Korean J Radiol.
2009 Dec;10(6):645-648. 10.3348/kjr.2009.10.6.645.
Metastatic Gastric Linitis Plastica from Bladder Cancer Mimicking a Primary Gastric Carcinoma: a Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 150-713, Korea. bookdoo7@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul 150-713, Korea.
- KMID: 1102570
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2009.10.6.645
Abstract
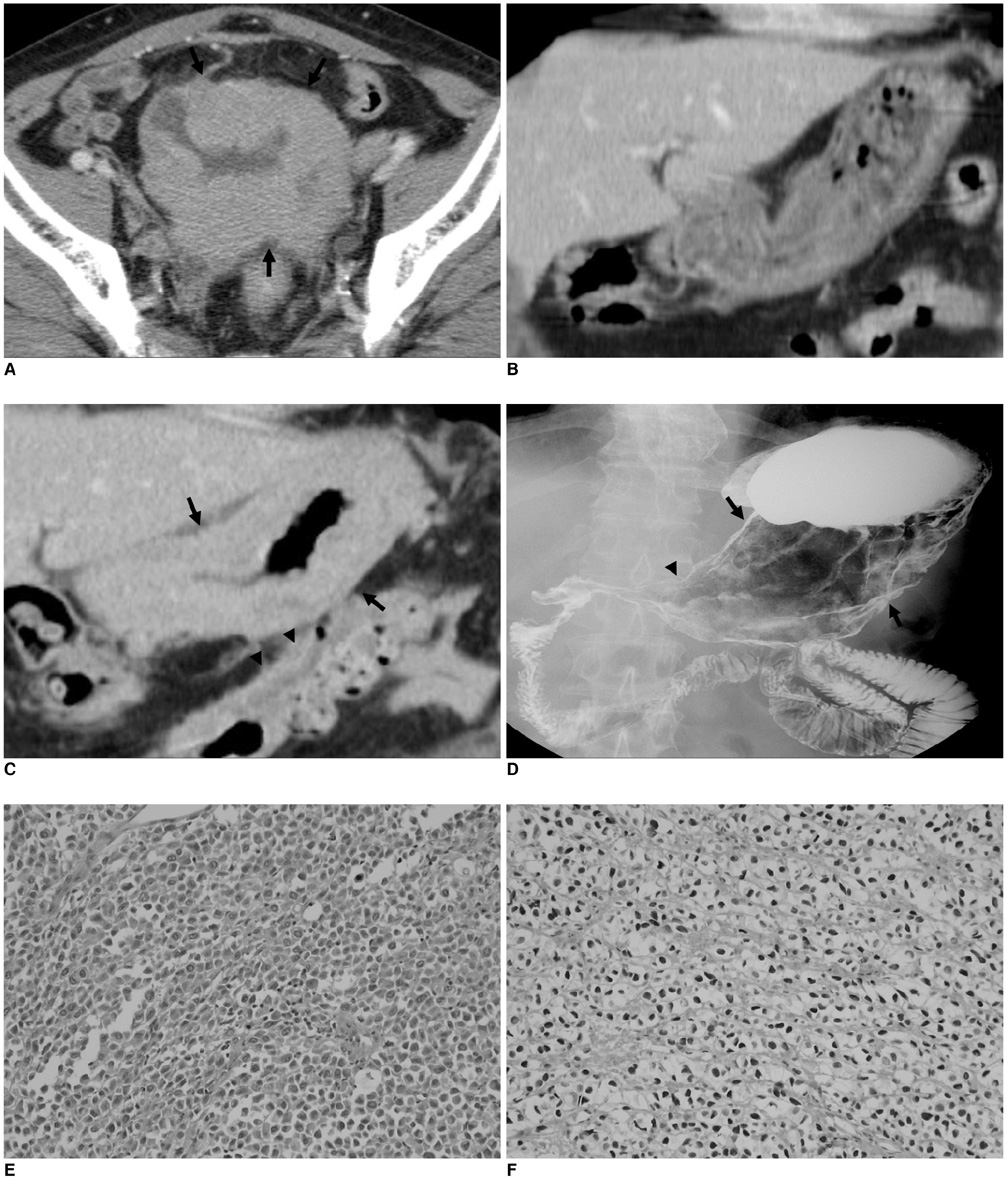
- Primary gastric carcinoma is the most common cause of linitis plastica. Less frequently, metastatic gastric cancer from the breast, omental metastases and non-Hodgkin lymphoma involving the stomach have been reported to show similar radiographic findings as for linitis plastica. A metastatic gastric cancer from bladder cancer is extremely rare. We present an unusual case, the first to our knowledge, of gastric linitis plastica that resulted from a metastatic urothelial carcinoma of the bladder.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gore RM, Levine MS. Textbook of gastrointestinal radiology. 2008. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;628–649.2. Kim SY, Kim KW, Kim AY, Ha HK, Kim JS, Park SH, et al. Bloodborne metastatic tumors to the gastrointestinal tract: CT findings with clinicopathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:1618–1626.3. Menuck LS, Amberg JR. Metastatic disease involving the stomach. Am J Dig Dis. 1975. 20:903–913.4. Wallmeroth A, Wagner U, Moch H, Gasser TC, Sauter G, Mihatsch MJ. Patterns of metastasis in muscle-invasive bladder cancer (pT2-4): an autopsy study on 367 patients. Urol Int. 1999. 62:69–75.5. Pak K, Ishida A, Arai Y, Tomoyoshi T. An autopsy case of untreated bladder cancer. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1987. 33:1261–1265.6. Kanne JP, Mankoff DA, Baird GS, Minoshima S, Livingston RB. Gastric linitis plastica from metastatic breast carcinoma: FDG and FES PET appearances. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007. 188:W503–W505.7. Levine MS, Kong V, Rubesin SE, Laufer I, Herlinger H. Schirrous carcinoma of the stomach: radiologic and endoscopic diagnosis. Radiology. 1990. 175:151–154.8. Ha HK, Jee KR, Yu E, Yu CS, Rha SE, Lee IJ, et al. CT features of metastatic linitis plastica to the rectum in patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:463–466.9. Gollub MJ, Schwartz MB, Shia J. Scirrhous metastases to the gastrointestinal tract at CT: the malignant target sign. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009. 192:936–940.10. Kunju LP, Mehra R, Snyder M, Shah RB. Prostate-specific antigen, high-molecular-weight cytokeratin (clone 34betaE12), and/or p63: an optimal immunohistochemical panel to distinguish poorly differentiated prostate adenocarcinoma from urothelial carcinoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 2006. 125:675–681.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Linitis Plastica of the Rectum: A Clinico-Pathologic Analysis of Five Cases with Special Reference to Comparison with Gastric Form
- Primary Linitis Plastica of the Colon with Mucinous Adenocarcinoma in Young Woman
- Synchronously Diagnosed Gastric Metastasis from Invasive Lobular Breast Carcinoma, Mimicking Primary Gastric Carcinoma
- A Case of Gastric Syphilis Mimicking Advanced Gastric Cancer
- Primary Gastric Small Cell Carcinoma (Presenting as Linitis Plastica) Diagnosed Using Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Biopsy: A Case Report