J Vet Sci.
2007 Jun;8(2):175-180. 10.4142/jvs.2007.8.2.175.
Purification and characterization of two larval glycoproteins from the cattle tick, Boophilus annulatus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Molecular Biology Department, National Research Centre, Cairo, Egypt. yassershahein_nrc@yahoo.com
- 2Radiation Biology Department, NCRRT, Cairo, Egypt.
- 3Animal Health Department, Desert Research Centre, Mataria, Cairo, Egypt.
- KMID: 1089670
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2007.8.2.175
Abstract
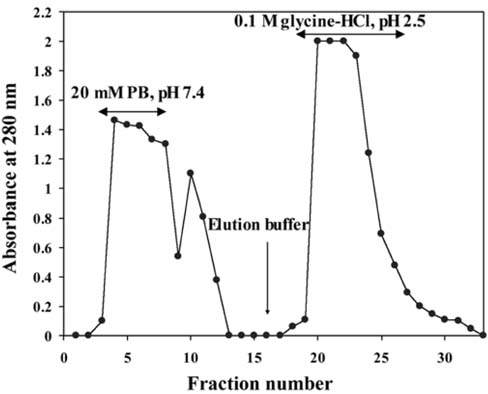
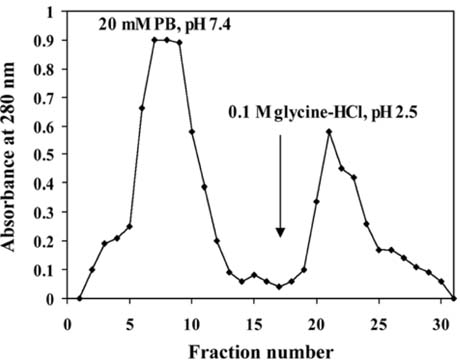
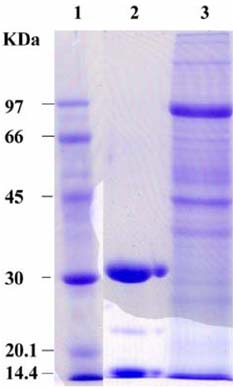
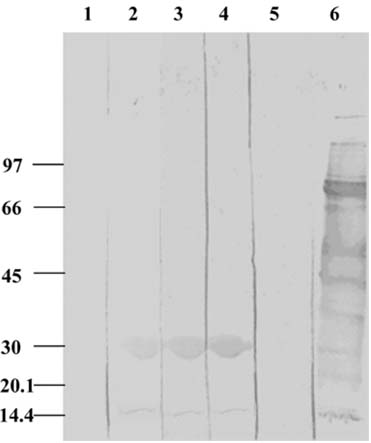
- The present study was conducted to identify new target immunogenic molecules from the larval stage of the cattle tick, Boophilus annulatus (Acari: Ixodidae). Two specific larval glycoproteins (GLPs) were isolated by two-step affinity chromatography. The larval immunogens were first purified with CNBr-Sepharose coupled to rabbit anti-larval immunoglobulins, and the glycoproteins were then purified with Con-A Sepharose. These glycoproteins have molecular weights of approximately 32 and 15 kDa with isoelectric points between 6.8 and 7.2. Antibodies against the two GLPs, labeled I and II, were detected in the anti-whole tick, -whole larval, and -gut antigens through immunoblot analysis. These results suggest that these GLPs are good immunogens and can be useful in the vaccination of cattle against tick infestation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Amino Acid Sequence
Animals
Cattle
Cattle Diseases/immunology/*parasitology/prevention & control
Chromatography, Affinity
Electrophoresis, Polyacrylamide Gel
Glycoproteins/immunology/*isolation & purification
Immunoblotting
Isoelectric Focusing
Ixodidae/chemistry/*immunology
Male
Molecular Weight
Rabbits
Sequence Analysis, Protein
Tick Infestations/immunology/parasitology/prevention & control/*veterinary
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aguirre DH, Viñabal AE, Salatin AO, Cafrune MM, Volpogni MM, Mangold AJ, Guglielmone AA. Susceptibility to two pyrethroids in Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) populations of northwest Argentina. Preliminary results. Vet Parasitol. 2000. 88:329–333.2. Allen JR, Humphreys SJ. Immunisation of guinea pigs and cattle against ticks. Nature. 1979. 280:491–493.
Article3. Bradford MM. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976. 72:248–254.
Article4. Brown SJ, Askenase PW. Amblyomma americanum: physiochemical isolation of a protein derived from the tick salivary gland that is capable of inducing immune resistance in guinea pigs. Exp Parasitol. 1986. 62:40–50.
Article5. Canales M, Enriquez A, Ramos E, Cabrera D, Dandie H, Soto A, Falcon V, Rodriguez M, de la Fuente J. Large-scale production in Pichia pastoris of the recombinant vaccine Gavac against cattle tick. Vaccine. 1997. 15:414–422.
Article6. Das G, Ghosh S, Khan MH, Sharma JK. Immunization of cross-bred cattle against Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum by purified antigens. Exp Appl Acarol. 2000. 24:645–659.7. Garcia-Garcia JC, Montero C, Redondo M, Vargas M, Canales M, Boue O, Rodriguez M, Joglar M, Machado H, Gonzalez IL, Valdes M, Mendez L, de la Fuente J. Control of ticks resistant to immunization with Bm86 in cattle vaccinated with the recombinant antigen Bm95 isolated from the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus. Vaccine. 2000. 18:2275–2287.
Article8. Garfin DE. Isoelectric focusing. Methods Enzymol. 1990. 182:459–477.
Article9. Ghosh S, Khan MH. Immunization of cattle against Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum using larval antigens. Indian J Exp Biol. 1999. 37:203–205.10. Ghosh S, Khan MH, Ahmed N. Cross-bred cattle protected against Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum by larval antigens purified by immunoaffinity chromatography. Trop Anim Health Prod. 1999. 31:263–273.11. Ghosh S, Khan MH, Gupta SC. Immunization of rabbits against Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum using homogenates from unfed immature ticks. Indian J Exp Biol. 1998. 36:167–170.12. Ghosh S, Singh NK, Das G. Assessment of duration of immunity in crossbred cattle immunized with glycoproteins isolated from Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum and Boophilus microplus. Parasitol Res. 2005. 95:319–326.
Article13. Laemmli UK. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970. 227:680–685.
Article14. Lodos J, Boue O, de la Fuente J. A model to simulate the effect of vaccination against Boophilus ticks on cattle. Vet Parasitol. 2000. 87:315–326.
Article15. McKenna RV, Riding GA, Jarmey JM, Pearson RD, Willadsen P. Vaccination of cattle against the Boophilus microplus using a mucin-like membrane glycoprotein. Parasite Immunol. 1998. 20:325–336.
Article16. Nolan J. Acaricide resistance in single and multi-host ticks and strategies for control. Parassitologia. 1990. 32:145–153.17. Patrick CD, Hair JA. Laboratory rearing procedures and equipment for multi-host ticks (Acarina: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1975. 12:389–390.
Article18. Pruett JH. Immunological control of arthropod ectoparasites-a review. Int J Parasitol. 1999. 29:25–32.
Article19. Rabilloud T, Carpentier G, Tarroux P. Improvement and simplification of low-background silver staining of proteins by using sodium dithionite. Electrophoresis. 1988. 9:288–291.
Article20. Riding GA, Jarmey J, McKenna RV, Pearson R, Cobon GS, Willadsen P. A protective "concealed" antigen from Boophilus microplus. Purification, localization and possible function. J Immunol. 1994. 153:5158–5166.21. Rodríguez M, Rubiera R, Penichet M, Montesinos R, Cremata J, Falcón V, Sánchez G, Bringas R, Cordovés C, Valdés M, Lleonart R, Herrera L, de la Fuente J. High level expression of the B. microplus Bm86 antigen in the yeast Pichia pastoris forming highly immunogenic particles for cattle. J Biotechnol. 1994. 33:135–146.
Article22. Sharma JK, Ghosh S, Khan MH, Das G. Immunoprotective efficacy of a purified 39 kDa nymphal antigen of Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2001. 33:103–116.23. Singh NK, Ghosh S. Experimental immunisation of crossbred cattle with glycoproteins isolated from the larvae of Hyalomma anatolicum anatolicum and Boophilus microplus. Exp Appl Acarol. 2003. 31:297–314.
Article24. Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1979. 76:4350–4354.
Article25. Willadsen P. Anti-tick vaccines. Parasitology. 2004. 129:Suppl S1. S367–S387.
Article26. Willadsen P. Novel vaccines for ectoparasites. Vet Parasitol. 1997. 71:209–222.
Article27. Willadsen P, Bird P, Cobon GS, Hungerford J. Commercialisation of a recombinant vaccine against Boophilus microplus. Parasitology. 1995. 110:Suppl S1. S43–S50.28. Willadsen P, Kemp DH. Vaccination with 'concealed' antigens for tick control. Parasitol Today. 1988. 4:196–198.
Article29. Willadsen P, Riding GA, McKenna RV, Kemp DH, Tellam RL, Nielsen JN, Lahnstein J, Cobon GS, Gough JM. Immunologic control of a parasitic arthropod. Identification of a protective antigen from Boophilus microplus. J Immunol. 1989. 143:1346–1351.30. Wong JYM, Opdebeeck JP. Larval membrane antigens protect Hereford cattle against infestation with Boophilus microplus. Parasite Immunol. 1990. 12:75–83.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prevalence of ixodid ticks on cattle in Mazandaran province, Iran
- Epizootiological study of theileriasis in Korea - Prevalence of the bovine theileriasis in relation to its vector, Haemaphysalis (Kaiseriana) longicornis Neumann. 1901
- Biological Parameters of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Fed on Rabbits, Sheep, and Cattle
- Evaluation of glycoproteins purified from adult and larval camel ticks (Hyalomma dromedarii) as a candidate vaccine
- Tick Bite by Larval Hemaphysalislongicornis