J Vet Sci.
2006 Mar;7(1):47-51. 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.1.47.
Concurrent response to challenge infection with Cryptosporidium parvum in immunosuppressed C57BL/6N mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-756, Korea.
- 2College of Animal Resources Science, Department of Veterinary Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon 200-701, Korea. advs@kangwon.ac.kr
- KMID: 1103553
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2006.7.1.47
Abstract
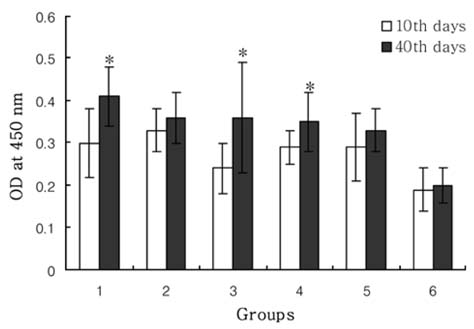
- We investigated the response to challenge infection with Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts in immunosuppressed C57BL/6N mice. In the primary infection, fecal oocyst shedding and parasite colonization were greater in immunosuppressed mice than in nonimmunosuppressed mice. Compared with primary infection, challenge infection with C. parvum didn't show any oocyst shedding and parasite colonization. Especially, oocyst shedding and parasite colonization from the mice infected with heatkilled oocysts were not detected. After challenge infection with C. parvum oocysts, however, these mice were shedding small numbers of oocysts and parasite colonization. Except normal control and uninfected groups, the antibody titers of other groups appear similar. Based on the fecal oocyst shedding, parasite colonization of ilea, and antibody titers in the mice, these results suggest that the resistance to challenge infection with C. parvum in immunosuppressed C57BL/6N mice has increased.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies, Protozoan/blood
Cryptosporidiosis/*immunology/*parasitology
Cryptosporidium parvum/*immunology
Dexamethasone/immunology
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Feces/parasitology
Female
Fluorescent Antibody Technique, Indirect
Histocytochemistry
Ileum/parasitology
Immunocompromised Host
Mice
Mice, Inbred C57BL
Oocysts/immunology
Random Allocation
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arrowood MJ, Sterling CR. Isolation of Cryptosporidium oocysts and sporozoites using discontinuous sucrose and isopycnic percoll gradients. J Parasitol. 1987. 73:314–319.
Article2. Benhamou Y, Kapel N, Hoang C, Matta H, Meillet D, Magne D, Raphael M, Gentilini M, Opolon P, Gobert JG. Inefficacy of inresrinal secretory immune response to Cryptosporidium in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1995. 108:627–635.
Article3. Casemore DP, Sands RL, Curry A. Cryptosporidium species a new human pathogen. J Clin Pathol. 1985. 38:1321–1336.4. Crawford FG, Vermund SH. Human cryptosporidiosis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1988. 16:113–159.
Article5. Fayer R. Ungar BLP. Cryptosporidium spp. and Cryptosporidiosis. Microbiol Rev. 1986. 50:458–483.6. Forney JR, Yang S, Healey MC. Protease activity associated with excystation of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts. J Parasitol. 1996. 82:889–892.
Article7. Heine J, Moon HW, Woodmansee DB. Persistent Cryptosporidium infection in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Infect Immun. 1984. 43:856–859.
Article8. Kilani RT, Sekla L. Purification of Cryptosporidium oocysts and sporozoites by cesium chloride and percoll gradients. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1987. 36:505–508.
Article9. Kim HC, Healey MC. Infectivity of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts following cryopreservation. J Parasitol. 2001. 87:1191–1194.
Article10. Mead JR, Arrowood MJ, Sidwell RW, Healey MC. Chronic Cryptosporidium parvum infection in congenitally immunodeficient SCID and nude mice. J Inf Dis. 1991. 163:1297–1304.
Article11. Moore JA, Frenkel JK. Respiratory and enteric cryptosporidiosis in humans. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1991. 115:1160–1162.12. Navin TR, Juranek DD. Cryptosporidiosis: Clinical, epidemiologic, and parasitologic review. Rev Infect Dis. 1984. 6:313–327.
Article13. Nydam DV, Lindergard G, Guard CL, Schaaf SL, Wade SE, Mohammed HO. Serological detection of exposure to Cryptosporidium parvum in cattle by ELISA and its evaluation in relation to coprological tests. Parasitol Res. 2002. 88:797–803.
Article14. O'Donoghue PJ. Cryptosporidium and Cryptosporidiosis in man and animals. Int J Parasitol. 1995. 25:139–195.15. Panciera RJ, Thomassen RW, Garner FM. Cryptosporidial infection in a calf. Vet Pathol. 1971. 8:479–484.
Article16. Perryman LE, Kegerreis KA, Mason PH. Effect of orally administered monoclonal antibody on persistent Cryptosporidium parvum infection in scid mice. Infect Immun. 1993. 61:4906–4908.
Article17. Petersen C. Cryptosporidiosis in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. 15:903–909.
Article18. Pollok RC, Farthing MJ, Bajaj-Elliott M, Sanderson IR, McDonald V. Interferon gamma induces enterocyte resistance against infection by the intracellular pathogen Cryptosporidium parvum. Gastroenterology. 2001. 120:99–107.
Article19. Rasmussen KR, Healey MC. Experimental cryptosporidium parvum infections in immunosuppressed adult mice. Infect Immun. 1992. 60:1648–1652.
Article20. Riggs MW, Schaefer DA, Kapil SJ, Barley-Maloney L, Perryman LE. Efficacy of monoclonal antibodies against defined antigens for passive immunotherapy of chronic gastrointestinal cryptosporidiosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. 46:275–282.
Article21. Tzipori S. Cryptosporidiosis in perspective. Adv Parasitol. 1988. 27:63–129.
Article22. Tzipori S, Ward H. Cryptosporidiosis: biology, pathogenesis and disease. Microbes Infect. 2002. 4:1047–1058.
Article23. Yang S, Healey MC. The immunosuppressive effects of dexamethasone adminiatered in drinking water to C57BL/6N mice infected with Cryptosporidium parvum. J Parasitol. 1993. 79:626–630.
Article24. Yang S, Healey MC. Patent gut infections in immunosuppressed adult C57BL/6N mice following intraperitoneal injection of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts. J Parasitol. 1994. 80:338–342.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Resistance to gamma-Irradiation between Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium muris Using In Vivo Infection
- Resistance of Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts following commercial bleach treatment
- Role of murine Peyer's patch lymphocytes against primary and challenge infections with Cryptosporidium parvum
- Genotype and animal infectivity of a human isolate of Cryptosporidium parvum in the Republic of Korea
- Time gap between oocyst shedding and antibody responses in mice infected with Cryptosporidium parvum