Korean J Radiol.
2012 Feb;13(1):12-19. 10.3348/kjr.2012.13.1.12.
Dynamic CT Perfusion Imaging for the Detection of Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis in Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Wonju Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Gangwon-do 220-701, Korea. cursor2@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Department of Neurology, Wonju Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Gangwon-do 220-701, Korea.
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, Wonju Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Gangwon-do 220-701, Korea.
- KMID: 1058788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.1.12
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Although the detection of crossed cerebellar diaschisis (CCD) by means of different imaging modalities is well described, little is known about its diagnosis by computed tomography perfusion (CTP) imaging. We investigated the detection rate of CCD by CTP imaging and the factors related to CCD on CTP images in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
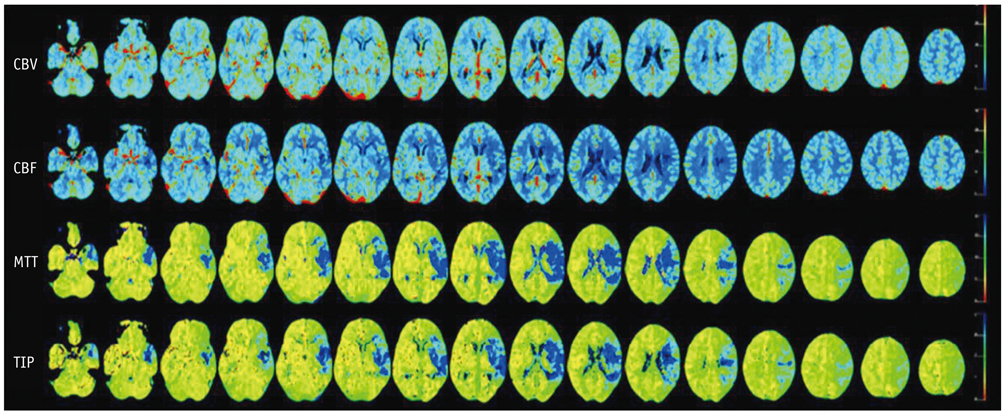
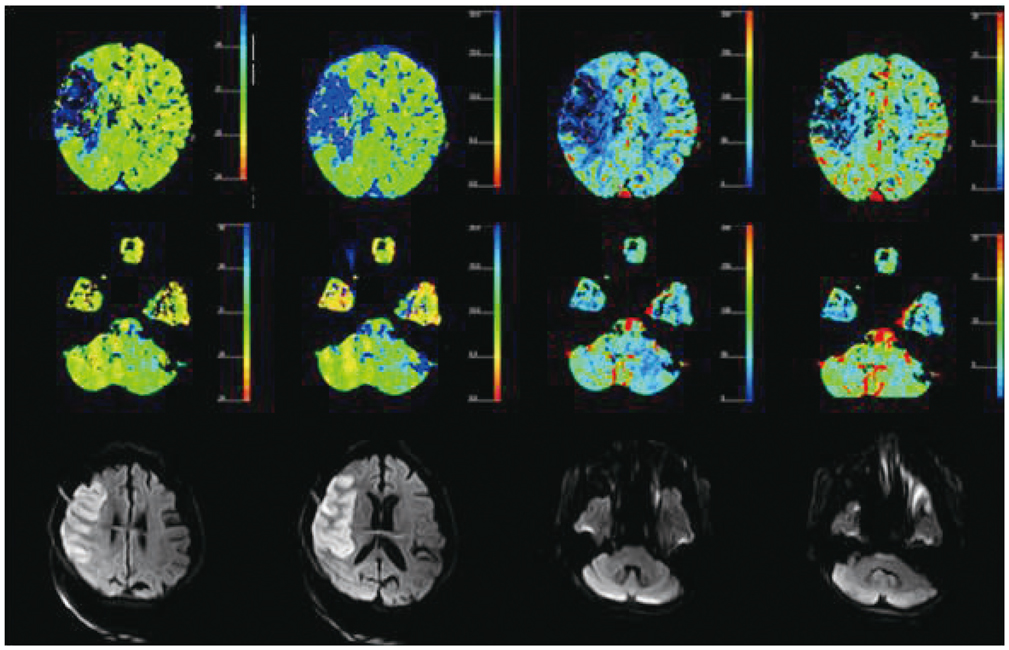
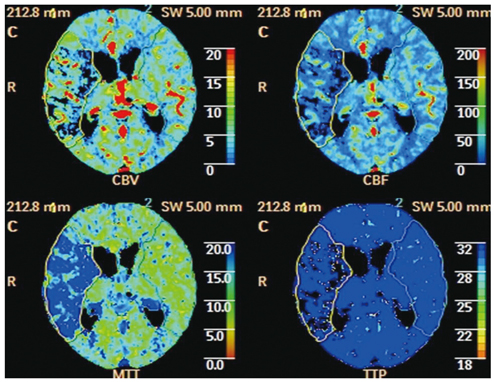
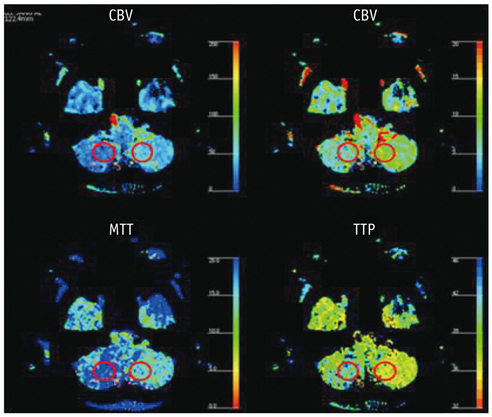
CT perfusion maps of cerebral blood volume (CBV), cerebral blood flow (CBF), mean transit time (MTT), and time-to-peak (TTP) obtained from 81 consecutive patients affected by an acute ischemic stroke were retrospectively reviewed. Whole-brain perfusion maps were obtained with a multichannel CT scanner using the toggling-table technique. The criteria for CCD was a unilateral supratentorial ischemic lesion and an accompanying decrease in perfusion of the contralateral cerebellar hemisphere on the basis of CTP maps by visual inspection without a set threshold. Maps were quantitatively analyzed in CCD positive cases.
RESULTS
The criteria for CCD were fulfilled in 25 of the 81 cases (31%). Detection rates per CTP map were as follows: MTT (31%) > TTP (21%) > CBF (9%) > CBV (6%). Supratentorial ischemic volume, degree of perfusion reduction, and infratentorial asymmetry index correlated strongly (R, 0.555-0.870) and significantly (p < 0.05) with each other in CCD-positive cases.
CONCLUSION
It is possible to detect CCD on all four of the CTP-based maps. Of these maps, MTT is most sensitive in detecting CCD. Our data indicate that CTP imaging is a valid tool for the diagnosis of CCD in patients affected by an acute hemispheric stroke.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Blood Flow Velocity
Cerebellar Diseases/*radiography
Cerebral Angiography/*methods
Cerebrovascular Circulation
Contrast Media/diagnostic use
Female
Humans
Iohexol/diagnostic use
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Male
Radiographic Image Interpretation, Computer-Assisted
Retrospective Studies
Stroke/*radiography
Tomography, X-Ray Computed/*methods
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baron JC, Bousser MG, Comar D, Castaigne P. "Crossed cerebellar diaschisis" in human supratentorial brain infarction. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1981. 105:459–461.2. Feeney DM, Baron JC. Diaschisis. Stroke. 1986. 17:817–830.3. Gold L, Lauritzen M. Neuronal deactivation explains decreased cerebellar blood flow in response to focal cerebral ischemia or suppressed neocortical function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002. 99:7699–7704.4. Chakravarty A. MR evaluation of crossed and uncrossed cerebral-cerebellar diaschisis. Acta Neurol Scand. 2003. 108:60–65.5. Takasawa M, Watanabe M, Yamamoto S, Hoshi T, Sasaki T, Hashikawa K, et al. Prognostic value of subacute crossed cerebellar diaschisis: single-photon emission CT study in patients with middle cerebral artery territory infarct. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002. 23:189–193.6. Sobesky J, Thiel A, Ghaemi M, Hilker RH, Rudolf J, Jacobs AH, et al. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute human stroke: a PET study of serial changes and response to supratentorial reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005. 25:1685–1691.7. Lin DD, Kleinman JT, Wityk RJ, Gottesman RF, Hillis AE, Lee AW, et al. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute stroke detected by dynamic susceptibility contrast MR perfusion imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009. 30:710–715.8. Yamada H, Koshimoto Y, Sadato N, Kawashima Y, Tanaka M, Tsuchida C, et al. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis: assessment with dynamic susceptibility contrast MR imaging. Radiology. 1999. 210:558–562.9. Wintermark M, Maeder P, Thiran JP, Schnyder P, Meuli R. Quantitative assessment of regional cerebral blood flows by perfusion CT studies at low injection rates: a critical review of the underlying theoretical models. Eur Radiol. 2001. 11:1220–1230.10. Axel L. Tissue mean transit time from dynamic computed tomography by a simple deconvolution technique. Invest Radiol. 1983. 18:94–99.11. Furtado AD, Lau BC, Vittinghoff E, Dillon WP, Smith WS, Rigby T, et al. Optimal brain perfusion CT coverage in patients with acute middle cerebral artery stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010. 31:691–695.12. Zilkha E, Ladurner G, Iliff LD, Du Boulay GH, Marshall J. Computer subtraction in regional cerebral blood-volume measurements using the EMI-Scanner. Br J Radiol. 1976. 49:330–334.13. Wiesendanger M. Constantin von Monakow (1853-1930): a pioneer in interdisciplinary brain research and a humanist. C R Biol. 2006. 329:406–418.14. Garg G, Tripathi M, MM DS, Sharma R. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis demonstrated by (18)F-FDG-PET/CT. Hell J Nucl Med. 2009. 12:171–172.15. Liu Y, Karonen JO, Nuutinen J, Vanninen E, Kuikka JT, Vanninen RL. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis in acute ischemic stroke: a study with serial SPECT and MRI. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2007. 27:1724–1732.16. Kajimoto K, Oku N, Kimura Y, Kato H, Tanaka MR, Kanai Y, et al. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis: a positron emission tomography study with L-[methyl-11C]methionine and 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose. Ann Nucl Med. 2007. 21:109–113.17. Youn SW, Kim JH, Weon YC, Kim SH, Han MK, Bae HJ. Perfusion CT of the brain using 40-mm-wide detector and toggling table technique for initial imaging of acute stroke. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008. 191:W120–W126.18. Lee IH, You JH, Lee JY, Whang K, Kim MS, Kim YJ, et al. Accuracy of the detection of infratentorial stroke lesions using perfusion CT: an experimenter-blinded study. Neuroradiology. 2010. 52:1095–1100.19. Yi CA, Na DG, Ryoo JW, Moon CH, Byun HS, Roh HG, et al. Multiphasic perfusion CT in acute middle cerebral artery ischemic stroke: prediction of final infarct volume and correlation with clinical outcome. Korean J Radiol. 2002. 3:163–170.20. Miura H, Nagata K, Hirata Y, Satoh Y, Watahiki Y, Hatazawa J. Evolution of crossed cerebellar diaschisis in middle cerebral artery infarction. J Neuroimaging. 1994. 4:91–96.21. Yamauchi H, Fukuyama H, Kimura J. Hemodynamic and metabolic changes in crossed cerebellar hypoperfusion. Stroke. 1992. 23:855–860.22. Infeld B, Davis SM, Lichtenstein M, Mitchell PJ, Hopper JL. Crossed cerebellar diaschisis and brain recovery after stroke. Stroke. 1995. 26:90–95.23. Murayama K, Katada K, Nakane M, Toyama H, Anno H, Hayakawa M, et al. Whole-brain perfusion CT performed with a prototype 256-detector row CT system: initial experience. Radiology. 2009. 250:202–211.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Crossed cerebello-cerebral diaschisis in cerebellar infraction
- Assessment of regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) in ischemic stroke using Tc-99m HMPAO SPECT: comparison with CT and MR findings
- Vascular Hyperemia and Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis in MELAS Patient Presented as Stroke-Like Episode and Seizure
- Diaschisis and Motor Recovery in Stroke Patients
- Arterial Spin Labeling Perfusion MRI of Crossed Cerebellar Diaschisis in a Patient with Simple Partial Status Epilepticus