Yonsei Med J.
2010 Sep;51(5):672-675. 10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.672.
Initial Experiences with Proton MR Spectroscopy in Treatment Monitoring of Mitochondrial Encephalopathy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. slee@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Pediatric Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1071417
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2010.51.5.672
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Mitochondrial encephalopathy (ME) is a rare disorder of energy metabolism. The disease course can roughly be evaluated by clinical findings. The purpose of this study was to evaluate metabolic spectral changes using proton MR spectroscopy (MRS), and to establish a way to monitor ME by neuroimaging.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Proton MRS data were retrospectively reviewed in 12 patients with muscle biopsy-confirmed ME (M : F = 7 : 5, Mean age = 4.8 years). All received 1H-MRS initially and also after a ketogenic diet and mitochondrial disease treatment cocktail (follow up average was 10.2 months). Changes of N-acetylaspartate/creatine (NAA/Cr) ratio, choline/creatine (Cho/Cr) ratio, and lactate peak in basal ganglia at 1.2 ppm were evaluated before and after treatment. Findings on conventional T2 weighted MR images were also evaluated.
RESULTS
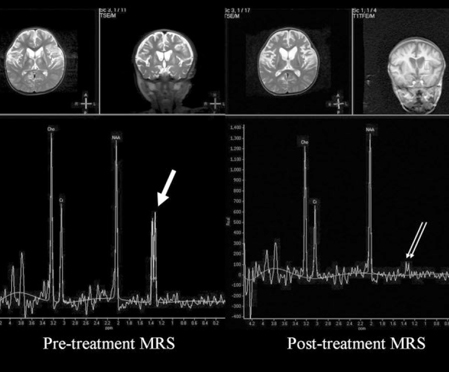
On conventional MRI, increased basal ganglia T2 signal intensity was the most common finding with ME (n = 9, 75%), followed by diffuse cerebral atrophy (n = 8, 67%), T2 hyperintense lesions at pons and midbrain (n = 4, 33%), and brain atrophy (n = 2, 17%). Lactate peak was found in 4 patients; 2 had disappearance of the peak on follow up MRS. Quantitative analysis showed relative decrease of Cho/Cr ratio on follow up MRS (p = 0.0058, paired t-test, two-tailed). There was no significant change in NAA/Cr ratio.
CONCLUSION
MRS is a useful tool for monitoring disease progression or impro-vement in ME, and decrease or disappearance of lactate peak and reduction of Cho/Cr fraction were correlated well with improvement of clinical symptoms.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Longo N. Mitochondrial encephalopathy. Neurol Clin. 2003. 21:817–831.
Article2. Chinnery PF, Turnbull DM. Clinical features, investigation, and management of patients with defects of mitochondrial DNA. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1997. 63:559–563.
Article3. Kang HC, Lee YM, Kim HD, Lee JS, Slama A. Safe and effective use of the ketogenic diet in children with epilepsy and mitochondrial respiratory chain complex defects. Epilepsia. 2007. 48:82–88.4. Kang HC, Kim HD, Lee YM, Han SH. Landau-Kleffner syndrome with mitochondrial respiratory chain-complex I deficiency. Pediatr Neurol. 2006. 35:158–161.
Article5. Yonemura K, Hasegawa Y, Kimura K, Minematsu K, Yamaguchi T. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in a case of mitochondrial myopathy, encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, and strokelike episodes. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001. 22:269–272.6. Clark JM, Marks MP, Adalsteinsson E, Spielman DM, Shuster D, Horoupian D, et al. MELAS: Clinical and pathologic correlations with MRI, xenon/CT, and MR spectroscopy. Neurology. 1996. 46:223–227.7. Barragán-Campos HM, Vallée JN, Lô D, Barrera-Ramírez CF, Argote-Greene M, Sánchez-Guerrero J, et al. Brain magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with mitochondrial cytopathies. Arch Neurol. 2005. 62:737–742.
Article8. Bianchi MC, Tosetti M, Battini R, Manca ML, Mancuso M, Cioni G, et al. Proton MR spectroscopy of mitochondrial diseases: analysis of brain metabolic abnormalities and their possible diagnostic relevance. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003. 24:1958–1966.9. Flemming K, Ulmer S, Duisberg B, Hahn A, Jansen O. MR spectroscopic findings in a case of Alpers-Huttenlocher syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 23:1421–1423.10. Pavlakis SG, Kingsley PB, Kaplan GP, Stacpoole PW, O'Shea M, Lustbader D. Magnetic resonance spectroscopy: use in monitoring MELAS treatment. Arch Neurol. 1998. 55:849–852.11. Salvan A, Vion-Dury J, Confort-Gouny S, Sangla I, Pouget J, Cozzone PJ. Brain metabolic profiles obtained by proton MRS in two forms of mitochondriopathies: Leber's hereditary optic neuropathy and chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia. Eur Neurol. 1998. 40:46–49.
Article12. Möller HE, Wiedermann D, Kurlemann G, Hilbich T, Schuierer G. Application of NMR spectroscopy to monitoring MELAS treatment: a case report. Muscle Nerve. 2002. 25:593–600.
Article13. Kuhl CK, Layer G, Träber F, Zierz S, Block W, Reiser M. Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy: correlation of P-31 exercise MR spectroscopy with clinical findings. Radiology. 1994. 192:223–230.
Article14. Kolb SJ, Costello F, Lee AG, White M, Wong S, Schwartz ED, et al. Distinguishing ischemic stroke from the stroke-like lesions of MELAS using apparent diffusion coefficient mapping. J Neurol Sci. 2003. 216:11–15.
Article15. Kim HS, Kim DI, Lee BI, Jeong EK, Choi C, Lee JD, et al. Diffusion-weighted image and MR spectroscopic analysis of a case of MELAS with repeated attacks. Yonsei Med J. 2001. 42:128–133.
Article16. Erickson JC, Jabbari B, Difazio MP. Basal ganglia injury as a complication of the ketogenic diet. Mov Disord. 2003. 18:448–451.
Article17. Prasad AN, Stafstrom CF, Holmes GL. Alternative epilepsy therapies: the ketogenic diet, immunoglobulins, and steroids. Epilepsia. 1996. 37:Suppl 1. S81–S95.
Article18. Pouwels PJ, Brockmann K, Kruse B, Wilken B, Wick M, Hanefeld F, et al. Regional age dependence of human brain metabolites from infancy to adulthood as detected by quantitative localized proton MRS. Pediatr Res. 1999. 46:474–485.
Article19. Gupta RK, Bhatia V, Poptani H, Gujral RB. Brain metabolite changes on in vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in children with congenital hypothyroidism. J Pediatr. 1995. 126:389–392.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy: Diffusion MR Imaging and Localized Proton MR Spectroscopic Findings in Two Infants
- Arterial Spin Labelling Perfusion, Proton MR Spectroscopy and Susceptibility-Weighted MR Findings of Acute Necrotizing Encephalopathy: a Case Report
- Localized Proton MR Spectroscopic Detection of Nonketotic Hyperglycinemia in an Infant
- Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Findings in Cirrhotic Patients with Hepatic Encephalopathy : The Significance of Decreased Myoinositol / Creatine Ratio
- In vivo Proton MR Spectroscopic Findings of Focal Hepatic Lesions: Initial Experience