Tenectomy of the Superior Oblique for Superior Oblique Overaction
- A Case of Brown's Syndrome Following Tucking of Superior Oblique Muscle
- Contralateral Inferior Oblique Muscle Overaction after Unilateral Inferior Oblique Weakening Procedures