Korean J Ophthalmol.
2008 Mar;22(1):43-48. 10.3341/kjo.2008.22.1.43.
Case Report: Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Small Incision Deep Lamellar Endothelial Keratoplasty
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. tychung@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary, Harvard Medical School, Boston, USA.
- KMID: 1107490
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2008.22.1.43
Abstract
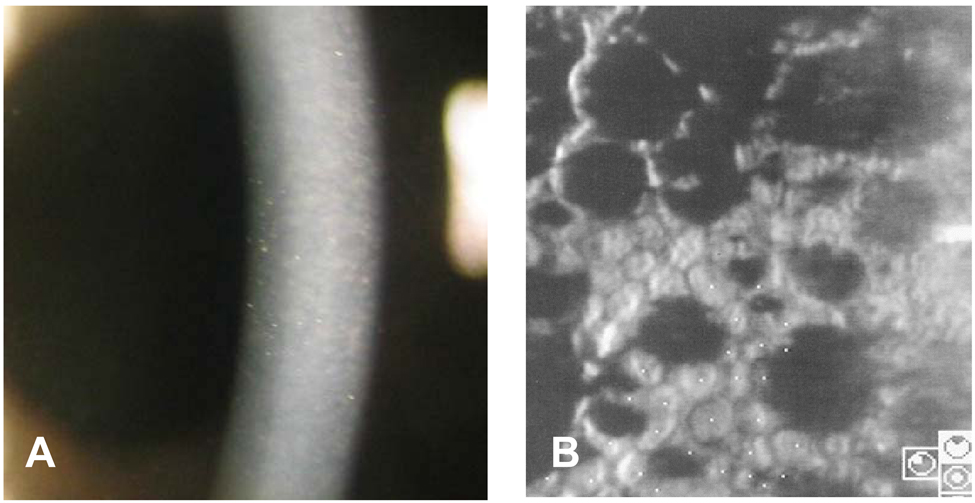
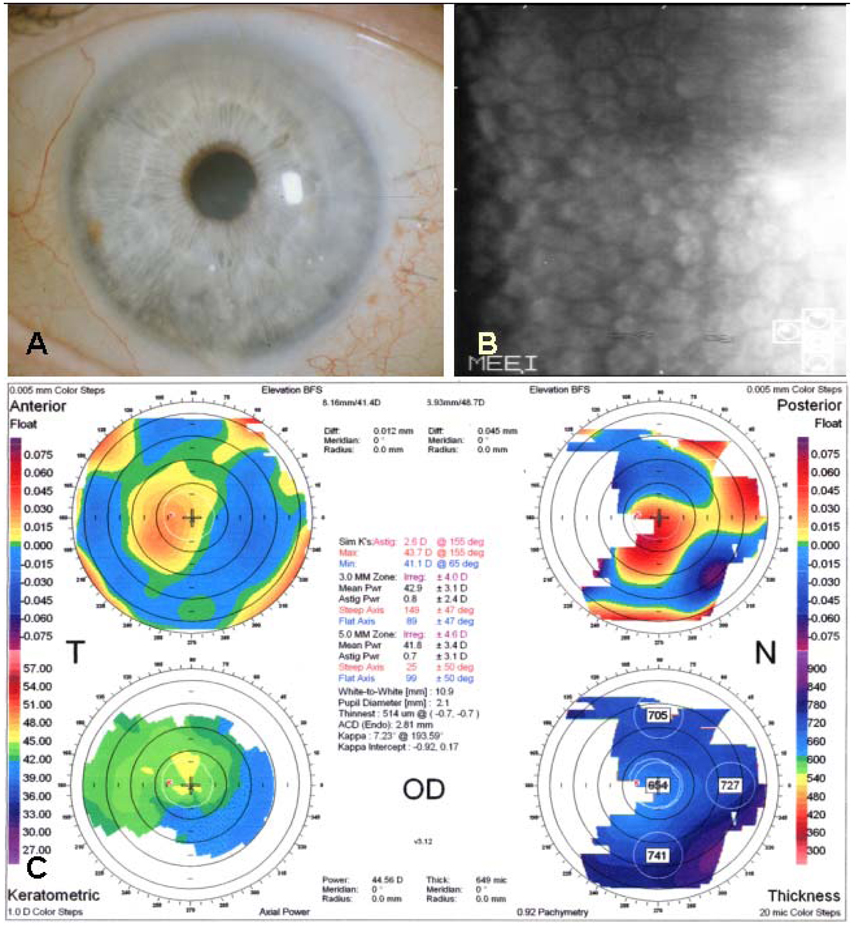
- PURPOSE: To report two cases of femtosecond laser-assisted small incision deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty (DLEK) for patients with corneal endothelial decompensation by Fuchs dystrophy and glaucoma METHODS: Femtosecond laser (IntraLase(R); IntraLase Corp., Irvine, CA) with 15 kHz of repetition rate, was used for a 9.5 mm diameter by 400 micrometer thickness donor corneal lamellar dissection. RESULTS: In Case 1, the graft was clear and compact without interface haze, Orbscan showed smooth and regular corneal surface, specular microscopy was unremarkable without sign of corneal endothelial damage, and Optical coherence tomography showed uniform graft well attached to recipient stroma with minimal interface reflection at 2 months postoperation. In Case 2, the graft was clear and compact with minimal interface haze at 1 month postoperation. Femtosecond laser-assisted small incision DLEK was safe and technically feasible in our cases; however, further evaluation is required to determine long-term effects.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Femtosecond LASER-Assisted Descemet's Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty
Byung Gil Moon, Jae Hyung Kim, Joo Eun Lee, Myoung Joon Kim, Jae Yong Kim, Hungwon Tchah
J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2011;52(6):679-689. doi: 10.3341/jkos.2011.52.6.679.
Reference
-
1. Melles GR, Eggink FA, Lander F, et al. A surgical technique for posterior lamellar keratoplasty. Cornea. 1998. 17:618–626.2. Melles GR, Lander F, Beekhuis WH, et al. Posterior lamellar keratoplasty for a case of pseudophakic bullous keratopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1999. 127:340–341.3. Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Endothelial replacement without surface corneal incisions or sutures: topography of the deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty procedure. Cornea. 2001. 20:14–18.4. Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty in the first United States patients: early clinical results. Cornea. 2001. 20:239–243.5. Melles GR, Lander F, Nieuwendaal C. Sutureless, posterior lamellar keratoplasty: a case report of a modified technique. Cornea. 2002. 21:325–327.6. Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Small incision deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty (DLEK): six-month results in the first prospective clinical study. Cornea. 2005. 24:59–65.7. Soong HK, Katz DG, Farjo AA, et al. Central lamellar keratoplasty for optical indications. Cornea. 1999. 18:249–256.8. Chau GK, Dilly SA, Sheard CE, Rostron CK. Deep lamellar keratoplasty on air with lyophilised tissue. Br J Ophthalmol. 1992. 76:646–650.9. Sugar A. Ultrafast (femtosecond) laser refractive surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2002. 13:246–249.10. Nordan LT, Slade SG, Baker RN, et al. Femtosecond laser flap creation for laser in situ keratomileusis: six-month follow-up of initial U.S. clinical series. J Refract Surg. 2003. 19:8–14.11. Binder PS. Flap dimensions created with the IntraLase FS laser. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004. 30:26–32.12. Kezirian GM, Stonecipher KG. Comparison of the IntraLase femtosecond laser and mechanical keratomes for laser in situ keratomileusis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2004. 30:804–811.13. Ing JJ, Ing HH, Nelson LR, et al. Ten-year postoperative results of penetrating keratoplasty. Ophthalmology. 1998. 105:1855–1865.14. Melles GR, Remeijer L, Geerards AJ, Beekhuis WH. The future of lamellar keratoplasty. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 1999. 10:253–259.15. Chung SE, Lee DH, Chung TY, Chung ES. Results of Deep Lamellar Endothelial Keratoplasty (DLEK). J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2006. 47:1743–1750.16. Azar DT, Jain S. Microkeratome-assisted posterior keratoplasty. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2002. 28:732–733.17. Wachtlin J, Langenbeck K, Schrunder S, et al. Immunohistology of corneal wound healing after photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis. J Refract Surg. 1999. 15:451–458.18. Jain S, Khoury JM, Chamon W, Azar DT. Corneal light scattering after laser in situ keratomileusis and photorefractive keratectomy. Am J Ophthalmol. 1995. 120:532–534.19. Kim SA, Choi ES, Lee TH, et al. Comparision of Corneal Endothelial Change in Femtosecond Laser and Microkeratome LASIK. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2005. 46:2059–2064.20. Sarayba MA, Ignacio TS, Binder PS, Tran DB. Comparative study of stromal bed quality by using mechanical, IntraLase femtosecond laser 15-and 30 kHz microkeratomes. Cornea. 2007. 26:446–451.21. Sarayba MA, Ignacio TS, Tran DB, Binder PS. A 60 kHz IntraLase femtosecond laser creates a smoother LASIK stromal bed surface compared to a Zyoptix XP mechanical microkeratome in human donor eyes. J Refract Surg. 2007. 23:331–337.22. Sarayba MA, Juhasz T, Chuck RS, et al. Femtosecond laser posterior lamellar keratoplasty: a laboratory model. Cornea. 2005. 24:328–333.23. Cheng YY, Pels E, Cleutjens JP, et al. Corneal Endothelial Viability After Femtosecond Laser Preparation of Posterior Lamellar Discs for Descemet-Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty. Cornea. 2007. 26:1118–1122.24. Jonas JB, Vossmerbaeumer U. Femtosecond laser penetrating keratoplasty with conical incisions and positional spikes. J Refract Surg. 2004. 20:397.25. Mian SI, Shtein RM. Femtosecond laser-assisted corneal surgery. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2007. 18:295–299.26. Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty visual acuity, astigmatism, and endothelial survival in a large prospective series. Ophthalmology. 2005. 112:1541–1548.27. Terry MA, Ousley PJ. Rapid visual rehabilitation after endothelial transplants with deep lamellar endothelial keratoplasty (DLEK). Cornea. 2004. 23:143–153.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Early Clinical Result of Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty Using FSlaser Versus Manual Trephine
- Early Result of Femtosecond Laser Assisted Descemet's Membrane Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty
- A Case Report of Fungal Keratitis Diagnosed by Femtosecond Laser Assisted Corneal Biopsy
- Early Results of Femtosecond Laser-Assisted Mushroom-Shaped Wound-Configurized Keratoplasty
- Long-term Clinical Outcomes of Femtosecond LASER-Assisted Descemet's Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty