Korean J Radiol.
2012 Feb;13(1):20-26. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.1.20.
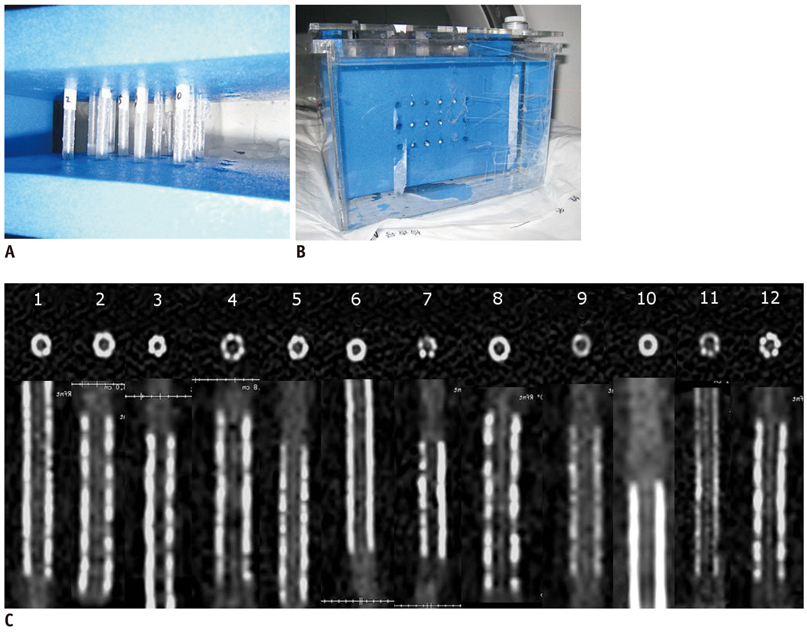
High-Definition Computed Tomography for Coronary Artery Stent Imaging: a Phantom Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Rui Jin Hospital, Medical School, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200025, P. R. China. chenkeminrjrd@hotmail.com
- 2CT Laboratory of GE Healthcare, Beijing Economic and Technology Development Area, Beijing, China.
- KMID: 1058789
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.1.20
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the performance of a high-definition CT (HDCT) for imaging small caliber coronary stents (< or = 3 mm) by comparing different scan modes of a conventional 64-row standard-definition CT (SDCT).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A cardiac phantom with twelve stents (2.5 mm and 3.0 mm in diameter) was scanned by HDCT and SDCT. The scan modes were retrospective electrocardiography (ECG)-gated helical and prospective ECG-triggered axial with tube voltages of 120 kVp and 100 kVp, respectively. The inner stent diameters (ISD) and the in-stent attenuation value (AVin-stent) and the in-vessel extra-stent attenuation value (AVin-vessel) were measured by two observers. The artificial lumen narrowing (ALN = [ISD - ISDmeasured]/ISD) and artificial attenuation increase between in-stent and in-vessel (AAI = AVin-stent - AVin-vessel) were calculated. All data was analyzed by intraclass correlation and ANOVA-test.
RESULTS
The correlation coefficient of ISD, AVin-vessel and AVin-stent between the two observers was good. The ALNs of HDCT were statistically lower than that of SDCT (30 +/- 5.7% versus 35 +/- 5.4%, p < 0.05). HDCT had statistically lower AAI values than SDCT (15.7 +/- 81.4 HU versus 71.4 +/- 90.5 HU, p < 0.05). The prospective axial dataset demonstrated smaller ALN than the retrospective helical dataset on both HDCT and SDCT (p < 0.05). Additionally, there were no differences in ALN between the 120 kVp and 100 kVp tube voltages on HDCT (p = 0.05).
CONCLUSION
High-definition CT helps improve measurement accuracy for imaging coronary stents compared to SDCT. HDCT with 100 kVp and the prospective ECG-triggered axial technique, with a lower radiation dose than 120 kVp application, may be advantageous in evaluating coronary stents with smaller calibers (< or = 3 mm).
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Holmes DR Jr, Leon MB, Moses JW, Popma JJ, Cutlip D, Fitzgerald PJ, et al. Analysis of 1-year clinical outcomes in the SIRIUS trial: a randomized trial of a sirolimus-eluting stent versus a standard stent in patients at high risk for coronary restenosis. Circulation. 2004. 109:634–640.2. Morice MC, Colombo A, Meier B, Serruys P, Tamburino C, Guagliumi G, et al. Sirolimus- vs paclitaxel-eluting stents in de novo coronary artery lesions: the REALITY trial: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2006. 295:895–904.3. Fischman DL, Leon MB, Baim DS, Schatz RA, Savage MP, Penn I, et al. A randomized comparison of coronary-stent placement and balloon angioplasty in the treatment of coronary artery disease. Stent Restenosis Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1994. 331:496–501.4. King SB 3rd, Smith SC Jr, Hirshfeld JW Jr, Jacobs AK, Morrison DA, Williams DO, et al. 2007 focused update of the ACC/AHA/SCAI 2005 guideline update for percutaneous coronary intervention: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. 51:172–209.5. Seifarth H, Ozgun M, Raupach R, Flohr T, Heindel W, Fischbach R, et al. 64- versus 16-slice CT angiography for coronary artery stent assessment: in vitro experience. Invest Radiol. 2006. 41:22–27.6. Das KM, El-Menyar AA, Salam AM, Singh R, Dabdoob WA, Albinali HA, et al. Contrast-enhanced 64-section coronary multidetector CT angiography versus conventional coronary angiography for stent assessment. Radiology. 2007. 245:424–432.7. Schuijf JD, Pundziute G, Jukema JW, Lamb HJ, Tuinenburg JC, van der Hoeven BL, et al. Evaluation of patients with previous coronary stent implantation with 64-section CT. Radiology. 2007. 245:416–423.8. Ehara M, Surmely JF, Kawai M, Katoh O, Matsubara T, Terashima M, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of 64-slice computed tomography for detecting angiographically significant coronary artery stenosis in an unselected consecutive patient population: comparison with conventional invasive angiography. Circ J. 2006. 70:564–571.9. Cademartiri F, Schuijf JD, Pugliese F, Mollet NR, Jukema JW, Maffei E, et al. Usefulness of 64-slice multislice computed tomography coronary angiography to assess in-stent restenosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007. 49:2204–2210.10. Wykrzykowska JJ, Arbab-Zadeh A, Godoy G, Miller JM, Lin S, Vavere A, et al. Assessment of in-stent restenosis using 64-MDCT: analysis of the CORE-64 Multicenter International Trial. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010. 194:85–92.11. Windecker S, Serruys PW, Wandel S, Buszman P, Trznadel S, Linke A, et al. Biolimus-eluting stent with biodegradable polymer versus sirolimus-eluting stent with durable polymer for coronary revascularisation (LEADERS): a randomised non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2008. 372:1163–1173.12. Maintz D, Seifarth H, Raupach R, Flohr T, Rink M, Sommer T, et al. 64-slice multidetector coronary CT angiography: in vitro evaluation of 68 different stents. Eur Radiol. 2006. 16:818–826.13. Suzuki S, Furui S, Kaminaga T, Yamauchi T, Kuwahara S, Yokoyama N, et al. Evaluation of coronary stents in vitro with CT angiography: effect of stent diameter, convolution kernel, and vessel orientation to the z-axis. Circ J. 2005. 69:1124–1131.14. Horiguchi J, Fujioka C, Kiguchi M, Yamamoto H, Kitagawa T, Kohno S, et al. Prospective ECG-triggered axial CT at 140-kV tube voltage improves coronary in-stent restenosis visibility at a lower radiation dose compared with conventional retrospective ECG-gated helical CT. Eur Radiol. 2009. 19:2363–2372.15. Suzuki S, Furui S, Kuwahara S, Mehta D, Kaminaga T, Miyazawa A, et al. Coronary artery stent evaluation using a vascular model at 64-detector row CT: comparison between prospective and retrospective ECG-gated axial scans. Korean J Radiol. 2009. 10:217–226.16. Mahesh M, Cody DD. Physics of cardiac imaging with multiple-row detector CT. Radiographics. 2007. 27:1495–1509.17. Halliburton SS. Options for reducing patient radiation dose with cardiovascular computed tomography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009. 25:153–164.18. Kerl JM, Schoepf UJ, Vogl TJ, Ackermann H, Vogt S, Costello P, et al. In vitro evaluation of metallic coronary artery stents with 64-MDCT using an ECG-gated cardiac phantom: relationship between in-stent visualization, stent type, and heart rate. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010. 194:W256–W262.19. Maintz D, Burg MC, Seifarth H, Bunck AC, Ozgun M, Fischbach R, et al. Update on multidetector coronary CT angiography of coronary stents: in vitro evaluation of 29 different stent types with dual-source CT. Eur Radiol. 2009. 19:42–49.20. Yang WJ, Pan ZL, Zhang H, Pang LF, Guo Y, Chen KM. Evaluation of coronary artery in-stent restenosis with prospectively ECG-triggered axial CT angiography versus retrospective technique: a phantom study. Radiol Med. 2011. 116:189–196.21. Horiguchi J, Kiguchi M, Fujioka C, Shen Y, Arie R, Sunasaka K, et al. Radiation dose, image quality, stenosis measurement, and CT densitometry using ECG-triggered coronary 64-MDCT angiography: a phantom study. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 190:315–320.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Coronary Stent Fracture in a Patient with an Atrial Septal Defect and Severe Pulmonary Hypertension
- MDCT Application for Coronary Artery Intervention
- Undermining and Ballooning the Proximal Part of the Left Main Coronary Artery Stent Resulting in an Iatrogenic Stent Deformation
- Cardiac CT
- A Hybrid Procedure for Coronary Artery Disease with Left Subclavian Artery Stenosis