J Vet Sci.
2006 Sep;7(3):271-275. 10.4142/jvs.2006.7.3.271.
Development and evaluation of indirect ELISA for the detection of antibodies against Japanese encephalitis virus in swine
- Affiliations
-
- 1National Veterinary Research and Quarantine Service, Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Anyang 430-824, Korea. yangdk@nvrqs.go.kr
- KMID: 1089912
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2006.7.3.271
Abstract
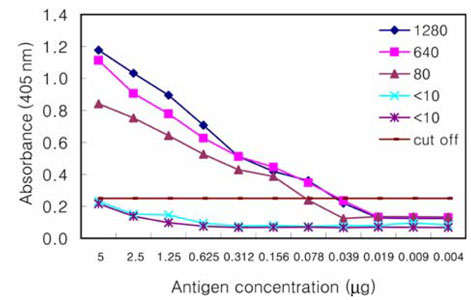
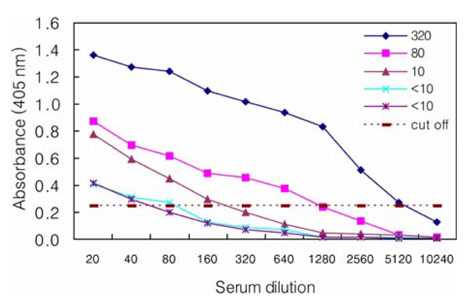
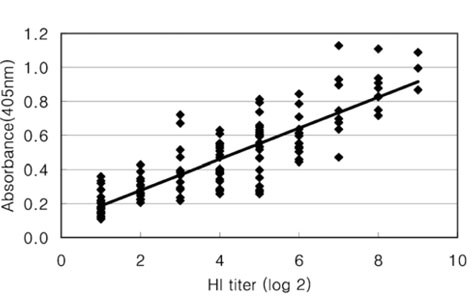
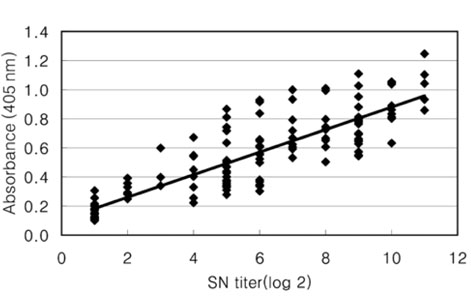
- The Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is one of causative agents of reproductive failure in pregnant sows. An indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (I-ELISA) was examined for its potential use in the rapid monitoring of the JEV, and the results were compared with those from the hemagglutination inhibition (HI) and serum neutralization (SN) tests. The comparative analysis showed that the results of I-ELISA showed a significant correlation with the conventional HI (r = 0.867) and SN tests (r = 0.804), respectively. When the I-ELISA results were compared with the traditional diagnostic assays, the sensitivity of the I-ELISA was 94.3% with the HI test and 93.7% with the SN test, respectively. The specificity was found to be 81.4% and 80.0% with the HI and SN tests, respectively. To determine the applicability of I-ELISA in the field, the serum samples from 720 pigs were collected from 4 regions in Korea between July and August 2004. The results indicated that 21.7% of screened pigs were seropositive for the JEV. The seropositive rates of JEV in the 4 provinces were 12.6% in Gyeonggi, 45.0% in Gyeongnam, 16.7% in Jeonbuk, and 12.2% in Jeju. The I-ELISA methodology developed in this study was shown to have considerable sensitivity and specificity through a comparison with HI and the SN tests. Therefore, it might be one of convenient methods for screening a large number of samples in various fields.
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Antibodies, Viral/blood
Antigens, Viral/immunology
Encephalitis Virus, Japanese/immunology/*isolation&purification
Encephalitis, Japanese/blood/immunology/*veterinary/virology
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay/methods/*veterinary
Female
Hemagglutination Inhibition Tests/veterinary
Korea
Neutralization Tests/veterinary
Swine
Swine Diseases/blood/immunology/*virology
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
The seroprevalence of Japanese encephalitis virus in goats raised in Korea
Dong-Kun Yang, Chang-Hee Kweon, Byoung-Han Kim, In-Jin Hwang, Mun-Il Kang, Byung-Jae So, Kyoung-Oh Cho
J Vet Sci. 2007;8(2):197-199. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.2.197.Development and Evaluation of Indirect ELISA for Detection of Antibodies to Getah Virus in Horse Serum
Seung Heon Lee, Dong-Kun Yang, Ha-Hyun Kim, Hyun-Ye Jo, Sung-Suk Choi, In-Soo Cho
J Bacteriol Virol. 2016;46(2):63-77. doi: 10.4167/jbv.2016.46.2.63.
Reference
-
1. Burke DS, Monath TP. Fields Virology. 2001. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott;991–1024.2. Chang KJ. Seasonal prevalence of anti-Japanese encephalitis virus antibody in pigs in different regions of Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002. 35:12–16.3. Chen WR, Tesh RB, Rico-Hesse R. Genetic variation of Japanese encephalitis virus in nature. J Gen Virol. 1990. 71:2915–2922.
Article4. Chow VT, Yong RY, Ngoh BL, Chan YC. Automated type specific ELISA probe detection of amplified NS3 gene products of dengue viruses. J Clin Pathol. 1997. 50:346–349.
Article5. Clarke DH, Casals J. Techniques for hemagglutination and hemagglutination-inhibition with arthropod-borne viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1958. 7:561–573.
Article6. Kwon HJ, Lee CK, Kang BJ, Lim YM. Studies on Japanese encephalitis live vaccine. I. Isolation of Japanese encephalitis virus (Anyang strain) from a new-born piglet. Res Rep Off Rural Dev. 1974. 18:21–28.7. Konishi E, Yamaoka M. Evaluation of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantitation of antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus in swine sera. J Virol Methods. 1982. 5:247–253.
Article8. Konishi E, Yamaoka M. Rapid enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of whole blood for detection of antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol Methods. 1983. 7:21–28.
Article9. Konishi E, Mason PW, Shope RE. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using recombinant antigens for serodiagnosis of Japanese encephalitis. J Med Virol. 1996. 48:76–79.
Article10. Marx F, Gritsun TS, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Gould EA. Diagnostic immunoassays for tick-borne encephalitis virus based on recombinant baculovirus protein expression. J Virol Methods. 2001. 91:75–84.
Article11. Paranjpe S, Banerjee K. Detection of Japanese encephalitis virus by reverse transcription/polymerase chain reaction. Acta Virol. 1998. 42:5–11.12. See E, Tan HC, Wang D, Ooi EE, Lee MA. Presence of hemagglutination inhibition and neutralization antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus in wild pigs on an offshore island in Singapore. Acta Trop. 2002. 81:233–236.
Article13. Shu PY, Chen LK, Chang SF, Yueh YY, Chow L, Chien LJ, Chin C, Lin TH, Huang JH. Antibody to the nonstructural protein NS1 of Japanese encephalitis virus: potential application of mAb-based indirect ELISA to differentiate infection from vaccination. Vaccine. 2001. 19:1753–1763.
Article14. Solomon T, Thao LT, Dung NM, Kneen R, Hung NT, Nisalak A, Vaughn DW, Farrar J, Hien TT, White NJ, Cardosa MJ. Rapid diagnosis of Japanese encephalitis by using an immunoglobulin M dot enzyme immunoassay. J Clin Microbiol. 1998. 36:2030–2034.
Article15. Ting SH, See E, Tan HC, Lee MA, Ooi EE. Development of a simplified assay for the detection of neutralizing antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus. J Virol Methods. 2001. 93:43–47.
Article16. Ting SH, Tan HC, Wong WK, Ng ML, Chan SH, Ooi EE. Seroepidemiology of neutralizing antibodies to Japanese encephalitis virus in Singapore: continued transmission despite abolishment of pig farming? Acta Trop. 2004. 92:187–191.
Article17. Xinglin J, Huanchun C, Xiang W, Changming Q. Quantitative and qualitative study of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to detect IgG against Japanese encephalitis virus in swine sera. Vet Res Commun. 2005. 29:159–169.
Article18. Yamamoto A, Nakayama M, Kurosawa Y, Sugo K, Karasawa H, Ogawa T, Takasaki T, Tashiro M, Kurane I. Development of a particle agglutination assay system for detecting Japanese encephalitis virus-specific human IgM, using hydroxyapatite-coated nylon beads. J Virol Methods. 2002. 104:195–201.
Article19. Yang DK, Kim BH, Kweon CH, Kwon JH, Lim SI, Han HR. Biophysical characterization of Japanese encephalitis virus (KV1899) isolated from pigs in Korea. J Vet Sci. 2004. 5:125–130.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Improvement of indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of Japanese encephalitis virus antibodies in swine sera
- Haemagglutination inhibition antibodies of Japanese encephalitis virus to bats, Korea
- Development of a blocking ELISA for detection of Japanese encephalitis virus antibodies in pig and horse sera
- Serological and molecular epidemiology of Japanese encephalitis virus infections in swine herds in China, 2006–2012
- Detection of Neutralizing Antibody Against Japanese Encephalitis Virus in Wild Boars of Korea